|
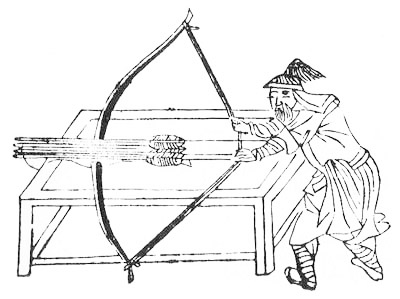
Cheng Zongyou
Cheng Zongyou 程宗猷 (1561-1636) was a Chinese martial arts, martial artist. He is noted for his publication ''Shaolin Gunfa Changzong'' or ''Elucidation of Shaolin Staff Techniques'', as well as the ''Gengyu Shengji'' (''Skills Beyond Farming'') which described various other weapons systems, including Japanese kenjutsu. Little is known of Cheng's life. He was born in Xiuning County into an upper-class family, and as such had a literary upbringing instead of the military (or criminal) childhood that was more common among professional martial artists of his era. He spent around a decade studying at the Shaolin Monastery, and described his training in some of his works. He also learned Japanese kenjutsu techniques from Liu Yunfeng, who had studied under various Japanese masters of the sword. His ''Shaolin Gunfa Changzong'' was the first documented explanation of Shaolin methods, which had previously been transmitted only orally. Mao Yuanyi, the editor of the ''Wubei Zhi'', was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martial Arts
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defense; military and law enforcement applications; combat sport, competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; and the preservation of a nation's intangible cultural heritage. Etymology According to Paul Bowman, the term ''martial arts'' was popularized by mainstream popular culture during the 1960s to 1970s, notably by Hong Kong martial arts films (most famously those of Bruce Lee) during the so-called "chopsocky" wave of the early 1970s. According to John Clements, the term '':wikt:martial art, martial arts'' itself is derived from an older Latin (language), Latin term meaning "arts of Mars (mythology), Mars", the Roman mythology, Roman god of war, and was used to refer to the combat systems of Europe (European martial arts) as early as the 1550s. The term martial science, or martial sciences, was commonly used to refer to the fighting arts of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenjutsu
is an umbrella term for all ('' ko-budō'') schools of Japanese swordsmanship, in particular those that predate the Meiji Restoration. Some modern styles of kendo and iaido that were established in the 20th century also included modern forms of kenjutsu in their curriculum. Kenjutsu, which originated with the samurai class of feudal Japan, means "methods, techniques, and the art of the Japanese sword". This is opposed to kendo, which means "the way of the sword" and uses a bamboo sword (shinai) and protective armour (bōgu). The exact activities and conventions undertaken when practicing ''kenjutsu'' vary from school to school, where the word school here refers to the practice, methods, ethics, and metaphysics of a given tradition, yet commonly include practice of battlefield techniques without an opponent and techniques whereby two practitioners perform '' kata'' (featuring full contact strikes to the body in some styles and no body contact strikes permitted in others). Altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiuning County
Xiuning County () is a county in the south of Anhui Province, People's Republic of China, under the jurisdiction of the prefecture-level city of Huangshan City. The southernmost county-level division in the province, it has a population of and an area of . The government of Xiuning County is located in Haiyang Town (). Xiuning County has jurisdiction over nine towns and twelve townships. Administrative divisions Xiuning County is divided to 10 towns and 11 townships. ;Towns ;Townships History and culture Xiuning County is historically renowned for producing more ''zhuàngyuán'' (: the scholar with the highest score in the national Imperial examination), than any other place in China. Accordingly, the large public space in Haiyang Town is called Zhuangyuan Square (). In 2009, the Xiuning County People's Government unveiled a monument commemorating the 1800th anniversary of Xiuning (208-2008). Climate Western attention In 2003, the Peabody Essex Museum, in Salem, Massachus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaolin Monastery
Shaolin Monastery (少林寺 ''Shàolínsì''), also known as Shaolin Temple, is a renowned monastic institution recognized as the birthplace of Chan Buddhism and the cradle of Shaolin Kung Fu. It is located at the foot of Wuru Peak of the Songshan mountain range in Dengfeng County, Henan Province, China. The name reflects its location in the ancient grove (林 lín) of Mount Shaoshi, in the hinterland of the Songshan mountains. Mount Song occupied a prominent position among Chinese sacred mountains as early as the 1st century BC, when it was proclaimed one of the Five Holy Peaks (五岳 wǔyuè). It is located some thirty miles (about forty-eight kilometers) southeast of Luoyang, the former capital of the Northern Wei Dynasty (386–534), and forty-five miles (about seventy-two kilometers) southwest of Zhengzhou, the modern capital of Henan Province.Shahar 2008 As the first Shaolin abbot, Batuo devoted himself to translating Buddhist scriptures and to preaching doctrines to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wubei Zhi
The ''Wubei Zhi'' (; ''Treatise on Armament Technology'' or ''Records of Armaments and Military Provisions''), also commonly known by its Japanese translated name Bubishi, is a military book in Chinese history. It was compiled in 1621 by Mao Yuanyi (茅元儀 ''Máo Yuányí''; 1594–1640?), an officer of waterborne troops in the Ming Dynasty. The ''Wubei Zhi'' contains 240 volumes, 10,405 pages, and more than 200,000 Chinese characters. Structure ''Wubei Zhi'' consists of five sections, "Bing Jue Ping", "Zhan Lue Kao", "Zhen Lian Zhi", "Jun Zi Sheng", and "Zhan Du Zai". *"Bing Jue Ping" (Commentary on Military Formulae) Containing 18 chapters, this section includes military theories from significant figures including but not limited to Sun Tzu. Some of these theories back to the last years of Eastern Zhou Dynasty, more than 1,800 years before the editor. *"Zhan Lue Kao" (Consideration of Tactics) This section consists of 31 chapters, and describes more than 600 specific exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Male Martial Artists
Chinese can refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Han Chinese, the largest ethnic group in the world and the majority ethnic group in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, and Singapore ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chinese c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1561 Births
Year 1561 ( MDLXI) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–June * January 31 – The Edict of Orleans suspends the persecution of the Huguenots in France. * March 1 – Kingston Grammar School is founded in England. * April 14 – The citizens of Nuremberg see what appears to be an aerial battle, followed by the appearance of a large black triangular object and a large crash (with smoke) outside the city. A ''news notice'' (an early form of newspaper) is printed on April 14, describing the event. * May 8 – Madrid is declared the capital of Spain, by Philip II. * June 4 ** The spire of Old St Paul's Cathedral in the City of London catches fire and crashes through the nave roof, probably as the result of a lightning strike. The spire is not rebuilt. ** The nobility of Harrien-Wierland and the town of Reval (on June 6) of the Livonian Order swear allegiance to Sweden. * J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martial Arts Writers
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman poet from Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of ''Epigrams'', published in Rome between AD 86 and 103, during the reigns of the emperors Domitian, Nerva and Trajan. In these short, witty poems he cheerfully satirises city life and the scandalous activities of his acquaintances, and romanticises his provincial upbringing. He wrote a total of 1,561 epigrams, of which 1,235 are in elegiac couplets. Martial has been called the greatest Latin epigrammatist, and is considered the creator of the modern epigram. Early life Knowledge of his origins and early life are derived almost entirely from his works, which can be more or less dated according to the well-known events to which they refer. In Book X of his ''Epigrams'', composed between 95 and 98, he mentions celebrating his fifty-seventh birthday; hence he was born during March 38, 39, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)