|
Chimerin 2
Chimerin 2 (beta-chimaerin) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CHN2'' gene. This gene is a member of the chimerin family and encodes a protein with a phorbol-ester/diacylglycerol-type zinc finger, a Rho-GAP domain and an SH2 domain. This protein has GTPase-activating protein activity that is regulated by phospholipid binding and binding of diacylglycerol (DAG) induces translocation of the protein from the cytosol to the Golgi apparatus The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ins ... membrane. The protein plays a role in the proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells. Decreased expression of this gene is associated with high-grade gliomas and breast tumors, and increased expression of this gene is associated with lymphomas. Mutations in this gene have been as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimerin
Chimerin is a type of nerve tissue protein. Chimerins are a family of non-protein kinase C phorbol ester receptors. They were the first phorbal ester receptors to be discovered within this family. They are represented as a family of four closely bound GAPs1 (GTPase-activating proteins). These small GTPases were once characterized as high affinity intracellular receptors for the second messenger diacylglycerol (DAG) and the phorbol ester tumor promoters. The name stems from their resemblance to the "chimera." Types Types include: * Chimerin 1 * Chimerin 2 There are four known isoforms of the chimerin protein. These include α1, α2, β1, and β2. α1-Chimerin was the first protein to be isolated from the brain. The other domains were discovered through alternative splicing. The α and β isoforms are almost identical, the key difference stems from the SH2 domain The SH2 (Src Homology 2) domain is a structurally conserved protein domain contained within the Src oncoprotein an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phorbol Esters
Phorbol esters are a class of chemical compounds found in a variety of plants, particularly in the families Euphorbiaceae and Thymelaeaceae. Chemically, they are ester In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ... derivative (chemistry), derivatives of the tetracyclic diterpenoid phorbol. Biological activity Protein kinase C (PKC) is a phorbol ester receptor. Phorbol esters can stimulate PKC in a similar way to Diglyceride, diglycerides. Phorbol esters are known for their ability to Tumor promotion, promote tumors. In particular, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) is used as a biomedical research tool in models of carcinogenesis. Plants that contain phorbol esters are often Poison, poisonous. References {{Chem-stub Phorbol esters, Diterpenes Carboxylate esters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
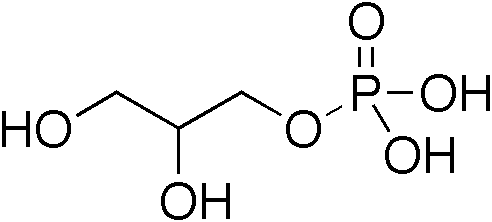
Diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oils or animal fats. Food additive Diglycerides, generally in a mix with monoglycerides (E471), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Finger
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) in order to stabilize the fold. It was originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from the African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'') transcription factor IIIA. However, it has been found to encompass a wide variety of differing protein structures in eukaryotic cells. ''Xenopus laevis'' TFIIIA was originally demonstrated to contain zinc and require the metal for function in 1983, the first such reported zinc requirement for a gene regulatory protein followed soon thereafter by the Krüppel factor in ''Drosophila''. It often appears as a metal-binding domain in multi-domain proteins. Proteins that contain zinc fingers (zinc finger proteins) are classified into several different structural families. Unlike many other clearly defined supersecondary structures such as Greek keys or β hairpins, there are a number of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a protein domain common to many GTPases. Functions GTPases function as molecular switches or timers in many fundamental cellular processes. Examples of these roles include: * Signal transduction in response to activation of cell surface receptors, including transmembrane receptors such as those mediating taste, smell and vision. * Protein biosynthesis (a.k.a. translation) at the ribosome. * Regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, division and movement. * Translocation of proteins through membranes. * Transport of vesicles within the cell, and vesicle-mediated secretion and uptake, through GTPase control of vesicle coat assembly. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP. In the generalized recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells (intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus. It was identified in 1897 by the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi and was named after him in 1898. Discovery Owing to its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system. After first observing it under his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |