|
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell
In biology, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs)—also known as chimeric immunoreceptors, chimeric T cell receptors or artificial T cell receptors—are receptor proteins that have been engineered to give T cells the new ability to target a specific antigen. The receptors are chimeric in that they combine both antigen-binding and T cell activating functions into a single receptor. CAR T cell therapy uses T cells engineered with CARs to treat cancer. The premise of CAR T immunotherapy is to modify T cells to recognize cancer cells in order to more effectively target and destroy them. Scientists harvest T cells from people, genetically alter them, then infuse the resulting CAR T cells into patients to attack their tumors. CAR T cells can be derived either from T cells in a patient's own blood (autologously) or from the T cells of another, healthy, donor ( allogeneically). Once isolated from a person, these T cells are genetically engineered to express a specific CAR, which programs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAR T-cell Therapy
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods. The year 1886 is regarded as the birth year of the car, when German inventor Carl Benz patented his Benz Patent-Motorwagen. Cars became widely available during the 20th century. One of the first cars affordable by the masses was the 1908 Model T, an American car manufactured by the Ford Motor Company. Cars were rapidly adopted in the US, where they replaced animal-drawn carriages and carts. In Europe and other parts of the world, demand for automobiles did not increase until after World War II. The car is considered an essential part of the developed economy. Cars have controls for driving, parking, passenger comfort, and a variety of lights. Over the decades, additional features and controls have been added to vehicles, making them progressively more complex. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gideon Gross
Gideon Gross is an Israeli immunologist, inventor and farmer. Together with Zelig Eshhar at the Weizmann Institute of Science, they created the first chimeric antigen receptors (CARs). He was dean of the Faculty of Sciences & Technology of Tel-Hai Academic College from 2010 to 2014. He is also a specialist mango A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree '' Mangifera indica''. It is believed to have originated in the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in Sout ... farmer. References Living people Year of birth missing (living people) Israeli immunologists Israeli inventors Israeli farmers Weizmann Institute of Science faculty Tel-Hai Academic College faculty {{Israel-scientist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-cell Leukemia
A B-cell leukemia is any of several types of lymphoid leukemia which affect B cells. Types include (with ICD-O code): * 9823/3 - B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma * 9826/3 - Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, mature B-cell type * 9833/3 - B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia * 9835/3-9836/3 - Precursor B lymphoblastic leukemia * 9940/3 - Hairy cell leukemia See also * T-cell leukemia * B-cell lymphoma The B-cell lymphomas are types of lymphoma affecting B cells. Lymphomas are "blood cancers" in the lymph nodes. They develop more frequently in older adults and in immunocompromised individuals. B-cell lymphomas include both Hodgkin's lymphoma ... References External links {{Hematological malignancy histology Lymphocytic leukemia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
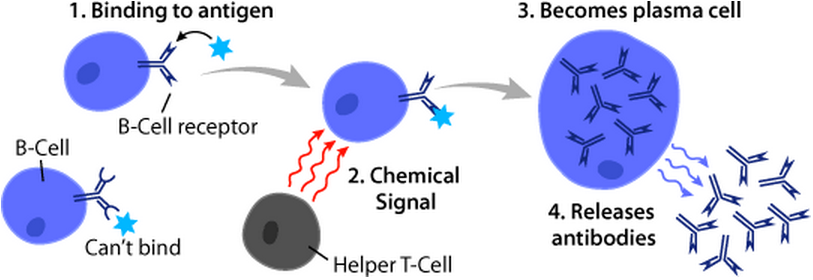
B Cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells Antigen presentation, present antigens (they are also classified as professional Antigen-presenting cell, antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells Cellular differentiation, mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD137
CD137 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor ( TNF) receptor family. Its alternative names are ''tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9'' (TNFRSF9), 4-1BB and ''induced by lymphocyte activation'' (ILA). It is of interest to immunologists as a co-stimulatory immune checkpoint molecule. Expression CD137 is expressed by activated T cells of both the CD4+ and CD8+ lineages. Although it is thought to function mainly in co-stimulating those cell types to support their activation by antigen presenting cells expressing its ligand (CD137L), CD137 is also expressed on dendritic cells, B cells, NK cells, neutrophils and macrophages. Specific effects on cells The best characterized activity of CD137 is its costimulatory activity for activated T cells. Crosslinking of CD137 enhances T cell proliferation, IL-2 secretion, survival and cytolytic activity. Further, it can enhance immune activity to eliminate tumors in mice. Interactions CD137 has been shown to interact with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD28
CD28 (Cluster of Differentiation 28) is one of the proteins expressed on T cells that provide co-stimulatory signals required for T cell activation and survival. T cell stimulation through CD28 in addition to the T-cell receptor ( TCR) can provide a potent signal for the production of various interleukins ( IL-6 in particular). CD28 is the receptor for CD80 (B7.1) and CD86 (B7.2) proteins. When activated by Toll-like receptor ligands, the CD80 expression is upregulated in antigen-presenting cells (APCs). The CD86 expression on antigen-presenting cells is constitutive (expression is independent of environmental factors). CD28 is the only B7 receptor constitutively expressed on naive T cells. Association of the TCR of a naive T cell with MHC:antigen complex without CD28:B7 interaction results in a T cell that is anergic. Furthermore, CD28 was also identified on bone marrow stromal cells, plasma cells, neutrophils and eosinophils, but the functional importance of CD28 o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MUC1
Mucin short variant S1, also called polymorphic epithelial mucin (PEM) or epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), is a mucin encoded by the ''MUC1'' gene in humans. Mucin short variant S1 is a glycoprotein with extensive O-linked glycosylation of its extracellular domain. Mucins line the apical surface of epithelial cells in the lungs, stomach, intestines, eyes and several other organs. Mucins protect the body from infection by pathogen binding to oligosaccharides in the extracellular domain, preventing the pathogen from reaching the cell surface. Overexpression of MUC1 is often associated with colon, breast, ovarian, lung and pancreatic cancers. Joyce Taylor-Papadimitriou identified and characterised the antigen during her work with breast and ovarian tumors. Structure MUC1 is a member of the mucin family and encodes a membrane bound, glycosylated phosphoprotein. MUC1 has a core protein mass of 120-225 kDa which increases to 250-500 kDa with glycosylation. It extends 200-500&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Genesys
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life Cell may also refer to: Locations * Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery with only a few monks or nuns * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Groups of people * Cell, a group of people in a cell group, a form of Christian church organization * Cell, a unit of a clandestine cell system, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Cellular organizational structure, such as in business management Science, mathematics, and technology Computing and telecommunications * Cell (EDA), a term used in an electronic circuit design schematics * Cell (microprocessor), a microprocessor architecture developed by Sony, Toshiba, and IBM * Memory cell (computing), the basic unit of (volatile or non-volatile) computer memory * Cell, a unit in a database table or spreadsheet, formed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
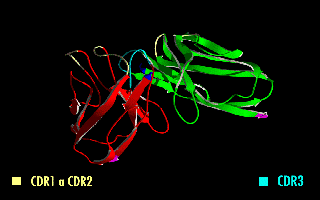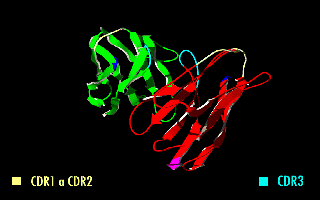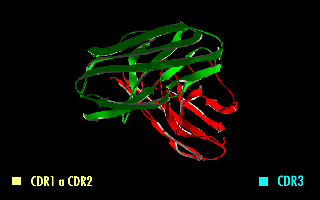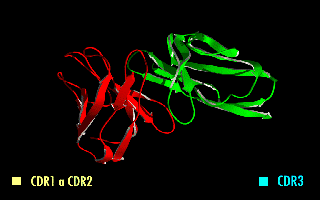
Single-chain Variable Fragment
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker peptide of ten to about 25 amino acids. The linker is usually rich in glycine for flexibility, as well as serine or threonine for solubility, and can either connect the N-terminus of the VH with the C-terminus of the VL, or ''vice versa''. This protein retains the specificity of the original immunoglobulin, despite removal of the constant regions and the introduction of the linker. The image to the right shows how this modification usually leaves the specificity unaltered. These molecules were created to facilitate phage display, where it is highly convenient to express the antigen-binding domain as a single peptide. As an alternative, scFv can be created directly from subcloned heavy and light chains derived from a hybridoma. ScFvs have many uses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, San Francisco
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is a public land-grant research university in San Francisco, California. It is part of the University of California system and is dedicated entirely to health science and life science. It conducts research and teaching in medical and biological sciences. UCSF was founded as Toland Medical College in 1864. in 1873, it became affiliated with the University of California as its Medical Department. In the same year, it incorporated the California College of Pharmacy and in 1881 it established a dentistry school. Its facilities were located in both Berkeley and San Francisco. In 1964, the school gained full administrative independence as a campus of the UC system, headed by its own chancellor, and in 1970 it gained its current name. Historically based at Parnassus Heights with satellite facilities throughout the city, UCSF developed a second major campus in the newly redeveloped Mission Bay district in the early 2000s. '' U.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Weiss (scientist)
Arthur Weiss is an American Immunologist who is currently an Ephraim P. Engleman Distinguished Professor of Medicine and a professor of microbiology and immunology at the University of California, San Francisco. He has been a member of the National Academy of Sciences The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nat ... since 2003. He specializes in studying T cell development and immune responses. His research focus has recently been shifted towards studying autoimmune diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. He is also a Howard Hughes Medical Investigator, a title he has held since 1982. References American immunologists Living people Year of birth missing (living people) University of California, San Francisco faculty Howard Hughes Medical Investigators {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD247
T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 zeta chain also known as T-cell receptor T3 zeta chain or CD247 (Cluster of Differentiation 247) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CD247'' gene. Some older literature mention a similar protein called "CD3 eta" in mice. It is now understood to be an isoform differing in the last exon. Genomics The gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 1 at location 1q22-q25 on the Crick (negative) strand. The encoded protein is 164 amino acids long with a predicted weight of 18.696 kilo Daltons. Function T-cell receptor zeta (ζ), together with T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers and CD3-gamma, -delta, and -epsilon, forms the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex. The zeta chain plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways. Low expression of the antigen results in impaired immune response. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |