|
Chetwynd Barracks
Chetwynd Barracks is a military installation at Chilwell in Nottinghamshire. History The Chilwell depot and barracks were built for the Royal Army Ordnance Corps shortly after the First World War on the former site of the National Shell Filling Factory, Chilwell which had been completely devastated by an explosion in July 1918. The site continued to be used as a central ordnance depot after the Second World War and, although the central vehicle kit store closed in 1958, when operations moved to Bicester, it continued to operate as a general stores depot and a vehicle workshop. The site was renamed Chetwynd Barracks, after Viscount Chetwynd who had been Managing Director of the National Shell Filling Factory, in 1995 and became the home of 49 (East) Brigade. Under Army 2020, 49 (East) Brigade was merged with 7th Armoured Brigade to become 7th Infantry Brigade and Headquarters East which relocated to Chetwynd Barracks on 13 February 2015. In late March 2016, the Ministry of Defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilwell
Chilwell is a village and residential suburb of Nottingham, in the borough of Broxtowe of Nottinghamshire, west of Nottingham city. Until 1974 it was part of Beeston and Stapleford Urban District, having been in Stapleford Rural District until 1935. History Roman Empire, Roman buildings, pottery and coins have been found in Chilwell. Chilwell was originally a Hamlet (place), hamlet on the road from Nottingham to Ashby-de-la-Zouch. It is mentioned in the Domesday Book, but along with Toton it became part of the parish of Attenborough, Nottinghamshire, Attenborough. Suburban development spread gradually from Beeston, Nottinghamshire, Beeston along Chilwell High Road. The area's population grew substantially during World War I, when most of the area of level ground between Chilwell and Toton was occupied by the National Shell Filling Factory, Chilwell, National Shell Filling Factory No. 6 and the original direct route between Chilwell and Toton became a gated military road, now k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godfrey Chetwynd, 8th Viscount Chetwynd
Godfrey John Boyle Chetwynd, 8th Viscount Chetwynd, CH (3 October 1863 – 22 March 1936) was a British peer and industrialist. Chetwynd was the second son of Captain Henry Weyland Chetwynd (1829–1893; the third son of the 6th Viscount Chetwynd) and his wife Julia Bosville Davidson (d. 1901; a maternal granddaughter of the 3rd Baron Macdonald of Sleat). On 12 April 1893, he married Baroness Hilda von Alvensleben-Rusteberg. They later divorced and on 10 February 1904, he married Hon. Mary Eden (the third daughter of the 4th Baron Auckland) and they had three children, Adam Duncan (1904–1965), John Julian (1906–1966), and (Mary Diana) Eve (1908–1997). In 1911, Chetwynd inherited his uncle's titles. Between 1915 and 1919, he was managing director of the National Shell Filling Factory No. 6, Chilwell, Nottinghamshire, which he designed and built; for which he was a made a Companion of Honour for his services to the war effort. References * Haslam, M.J. (Captain RAO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
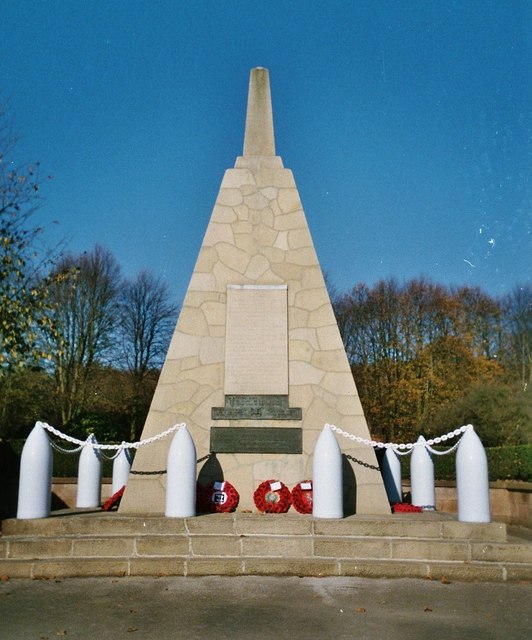
Chilwell Filling Factory Memorial
The memorial to munitions workers of National Filling Factory No.6, Chilwell is a Grade II listed building on the north side of Chetwynd Road inside Chetwynd Barracks, in Chilwell, near Nottingham. It commemorates the workers who died in accidents at National Shell Filling Factory, Chilwell during the First World War, particularly the large explosion on 1 July 1918. The large free-standing pyramidal monument, enclosed by chains carried on shell casings, was unveiled in 1919 and became a Grade II listed building in 1987. Background Munitions production in the UK expanded considerably after the outbreak of the First World War in 1914, but production failed to keep pace with the demand, with shortages leading to a Shell Scandal in 1915. The Munitions of War Act 1915 gave the government the power to establish different types of National Factories. National Filling Factory No 6 was established in Chilwell, Nottinghamshire, as a filling factory, where empty shell casings that wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corps Of Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the ''Sappers'', is a corps of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces and is headed by the Chief Royal Engineer. The Regimental Headquarters and the Royal School of Military Engineering are in Chatham in Kent, England. The corps is divided into several regiments, barracked at various places in the United Kingdom and around the world. History The Royal Engineers trace their origins back to the military engineers brought to England by William the Conqueror, specifically Bishop Gundulf of Rochester Cathedral, and claim over 900 years of unbroken service to the crown. Engineers have always served in the armies of the Crown; however, the origins of the modern corps, along with those of the Royal Artillery, lie in the Board of Ordnance established in the 15th century. In Woolwich in 1716, the Board formed the Royal Regime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the ''Sappers'', is a corps of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces and is headed by the Chief Royal Engineer. The Regimental Headquarters and the Royal School of Military Engineering are in Chatham in Kent, England. The corps is divided into several regiments, barracked at various places in the United Kingdom and around the world. History The Royal Engineers trace their origins back to the military engineers brought to England by William the Conqueror, specifically Bishop Gundulf of Rochester Cathedral, and claim over 900 years of unbroken service to the crown. Engineers have always served in the armies of the Crown; however, the origins of the modern corps, along with those of the Royal Artillery, lie in the Board of Ordnance established in the 15th century. In Woolwich in 1716, the Board formed the Royal Regime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
170 (Infrastructure Support) Engineer Group
170 (Infrastructure Support) Engineer Group is an engineering group of the British Army's Corps of Royal Engineers. Today the group controls all of the STREs of the army in addition to 20 Works Group (Air Support), the Royal Monmouthshire Royal Engineers, and 43 HQ and Support Squadron. History Military Works Force In 1978, following the 1975 Mason Review, the Military Works Force was formed at Chetwynd Barracks to control the Corps of Royal Engineers's works groups. It controlled the specialist engineering units and helped in commanding and providing those special services. The group was originally formed with the control of just two Commanders Royal Engineers (CREs) each with three Specialist Teams Royal Engineers (STREs), but this force was later expanded. At one time, the command controlled 530 STRE (Maintenance), but it is unknown when this STRE was formed, disbanded, and assigned to the group.Watson and Rinaldi, p. 218 The four CREs of the command included; * Headquar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headquarters East
The 7th Light Mechanised Brigade Combat Team is a formation in the British Army with a direct lineage to 7th Armoured Brigade and a history that stretches back to the Napoleonic Wars. It saw active service in the Crimean War, the Second Boer War and both the First and the Second World Wars. In 2014, the 7th Armoured Brigade was re-designated as 7th Infantry Brigade, thereby ensuring that the famed "Desert Rats" continue in the British Army's Order of battle. History Waterloo Campaign When Wellington organized his troops into numbered divisions for the Peninsular War, the component brigades were named for the commanding officer. For the Hundred Days Campaign, he numbered his British infantry brigades in a single sequence, 1st to 10th. The 7th Brigade formed part of the 7th Division under the command of Major-general Kenneth MacKenzie. It consisted of: * 2nd Battalion, 25th (the King's Own Borderers) Regiment of Foot * 2nd Battalion, 37th (the North Hampshire) Regiment of Foot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th Armoured Brigade (United Kingdom)
The 7th Armoured Brigade was an armoured brigade formation of the British Army. The brigade is also known as the "Desert Rats", a nickname formerly held by the 7th Armoured Division, of which the brigade formed a part of during the Second World War until late 1941.7th Armoured Brigade at www.army.mod.uk accessed on 21 Sep 09. History The brigade was raised from garrison troops stationed in North Africa in 1938. It was initially known as the Light Armoured Brigade which was part of the Mobile Division in . When the Mobile Division became[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Future Of The British Army (Army 2020 Refine)
Army 2020 Refine was the name given to the restructuring of the British Army, in light of the Strategic Defence and Security Review 2015. Army 2020 Refine The Strategic Defence and Security Review 2015 announced that the structure of the Reaction and Adaptable Forces would further change, in an evolution of the previous Army 2020 plan. The main changes of Army 2020 Refine were: *Creation of two new "Strike brigades", to be formed by converting an Armoured Infantry brigade and an Infantry brigade. These will be formed by 2025, comprising 5,000 personnel each, equipped with Ajax vehicles. *The UK's 3rd division will, by 2025, comprise two armoured infantry brigades, a strike brigade, and a strike experimentation group (which would later convert to a second Strike brigade). *Creation of a Specialised Infantry Group, to be formed by converting four infantry battalions and creation of a new battalion and training cell. *Two innovative brigades were to be established, comprising a mix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
49th Infantry Brigade (United Kingdom)
The 49th Infantry Brigade, later known as 49th (Eastern) Infantry Brigade during the Cold War, was a brigade of the British Army. First World War The brigade started its existence as part of the 16th (Irish) Division, part of Kitchener's Army in the First World War. The 16th Division served through the war on the Western Front. Cold War The 49th Brigade also served in Kenya during the Mau Mau Uprising from 1953 to 1955-6, incorporating the 1st Battalion, Royal Northumbrian Fusiliers, and the 1st Battalion, Royal Innskilling Fusiliers, joined by the 1st Battalion, Royal Irish Fusiliers, from January 1955. However the core of the brigade's present history descends from the 49th (West Riding) Division, which fought in both World Wars. In the Second World War, the division was involved in the Norwegian Campaign, the guarding of Iceland, and Operation Overlord, where it landed in Normandy under XXX Corps. It was part of the reformed Territorial Army (as an armoured formation fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MoD Bicester
MoD Bicester is a large military storage and distribution centre just outside Bicester in Oxfordshire. History The site dates back to September 1942 when a depot was constructed near Bicester to provide logistical support for operations in Europe during the Second World War. It is serviced by the Bicester Military Railway. In 1961 the ordnance depots at Didcot and Branston were closed and a Central Ordnance Depot was created at Bicester. Between 1980 and 1982 the ordnance depots at Chilwell and Ruddington were also closed resulting in an increased role for the remaining central ordnance depots at Bicester and Donnington. The depot became known as the Defence Storage and Distribution Centre in April 1999. A bomb disposal training base, built at a cost of circa £100 million and including a cave complex, a dive pool and roadways was established at St George's Barracks on the site in March 2013. Then in September 2014, 23 Pioneer Regiment, which had been based at St David's Barr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Defence (United Kingdom)
The Ministry of Defence (MOD or MoD) is the department responsible for implementing the defence policy set by His Majesty's Government, and is the headquarters of the British Armed Forces. The MOD states that its principal objectives are to defend the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and its interests and to strengthen international peace and stability. The MOD also manages day-to-day running of the armed forces, contingency planning and defence procurement. The expenditure, administration and policy of the MOD are scrutinised by the Defence Select Committee, except for Defence Intelligence which instead falls under the Intelligence and Security Committee of Parliament. History During the 1920s and 1930s, British civil servants and politicians, looking back at the performance of the state during the First World War, concluded that there was a need for greater co-ordination between the three services that made up the armed forces of the United Kingdom: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





-_D-day_6_June_1944_H37362.jpg)
_(Tony_Radakin_cropped).jpg)