|
Chief Cells
In human anatomy, there are three types of chief cells, the gastric chief cell, the parathyroid chief cell, and the type 1 chief cells found in the carotid body. Cell types The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a cell in the stomach that releases pepsinogen and chymosin. Pepsinogen is activated into the digestive enzyme pepsin when it comes in contact with hydrochloric acid produced by gastric parietal cells.MeSH https://www.nlm.nih.gov/cgi/mesh/2012/MB_cgi?mode=&term=Chief+Cells,+Gastric&field=entry This type of cell also secretes gastric lipase enzymes, which help digest triglycerides into free fatty acids and di- and mono-glycerides. There is also evidence that the gastric chief cell secretes leptin in response to the presence of food in the stomach. Leptin has been found in the pepsinogen granules of chief cells. Gastric pit cells are replaced every 2–4 days. This high rate of turnover is a protective mechanism designed to protect the epith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Chief Cell
A gastric chief cell (or peptic cell, or gastric zymogenic cell) is a type of gastric gland cell that releases pepsinogen and gastric lipase. It is the cell responsible for secretion of chymosin in ruminant animals. The cell stains basophilic upon H&E staining due to the large proportion of rough endoplasmic reticulum in its cytoplasm. Gastric chief cells are generally located deep in the mucosal layer of the stomach lining, in the fundus and body of the stomach.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stomachnormalhistology.html Chief cells release the zymogen (enzyme precursor) pepsinogen when stimulated by a variety of factors including cholinergic activity from the vagus nerve and acidic condition in the stomach. Gastrin and secretin may also act as secretagogues. It works in conjunction with the parietal cell, which releases gastric acid, converting the pepsinogen into pepsin. Nomenclature The terms ''chief cell'' and '' zymogenic cell'' are often used without the word "gastric" to name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
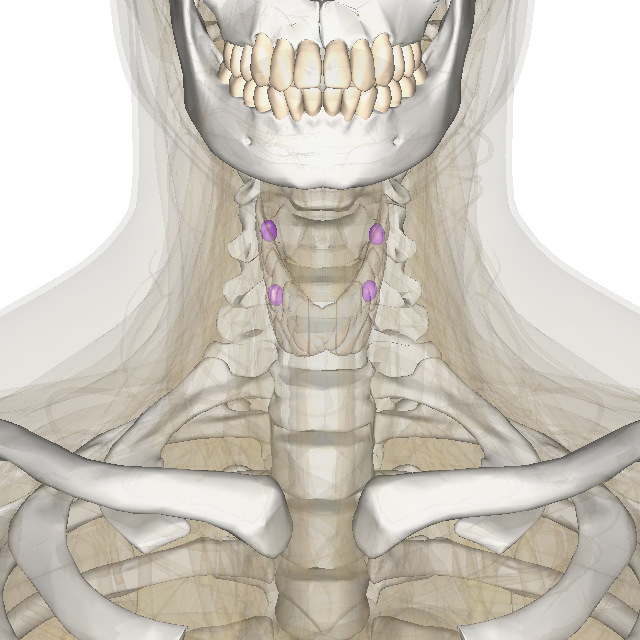
Parathyroid Chief Cell
Parathyroid chief cells (also called parathyroid principal cells or simply parathyroid cells, C-cells, or parafollicular cells) are one of the two cell types of the parathyroid glands, along with oxyphil cells. The chief cells are much more prevalent in the parathyroid gland than the oxyphil cells. It is perceived that oxyphil cells may be derived from chief cells at puberty, as they are not present at birth like chief cells. Most individuals display four parathyroid glands adjacent to the thyroid gland anterior in the neck. Histology The chief cells are organized as dense cords surrounding the capillaries in the parathyroid. Chief cells appear as a dark purple in an H&E stain, with the oxyphil cells staining as a lighter pink. They are polygonal in shape with a round nucleus. Chief cells spend most time inactive due to normal calcium level conditions. These inactive cells are classified as cuboidal. They have low levels of secretory granules, as opposed to active chief cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepsinogen
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site. It is one of three principal endopeptidases (enzymes cutting proteins in the middle) in the human digestive system, the other two being chymotrypsin and trypsin. There are also exopeptidases which remove individual amino acids at both ends of proteins (carboxypeptidases produced by the pancreas and aminopeptidases secreted by the small intestine). During the process of digestion, these enzymes, each of which is specialized in severing links between particular types of amino acids, collaborate to break down dietary proteins into their components, i.e., peptides and amino acids, which can be readily absorbed by the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chymosin
Chymosin or rennin is a protease found in rennet. It is an aspartic endopeptidase belonging to MEROPS A1 family. It is produced by newborn ruminant animals in the lining of the abomasum to curdle the milk they ingest, allowing a longer residence in the bowels and better absorption. It is widely used in the production of cheese. Bovine chymosin is now produced recombinantly in , '' Aspergillus niger var awamori'', and as alternative resource. Occurrence The chymosin is found in a wide range of tetrapods, although it is best known to be produced by ruminant animals in the lining of the abomasum. Chymosin is produced by gastric chief cells in newborn mammals to curdle the milk they ingest, allowing a longer residence in the bowels and better absorption. Non-ruminant species that produce chymosin include pigs, cats, seals,Staff, Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) Database. Last updated February 21, 199Chymosin pseudogene; CYMP prochymosin, included, in the OMIM/re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Cells
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions of the stomach. They contain an extensive secretory network of canaliculi from which the HCl is secreted by active transport into the stomach. The enzyme hydrogen potassium ATPase (H+/K+ ATPase) is unique to the parietal cells and transports the H+ against a concentration gradient of about 3 million to 1, which is the steepest ion gradient formed in the human body. Parietal cells are primarily regulated via histamine, acetylcholine and gastrin signalling from both central and local modulators. Structure Canaliculus A canaliculus is an adaptation found on gastric parietal cells. It is a deep infolding, or little channel, which serves to increase the surface area, e.g. for secretion. The parietal cell membrane is dynamic; the numbers of canal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parathyroid Gland
Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid gland in variable locations. The parathyroid gland produces and secretes parathyroid hormone in response to a low blood calcium, which plays a key role in regulating the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones. Parathyroid glands share a similar blood supply, venous drainage, and lymphatic drainage to the thyroid glands. Parathyroid glands are derived from the epithelial lining of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches, with the superior glands arising from the fourth pouch and the inferior glands arising from the higher third pouch. The relative position of the inferior and superior glands, which are named according to their final location, changes because of the migration of embryological tissues. Hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism, characterized by alterations in the blood calcium levels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parathyroid Hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine. PTH influences bone remodeling, which is an ongoing process in which bone tissue is alternately resorbed and rebuilt over time. PTH is secreted in response to low blood serum calcium (Ca2+) levels. PTH indirectly stimulates osteoclast activity within the bone matrix ( osteon), in an effort to release more ionic calcium (Ca2+) into the blood to elevate a low serum calcium level. The bones act as a (metaphorical) "bank of calcium" from which the body can make "withdrawals" as needed to keep the amount of calcium in the blood at appropriate levels despite the ever-present challenges of metabolism, stress, and nutritional variations. PTH is "a key that unlocks the bank vault" to remove the calcium. PTH is secreted primarily by the chief cells of the par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology Of Fundic Gland Polyp, High Magnification, Annotated
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία ''-logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks"). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |