|
Chedabucto Fault
The Chedabucto Fault is a Fault (geology), fault that divides Mainland Nova Scotia from the Minas Basin in the west to Chedabucto Bay in the east into the Avalonia, Avalon zone in the north and the Meguma Zone in the south. The Avalon and Meguma terrane, Meguma Zones are different because they belonged to different land masses that were widely separated from one another. The Avalon Zone was a part of Laurasia, while the Meguma Zone was a part of Gondwana. It marks the southern margin of the Cobequid Mountains. The Cobequid fault, Cobequid-Chedabucto Fault Zone is the most prominent geological feature of Nova Scotia. ReferencesCobequid-Chedabucto Fault at Cape Chignecto, Nova Scotia *[https://notyourgrandfathersmining.ca/geo-cc-fault-system Cobequid-Chedabucto Fault System] [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainland Nova Scotia
The Nova Scotia peninsula is a peninsula on the Atlantic coast of North America. Location The Nova Scotia peninsula is part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada and is connected to the neighbouring province of New Brunswick through the Isthmus of Chignecto. It fronts the open Atlantic Ocean on the south and southeast, the Gulf of Maine to the west, the Bay of Fundy and its sub-basins to the northwest, the Northumberland Strait to the north, and the Strait of Canso to the east. The narrow and deep waters of the Strait of Canso separate the peninsula from Cape Breton Island, the second largest land mass constituting the province of Nova Scotia. In addition to Cape Breton Island, other much smaller islands are geologically associated with the Nova Scotia peninsula, including Boularderie Island, Brier Island, Long Island, Pictou Island, Tancook Island and various smaller islands along the Atlantic coast. Geology The peninsula can be divided into two distinct geological regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minas Basin
, image = Lookout On Way to Cape Split - 25006718579.jpg , alt = , caption = Looking east across the Southern Bight of Minas Basin from The Lookoff , image_bathymetry = , alt_bathymetry = , caption_bathymetry = , location = Nova Scotia , group = , coordinates = , type = Inlet , etymology = , part_of = Bay of Fundy , inflow = , rivers = , outflow = , oceans = , catchment = , basin_countries = , agency = , designation = , date-built = , engineer = , date-flooded = , length = , width = , area = , depth = , max-depth = , volume = , residence_time = , salinity = , shore = , elevation = , temperature_high = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
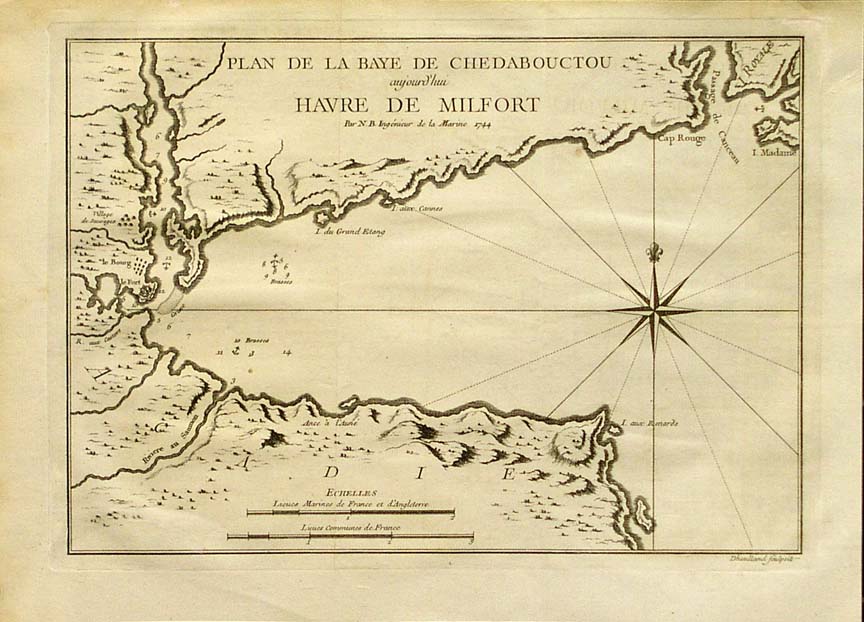
Chedabucto Bay
Chedabucto Bay is a large bay on the eastern coast of mainland Nova Scotia between the Atlantic Ocean and the Strait of Canso next to Guysborough County. At the entrance to Chedabucto Bay is the community of Canso at the head is the community of Guysborough and on the other end is the town of Mulgrave. Geography Chedabucto Bay was formed by the drowning of part of an ancient river system and owes its origin and shape to position of the Chedabucto Fault, which runs across central Nova Scotia from the Bay of Fundy to the Canso peninsula. History Colonial Merchants in La Rochelle, France enjoyed a fishing monopoly in Acadia and formed the Company of Acadia which established a small fortification on Chedabucto Bay named Fort St. Louis. The principal ports were at Chedabucto, which accounted for fifty fishers in 1686. In 1690, Captain Cyprian Southack proceeded to Chedabucto to take Fort St. Louis at the present-day village of Guysborough which, unlike Port-Royal, put up a figh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent underlie south-west Great Britain, southern Ireland, and the eastern coast of North America. It is the source of many of the older rocks of Western Europe, Atlantic Canada, and parts of the coastal United States. Avalonia is named for the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland. Avalonia developed as a volcanic arc on the northern margin of Gondwana. It eventually rifted off, becoming a drifting microcontinent. The Rheic Ocean formed behind it, and the Iapetus Ocean shrank in front. It collided with the continents Baltica, then Laurentia, and finally with Gondwana, ending up in the interior of Pangea. When Pangea broke up, Avalonia's remains were divided by the rift which became the Atlantic Ocean. Extent When the term "Avalon" was first coined by Canadian geologist Harold Williams in 1964, he included only Precambrian rocks in eastern Newfoundland. More than a decade later he ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meguma Terrane
The Meguma terrane, also known as Megumia, is a terrane exposed in southern Nova Scotia, that became joined to the present North American landmass as part of the Appalachian orogeny. The exposed part of the Meguma terrane, the Meguma Group, is largely composed of thick Cambrian to Ordovician turbidites that have been interpreted as submarine fan deposits. The Meguma terrane is joined to the Avalon terrane along the Minas Fault Zone, which runs east–west from Chedabucto Bay to Cobequid Bay and the Minas Basin. The Meguma Group is intruded by numerous Devonian and Carboniferous plutons. The extent of the formation is unclear; some geologists believe that a magnetic anomaly along the coast of Cape Cod may represent a suture between the Meguma and Avalon terranes in that region. Unlike the Avalon terrane, the Meguma terrane has not been definitely associated with a territory on the other side of the Atlantic. It may be represented in either the Galicia-Tras-Os-Montes Zone in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pangaea, drifting farther north after the split and finally broke apart with the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean c. 56 Mya. The name is a portmanteau of Laurentia and Asia. Laurentia, Avalonia, Baltica, and a series of smaller terranes, collided in the Caledonian orogeny c. 400 Ma to form Laurussia (also known as Euramerica, or the Old Red Sandstone Continent). Laurussia then collided with Gondwana to form Pangaea. Kazakhstania and Siberia were then added to Pangaea 290–300 Ma to form Laurasia. Laurasia finally became an independent continental mass when Pangaea broke up into Gondwana and Laurasia. Terminology and origin of the concept Laurentia, the Palaeozoic core of North America and continental fragments that now make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland. Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several cratons. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period, it merged with Laurasia to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea. Gondwana (and Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobequid Mountains
The Cobequid Mountains, also sometimes referred to as the Cobequid Hills, is a Canadian mountain range located in Nova Scotia in the mainland portion of the province. Geologic history Geologically, the Cobequid Mountains are considered part of the Appalachians. The range stretches from Cape Chignecto in Cumberland County in the west through to Pictou County in the east. The Cobequid Mountains trace their geologic history to the Precambrian and Devonian ages; consequently the mountains are composed of a combination of sediments, granites, and volcanic rock all of which has been crushed and folded by continental drift when this part of Nova Scotia was located at the centre of the Pangea supercontinent. Subsequent erosion over millions of years has resulted in the present-day low range of mountains and rolling hills. The part of northern Nova Scotia which contains the Cobequid Mountains is believed to have been linked with what is now northern Europe. Its collision with a section ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobequid Fault
The Cobequid Fault is a fault that is the extension of the Chedabucto Fault. This fault runs from Truro to Cape Chignecto south of the Cobequid Hills. Both the Cobequid fault and the Chedabucto Fault form the Minas Fault zone splitting Nova Scotia into the Avalon Zone and the Meguma Zone. Movement on the Cobequid Fault started before 400 million years ago and end around 40 million years ago. Between that time around 350 million years violent volcanic eruptions at Spicers Cove north Cape Chignecto Provincial Park and 50 million years after grey sandstone rich in fossil plants were deposited. At Five Islands Provincial Park 5 is a number, numeral, and glyph. 5, five or number 5 may also refer to: * AD 5, the fifth year of the AD era * 5 BC, the fifth year before the AD era Literature * 5 (visual novel), ''5'' (visual novel), a 2008 visual novel by Ram * 5 (comic ... there are red rocks formed by the large accumulation of mud, sand and gravel around 210 million years ago. Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |