|
Chloropicophyceae
Chloropicophyceae is a class of green algae in the division Chlorophyta that, along with Picocystophyceae, coincides with the traditional "prasinophyte clade VII". Description Members of this class are coccoid green cells, with a diameter of 1.5–4 µm, found in marine waters, with one Cell nucleus, nucleus, one mitochondrion, and one chloroplast surrounded by two membranes, containing starch, starch grain; their single chloroplast has chlorophyll, chlorophylls ''chlorophyll a, a'' and ''chlorophyll b, b''; they lack pyrenoid and flagella; and they have a layered cell wall. Their sexual reproduction is unknown. Taxonomy In total, this class contains eight newly described species, belonging to two genera. The taxonomy goes as follows : *Division Chlorophyta Reichenbach 1834 ** Class Chloropicophyceae Lopes dos Santos & Eikrem 2017 *** Order Chloropicales Lopes dos Santos & Eikrem 2017 **** Family Chloropicaceae Lopes dos Santos & Eikrem 2017 ***** Genus ''Chloropicon'' Lopes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroparvula
''Chloroparvula'' is a genus of green algae in the class Chloropicophyceae. Description Members of this genus are distinguished from other species of Chloropicophyceae Chloropicophyceae is a class of green algae in the division Chlorophyta that, along with Picocystophyceae, coincides with the traditional "prasinophyte clade VII". Description Members of this class are coccoid green cells, with a diameter of ... by having a thick and smooth wall, sometimes with fibrils, and a string-like ornamentation. Taxonomy The name ''Chloroparvula'' references both its green color (''chloro-'') and its small size (-''parvula''). There are two species in the genus: * '' Chloroparvula pacifica'' Lopes dos Santos & Eikrem 2017 (type species) * '' Chloroparvula japonica'' Lopes dos Santos & Eikrem 2017 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q112425427, algaebase=52334, worms=1361157 Chlorophyta Green algae genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloropicon
''Chloropicon'' is a genus of green algae in the class Chloropicophyceae. Description Members of this genus are coccoid cells measuring 2–4 µm, characterized by having one green, often crescent-shaped chloroplast shaped with a starch grain, thylakoids that occur singly and in stacks of three, one central nucleus, one mitochondrion located between the nucleus and the chloroplast, 1–2 vacuoles present at the cell periphery that may contain particles, and a smooth surface of the cell wall A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech .... Taxonomy The name ''Chloropicon'' references both its green color (''chloro-'') and its small size (-''picon''). There are 6 species in the genus: * ''Chloropicon sieburthii'' Lopes dos Santos & Eikrem 2017 (type species) *''Chloropicon pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorophyta
Chlorophyta or Prasinophyta is a taxon of green algae informally called chlorophytes. The name is used in two very different senses, so care is needed to determine the use by a particular author. In older classification systems, it refers to a highly paraphyletic group of ''all'' the green algae within the green plants (Viridiplantae) and thus includes about 7,000 species of mostly aquatic photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. In newer classifications, it refers to the sister clade of the streptophytes/ charophytes. The clade Streptophyta consists of the Charophyta in which the Embryophyta (land plants) emerged. In this latter sense the Chlorophyta includes only about 4,300 species. About 90% of all known species live in freshwater. Like the land plants ( embryophytes: bryophytes and tracheophytes), green algae (chlorophytes and charophytes besides embryophytes) contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b and store food as starch in their plastids. With the exception of Palm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prasinophyte
The prasinophytes are a group of unicellular green algae. Prasinophytes mainly include marine planktonic species, as well as some freshwater representatives.Sym, S. D. and Pienaar, R. N. 1993. The class Prasinophyceae. In Round, F. E. and Chapman, D. J. (eds) ''Progress in Phycological Research'', Vol. 9. Biopress Ltd., Bristol, pp. 281-376. The prasinophytes are morphologically diverse, including flagellates with one to eight flagella and non-motile (coccoid) unicells. The cells of many species are covered with organic body scales; others are naked. Well studied genera include '' Ostreococcus'', considered to be the smallest (ca. 0.95 μm) free-living eukaryote, and '' Micromonas'', both of which are found in marine waters worldwide. Prasinophytes have simple cellular structures, containing a single chloroplast and a single mitochondrion. The genomes are relatively small compared to other eukaryotes (about 12 Mbp for '' Ostreococcus'' and 21 Mbp for '' Micromonas''). At least one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picocystis Salinarum
''Picocystis'' is a monotypic genus of green algae, the sole species is ''Picocystis salinarum''. It is placed within its own class, Picocystophyceae in the division Chlorophyta. Structure ''Picocystis salinarum'' cells under normal conditions have a spherical or oval shape. Their size ranges from 2 to 3μm (micrometer, 10^-6) in diameter. Under conditions of nutrient depletion they appear to form a trillobe shape. This trillobe shape gives it the nickname Mickey Mouse, due to its appearance to the famous character's head. The general appearance resembles that of a standard green algae. The pigments are composed mainly from chlorophyll a and b and the carotenoids violaxanthin, alloxanthin, monadoxanthin, neoxanthin, lutein, diatoxanthin and zeaxanthin. The cell wall is mainly composed of polymers of the monosaccharide arabinose, polyarabinose. Habitat The species have been found in saline or hypersaline alkaline In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picocystophyceae
''Picocystis'' is a monotypic genus of green algae, the sole species is ''Picocystis salinarum''. It is placed within its own class, Picocystophyceae in the division Chlorophyta. Structure ''Picocystis salinarum'' cells under normal conditions have a spherical or oval shape. Their size ranges from 2 to 3μm (micrometer, 10^-6) in diameter. Under conditions of nutrient depletion they appear to form a trillobe shape. This trillobe shape gives it the nickname Mickey Mouse, due to its appearance to the famous character's head. The general appearance resembles that of a standard green algae. The pigments are composed mainly from chlorophyll a and b and the carotenoids violaxanthin, alloxanthin, monadoxanthin, neoxanthin, lutein, diatoxanthin and zeaxanthin. The cell wall is mainly composed of polymers of the monosaccharide arabinose, polyarabinose. Habitat The species have been found in saline or hypersaline alkaline In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلو ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
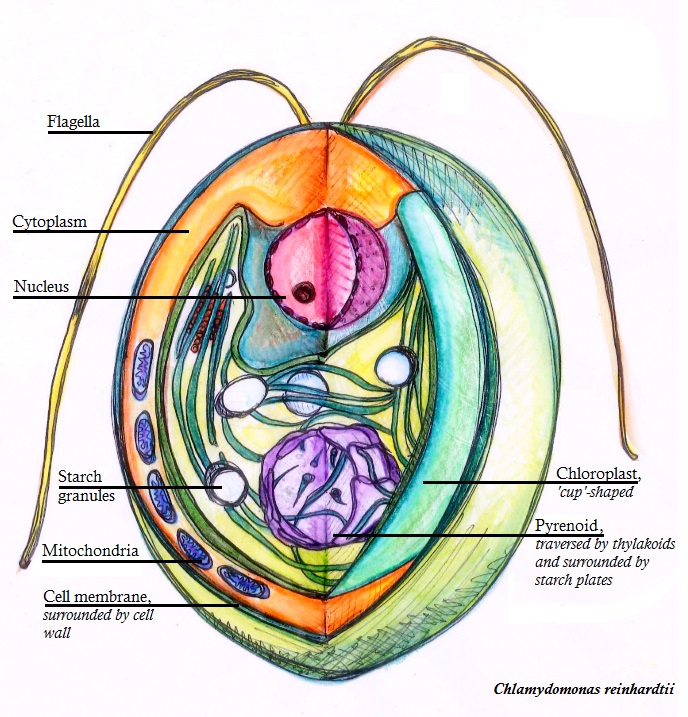
Pyrenoid
Pyrenoids are sub-cellular micro-compartments found in chloroplasts of many algae,Giordano, M., Beardall, J., & Raven, J. A. (2005). CO2 concentrating mechanisms in algae: mechanisms, environmental modulation, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 56, 99-131. and in a single group of land plants, the hornworts.Villarreal, J. C., & Renner, S. S. (2012) Hornwort pyrenoids, carbon-concentrating structures, evolved and were lost at least five times during the last 100 million years. ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences'',109(46), 1873-1887. Pyrenoids are associated with the operation of a carbon-concentrating mechanism (CCM). Their main function is to act as centres of carbon dioxide (CO2) fixation, by generating and maintaining a CO2 rich environment around the photosynthetic enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO). Pyrenoids therefore seem to have a role analogous to that of carboxysomes in cyanobacteria. Algae are restricted to aqueous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraphytina
The Tetraphytina (Cavalier-Smith 2008) or 'core Chlorophyta' are a proposed derived Chlorophyta Chlorophyta or Prasinophyta is a taxon of green algae informally called chlorophytes. The name is used in two very different senses, so care is needed to determine the use by a particular author. In older classification systems, it refers to a ... clade. The basal Tetraphytina clades are the Pedinophyceae and the Chlorophytina. Below is a cladogram based on Leliaert et al. References {{Green algae-stub Chlorophyta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorokybus Atmophyticus
''Chlorokybus'' is a multicellular (sarcinoid) genus of basal green algae or charophyte, a soil alga Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mi .... It has been classified as the sole member of the family Chlorokybaceae, which is the sole member of the order Chlorokybales, in turn the sole member of the class Chlorokybophyceae. Taxonomy ''Chlorokybus atmophyticus'' was once thought to be the only species in the genus. In 2021, a study showed that there were at least four other species, morphologically indistinguishable, but with deep genomic differences, suggesting divergences possibly about 76 million years ago. ''Chlorokybus'' has been found in Eurasia, Central and South America. ''Chlorokybus'' was placed in a new class, order and family. The new class Chlorokybophyceae was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote that develops into an organism composed of cells with two sets of chromosomes ( diploid). This is typical in animals, though the number of chromosome sets and how that number changes in sexual reproduction varies, especially among plants, fungi, and other eukaryotes. Sexual reproduction is the most common life cycle in multicellular eukaryotes, such as animals, fungi and plants. Sexual reproduction also occurs in some unicellular eukaryotes. Sexual reproduction does not occur in prokaryotes, unicellular organisms without cell nuclei, such bacteria and archaea. However, some process in bacteria may be considered analogous to sexual reproduction in that they incorporate new genetic information, including bacterial conjugation, transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. Cell walls are absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, but are present in some other ones like fungi, algae and plants, and in most prokaryotes (except mollicute bacteria). A major function is to act as pressure vessels, preventing over-expansion of the cell when water enters. The composition of cell walls varies between taxonomic group and species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin. Often, other polymers such as lignin, suberin or cutin are anchored to or embedded in plant cell walls. Algae possess cell walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides such as carrageenan and agar that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagella
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means "whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Eukary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |