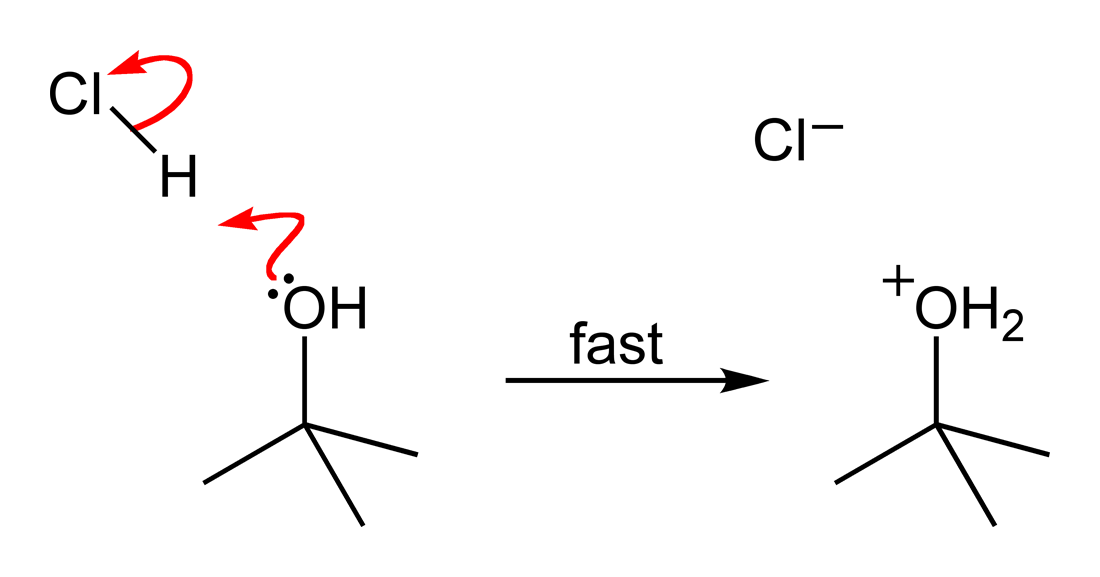|
Chlorobutane
Butyl chloride (C4H9Cl) may refer to: * ''n''-Butyl chloride (butan-1-chloride) * ''sec''-Butyl chloride (butan-2-chloride) * Isobutyl chloride Isobutyl chloride (1-chloro-2-methylpropane) is an organochlorine compound. It is a chlorinated derivative of isobutane. Synthesis Isobutyl chloride can be synthesized in a substitution reaction by reacting isobutanol with hydrochloric acid ... (1-chloro-2-methylpropane) * ''tert''-Butyl chloride (2-chloro-2-methylpropane) {{Chemistry index Chloroalkanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isobutyl Chloride
Isobutyl chloride (1-chloro-2-methylpropane) is an organochlorine compound. It is a chlorinated derivative of isobutane. Synthesis Isobutyl chloride can be synthesized in a substitution reaction by reacting isobutanol with hydrochloric acid Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...: :(CH3)2CH-CH2-OH\ +\ HCl -> ce_\text(CH3)2CH-CH2-Cl References Chloroalkanes {{Organohalide-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tert-Butyl Chloride
''tert''-Butyl chloride is the organochloride with the formula . It is a colorless, flammable liquid. It is sparingly soluble in water, with a tendency to undergo hydrolysis to the corresponding ''tert''-butyl alcohol. It is produced industrially as a precursor to other organic compounds.M. Rossberg et al. "Chlorinated Hydrocarbons" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'' 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Synthesis ''tert''-Butyl chloride is produced by the reaction of ''tert''-butyl alcohol with hydrogen chloride. In the laboratory, concentrated hydrochloric acid is used. The conversion entails a SN1 reaction as shown below.James F. Norris and Alanson W. Olmsted "''tert''-Butyl Chloride" Org. Synth. 1928, volume 8, pp. 50. The overall reaction, therefore, is: : Because ''tert''-butanol is a tertiary alcohol, the relative stability of the ''tert''-butyl carbocation in the step 2 allows the SN1, SN1 mechanism to be followed, whereas a primary alcohol would follow a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |