|
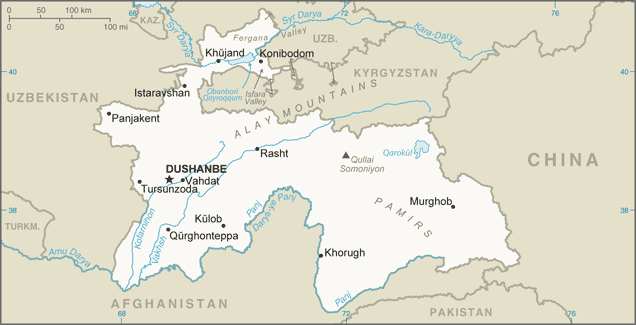
China–Tajikistan Border
The China–Tajikistan border is in length and runs from the tripoint with Kyrgyzstan following a roughly north–south line across various mountain ridges and peaks of the Pamir range down to the tripoint with Afghanistan. The border divides Murghob District, Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region in Tajikistan from Akto County, Kizilsu Kyrgyz Autonomous Prefecture (to the north) and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County, Kashgar Prefecture (to the south) in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China. History The origins of the border date from the mid-19th century, when the Russian empire expanded into Central Asia and established control over the Lake Zaysan region. The establishment of the border between the Russian Empire and the Qing Empire, not too different from today's Sino-Kazakh/Kyrgyz/Tajik border was provided for in the Convention of Peking of 1860; the actual border line pursuant to the convention was drawn by the Treaty of Tarbagatai (1864) and the Treaty of Uliassuha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tajikistan Map TI-map
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Central Asia. It has an area of and an estimated population of 9,749,625 people. Its capital and largest city is Dushanbe. It is bordered by Afghanistan to the south, Uzbekistan to the west, Kyrgyzstan to the north, and China to the east. It is separated narrowly from Pakistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor. The traditional homelands of the Tajiks include present-day Tajikistan as well as parts of Afghanistan and Uzbekistan. The territory that now constitutes Tajikistan was previously home to several ancient cultures, including the city of Sarazm of the Neolithic and the Bronze Age and was later home to kingdoms ruled by people of different faiths and cultures, including the Oxus civilization, Andronovo culture, Buddhism, Nestorian Christiani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing dynasty, Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the Russian Empire Census, 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, movies/videos, moving images, and millions of books. In addition to its archiving function, the Archive is an activist organization, advocating a free and open Internet. , the Internet Archive holds over 35 million books and texts, 8.5 million movies, videos and TV shows, 894 thousand software programs, 14 million audio files, 4.4 million images, 2.4 million TV clips, 241 thousand concerts, and over 734 billion web pages in the Wayback Machine. The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hundreds of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakhan Corridor
The Wakhan Corridor ( ps, واخان دهلېز, translit=wāxān dahléz, fa, دالان واخان, translit=dâlân vâxân) is a narrow strip of territory in Badakhshan Province of Afghanistan, extending to Xinjiang in China and separating the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region of Tajikistan from the Gilgit-Baltistan region of Pakistan-administered Kashmir.International Boundary Study of the Afghanistan–USSR Boundary (1983) by the US Bureau of Intelligence and Research Pg. 7 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Game
The Great Game is the name for a set of political, diplomatic and military confrontations that occurred through most of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century – involving the rivalry of the British Empire and the Russian Empire over Afghanistan and neighbouring territories in Central and South Asia, such as Turkestan, and having direct consequences in Persia, British India, and Tibet. Britain concluded, from Russia's military expansion in Central Asia and from diplomatic and intelligence information, that Russia planned to invade India as an ultimate goal. Meanwhile, the Russian Empire had analysed Britain's political behavior as planning the expansion of British interests in Central Asia. As a result, there was an atmosphere of deep distrust, and talk of war between these two major European empires of that time, culminating in several regional wars, and years of diplomatic intrigue and negotiations. Britain made it a high priority to protect all approache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzungarian Alatau
The Dzungarian Alatau ( mn, Зүүнгарын Алатау, ''Züüngaryn Alatau''; ; kk, Жетісу Алатауы, ''Jetısu Alatauy''; russian: Джунгарский Алатау, ''Dzhungarskiy Alatau'') is a mountain range that lies on the boundary of the Dzungaria region of China and the Zhetysu region of Kazakhstan. It has a length of and a maximum elevation of . Features The Dzhungraian Alatau consists of foothills, ridges, forts, and alpine meadows of the Northern Tian Shan (Trans-Ili Alatau, Ktmen). It is located at an altitude of 2,000m above sea level, and is over 400km long in the latitudinal direction. The Dzhungraian Alatau consists of two ranges that are distinctly parallel to each other: the northern (or main), and the southern range. The area includes several sub-parallel high mountain ranges, accompanied by low and short ranges and their spurs. It also holds the largest waterfall in Central Asia. A distinctive feature of the Dzunguarain Alatau is a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Saint Petersburg (1881)
The Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1881) (), also known as Treaty of Ili (), was a treaty between the Russian Empire and the Qing dynasty that was signed in Saint Petersburg, Russia, on . It provided for the return to China of the eastern part of the Ili Basin region, also known as Zhetysu, which had been occupied by Russia since 1871 during the Dungan Revolt. Background During the Russian conquest of Turkestan, Russia gained control of eastern Kazakhstan up to the current Chinese border. During the Dungan Revolt, China lost control of much of its western territory, and power passed to various factions. In 1871, Russia occupied the Ili territory. There was talk of permanent annexation, but Saint Petersburg declared that it was occupying the territory to protect its citizens. Chinese authority in Xinjiang was re-established by 1877. Wanyan Chonghou was sent to Russia to negotiate. In September 1879, he concluded the Treaty of Livadia. Russia would retain the Tekes valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ili River
The Ili ( ug, ئىلى دەرياسى, Ili deryasi, Ili dəryasi, 6=Или Дәряси; kk, Ile, ; russian: Или; zh, c=伊犁河, p=Yīlí Hé, dng, Йили хә, Xiao'erjing: اِلِ حْ; mn, Ил, literally "Bareness") is a river situated in Northwest China and Southeastern Kazakhstan. It flows from the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture of the Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region to the Almaty Region in Kazakhstan. It is long (including its source river Tekes),Или of which is in Kazakhstan. The river originates from the Tekes and Künes rivers in Eastern [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
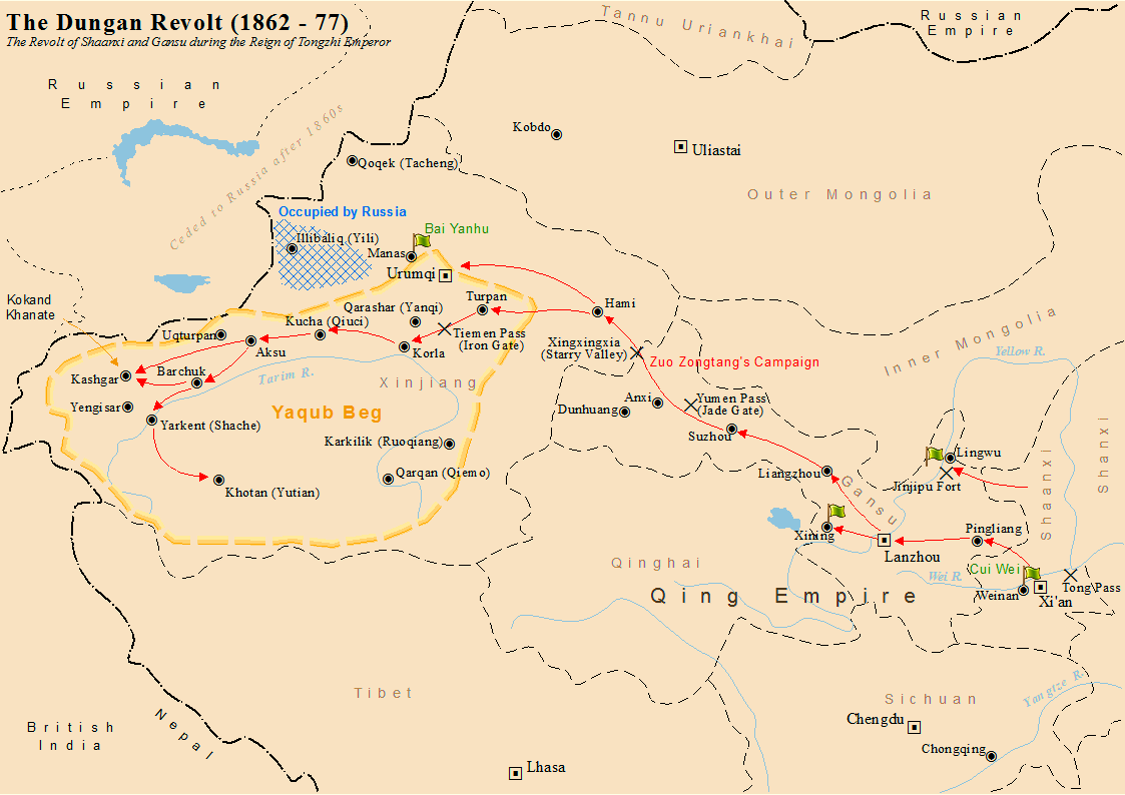
Zuo Zongtang
Zuo Zongtang, Marquis Kejing ( also spelled Tso Tsung-t'ang; ; November 10, 1812 – September 5, 1885), sometimes referred to as General Tso, was a Chinese statesman and military leader of the late Qing dynasty. Born in Xiangyin County, Hunan Province, Zuo sat for the imperial examination in his youth but obtained only a ''juren'' degree. He then spent his time studying agriculture, geography and military strategy. In 1851, he started his career in the Qing military by participating in the campaign against the Taiping Rebellion. In 1862, he was recommended by Zeng Guofan to serve as the provincial governor of Zhejiang Province. During his term, he coordinated Qing forces to attack the Taiping rebels with support from British and French forces. For this success, he was promoted to Viceroy of Min-Zhe. After capturing Hangzhou from the Taiping rebels in 1864, he was enfeoffed as a first class count. In 1866, as part of the Qing government's Self-Strengthening Movement, Zu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dungan Revolt (1862–1877)
The Dungan Revolt (1862–1877) or Tongzhi Hui Revolt (, Xiao'erjing: تُجِ خُوِ لُوًا, dng, Тунҗы Хуэй Луан) or Hui (Muslim) Minorities War was a war fought in 19th-century western China, mostly during the reign of the Tongzhi Emperor (r. 1861–1875) of the Qing dynasty. The term sometimes includes the Panthay Rebellion in Yunnan, which occurred during the same period. However, this article refers specifically to two waves of uprising by various Chinese Muslims, mostly Hui people, in Shaanxi, Gansu and Ningxia provinces in the first wave, and then in Xinjiang in the second wave, between 1862 and 1877. The uprising was eventually suppressed by Qing forces led by Zuo Zongtang. The conflict began with riots by the Hui and massacres of the Han Chinese, followed by the revenge massacres of the Hui by the Han. It resulted in massive demographic shifts in Northwest China, and led to a population loss of 21 million people from a combination of mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Tarbagatai
The Treaty of Tarbagatai () or Treaty of Chuguchak () of 7 October O.S./nowiki> 1864 was a border protocol between Qing dynasty">Qing China and the Russian Empire that defined most of the western extent of their border in central Asia, between Outer Mongolia and the Khanate of Kokand. The signatories were, for Russia, Ivan Zakharov, consul-general of Ili, and Ivan Fedorovich Babkov, colonel of the Separate Siberian Corps of the General Staff, and, for China, Ming I, general of Uliastai; Hsi Lin, ''amban'' of Tarbagatai; and Bolgosu, Tarbagatai brigade commander. By this agreement, Russia gained about 350,000 square miles of territory at the expense of Chinese Xinjiang, and Lake Balkhash went from lying on the border to being entirely surrounded by Russia. It is sometimes numbered among the "unequal treaties". A Russian and Chinese border commission assembled at T'a-ch'eng (also known as Tarbagatai or Chuguchak) in China on 13 May 1861 in order to map the western border in acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)