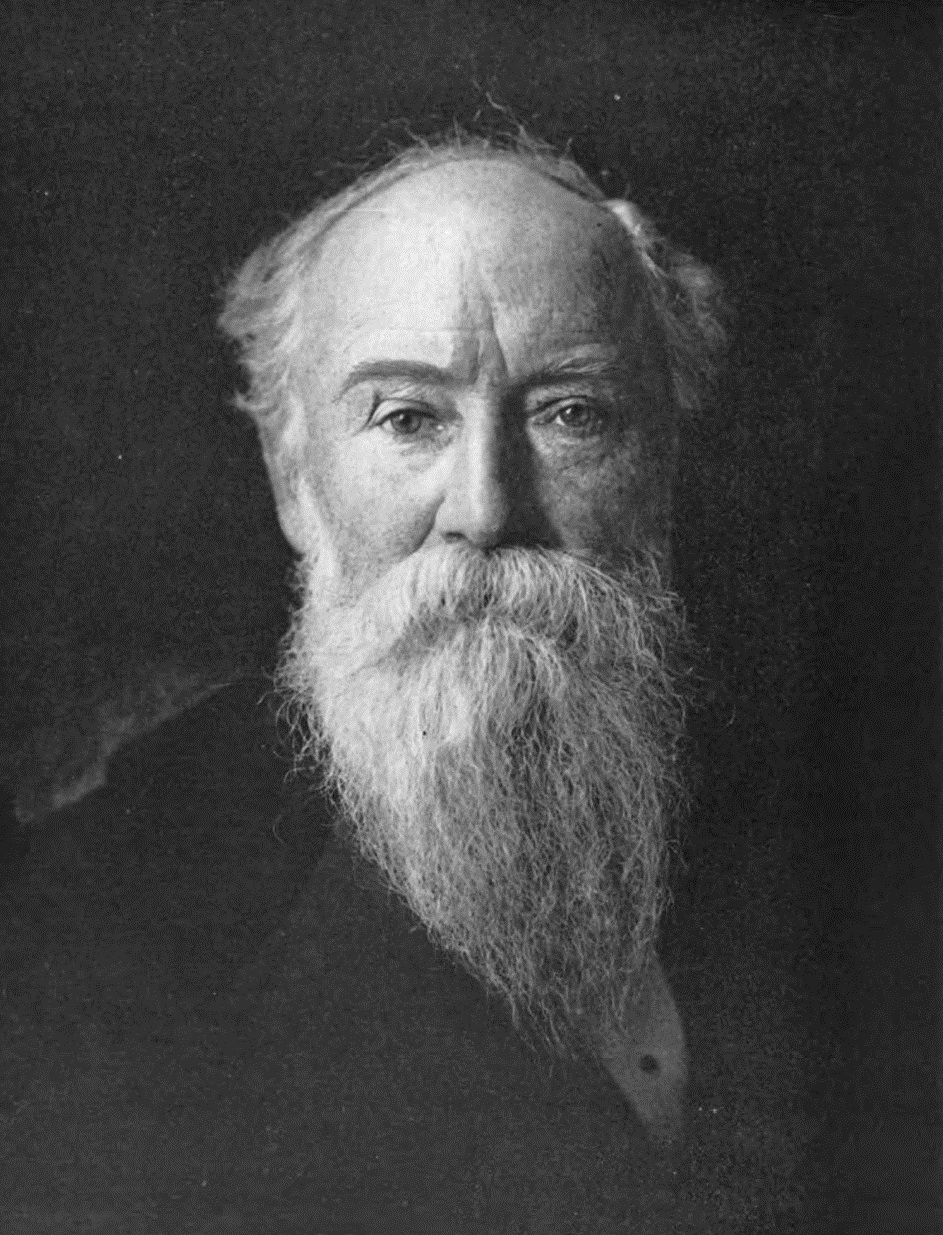|
Chautauqua Lake Central School
Chautauqua ( ) was an adult education and social movement in the United States, highly popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Chautauqua assemblies expanded and spread throughout rural America until the mid-1920s. The Chautauqua brought entertainment and culture for the whole community, with speakers, teachers, musicians, showmen, preachers, and specialists of the day. Former U.S. President Theodore Roosevelt was quoted as saying that Chautauqua is "the most American thing in America." History The First Chautauquas In 1873, the first Chautauqua, Lakeside Chautauqua on Ohio's Lake Erie, was formed by the Methodists. The next year, 1874, the New York Chautauqua Assembly was organized by Methodist minister John Heyl Vincent and businessman Lewis Miller at a campsite on the shores of Chautauqua Lake in the state of New York. Two years earlier, Vincent, editor of the ''Sunday School Journal'', had begun to train Sunday school teachers in an outdoor summer sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chautauqua (pemberton0201)
Chautauqua ( ) is an adult education and social movement in the United States that peaked in popularity in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Chautauqua assemblies expanded and spread throughout rural America until the mid-1920s. The Chautauqua brought entertainment and culture for the whole community, with speakers, teachers, musicians, showmen, preachers, and specialists of the day. U.S. President Theodore Roosevelt said that Chautauqua is "the most American thing in America". History The First Chautauquas In 1873, Methodists formed the first Chautauqua, Lakeside Chautauqua on Ohio's Lake Erie. In 1874, Methodist Episcopal minister John Heyl Vincent and businessman Lewis Miller organized the New York Chautauqua Assembly at a campsite on the shores of Chautauqua Lake in the state of New York. Two years earlier, Vincent, editor of the ''Sunday School Journal'', had begun to train Sunday school teachers in an outdoor summer school format. The gatherings grew in popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acres Of Diamonds
Russell Herman Conwell (February 15, 1843 – December 6, 1925) was an American Baptist minister, orator, philanthropist, author, lawyer, and writer. He is best remembered as the founder and first president of Temple University in Philadelphia, as the Pastor of The Baptist Temple, and for his inspirational lecture, "Acres of Diamonds". He was born in South Worthington, Massachusetts. Biography Early life The son of Massachusetts farmers, Conwell left home to attend the Wilbraham Wesleyan Academy and later Yale University. In 1862, before graduating from Yale, he enlisted in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Conwell desired to enlist in the war effort shortly after its outbreak in 1861, but could not initially gain the approval of his father, Martin Conwell. His abolitionist father ultimately changed his mind, allowing Conwell to enlist in Company "F" of the 27th Massachusetts Volunteers, better known as the "Mountain Boys". Conwell and the Mountain Boys served in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
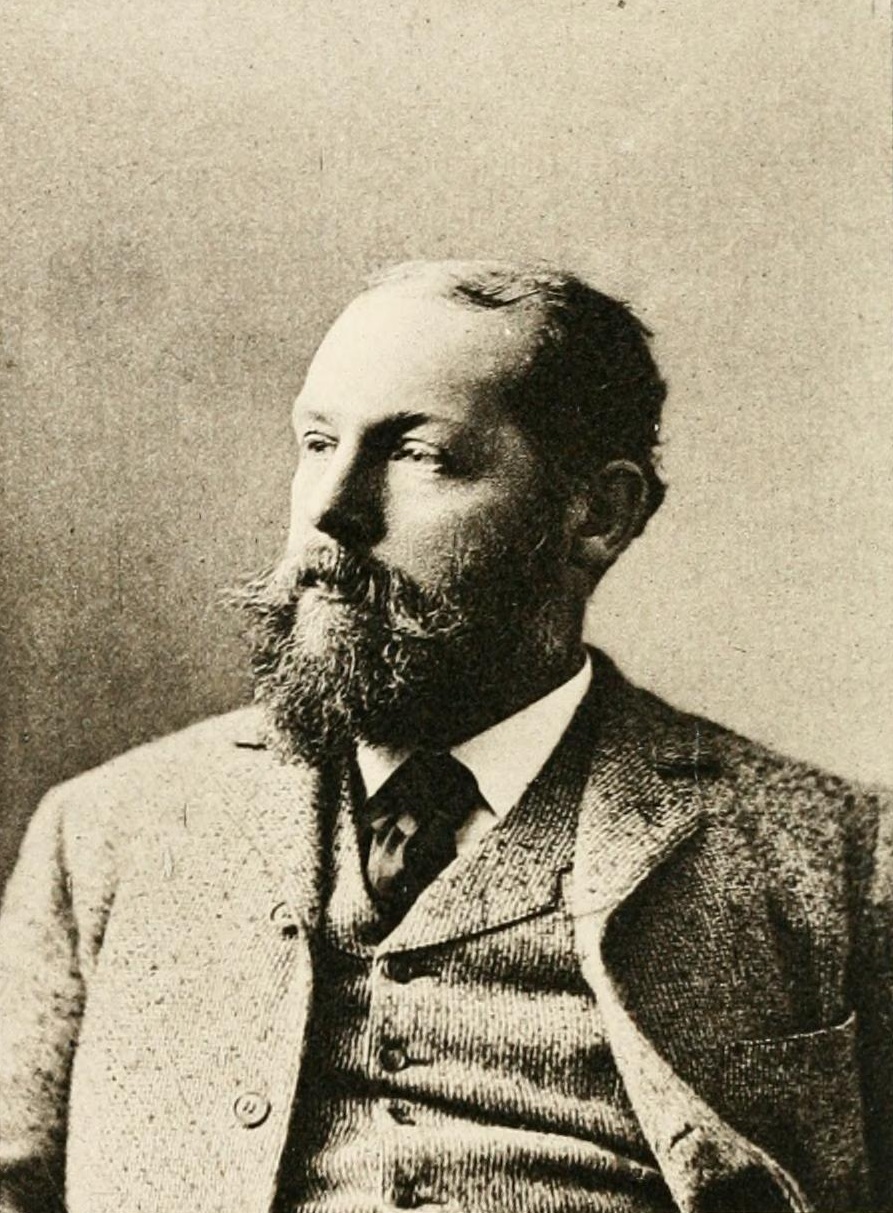
Russell Conwell
Russell Herman Conwell (February 15, 1843 – December 6, 1925) was an American Baptist minister, orator, philanthropist, author, lawyer, and writer. He is best remembered as the founder and first president of Temple University in Philadelphia, as the Pastor of The Baptist Temple, and for his inspirational lecture, "Acres of Diamonds". He was born in South Worthington, Massachusetts. Biography Early life The son of Massachusetts farmers, Conwell left home to attend the Wilbraham Wesleyan Academy and later Yale University. In 1862, before graduating from Yale, he enlisted in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Conwell desired to enlist in the war effort shortly after its outbreak in 1861, but could not initially gain the approval of his father, Martin Conwell. His abolitionist father ultimately changed his mind, allowing Conwell to enlist in Company "F" of the 27th Massachusetts Volunteers, better known as the "Mountain Boys". Conwell and the Mountain Boys served in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan (March 19, 1860 – July 26, 1925) was an American lawyer, orator and politician. Beginning in 1896, he emerged as a dominant force in the History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, running three times as the party's nominee for President of the United States in the 1896 United States presidential election, 1896, 1900 United States presidential election, 1900, and the 1908 United States presidential election, 1908 elections. He served in the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives from 1891 to 1895 and as the United States Secretary of State, Secretary of State under Woodrow Wilson. Because of his faith in the wisdom of the common people, Bryan was often called "The Great Commoner", and because of his rhetorical power and early notoriety, "The Boy Orator". Born and raised in Illinois, Bryan moved to Nebraska in the 1880s. He won election to the House of Representatives in the 1890 United States House ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Luther Mott
Frank Luther Mott (April 4, 1886 – October 23, 1964) was an American historian and journalist, who won the 1939 Pulitzer Prize for History for Volumes II and III of his series, ''A History of American Magazines''. Early life and education Mott was born in Rose Hill, Iowa. His parents were Mary E. (Tipton) and David Charles Mott, publishers of the weekly ''What Cheer, Iowa Patriot''. The Mott family owned a print shop in Keokuk County. He was a practicing Religious Society of Friends, Quaker. When he was 10 his father began publishing the Audubon, Iowa ''Republican'' and he assisted in the typesetting. He did the first three years of his college education at Simpson College and then completed his bachelor's degree at the University of Chicago. Mott attended Columbia University starting in 1917, earning his M.A. in 1919. Carl Van Doren, mentioned in the Franklin section below, was teaching at Columbia during this time, and the two may have met then. Mott earned his Ph.D. in 1928 f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Gilman
Arthur Delevan Gilman (November 5, 1821, Newburyport, Massachusetts – July 11, 1882, Syracuse, New York) was an American architect, designer of many Boston neighborhoods, and member of the American Institute of Architects. Life and career Gilman was a descendant of Edward Gilman, Sr., one of the first settlers of Exeter, New Hampshire. Gilman was educated at Trinity College in Hartford, Connecticut. In 1844 he published a paper on "American Architecture" in the ''North American Review'', which was translated into several foreign languages. He was then invited to deliver twelve lectures before the Lowell Institute, Boston, after which he went to Europe on a tour of professional observation. On his return to Boston, he advocated filling in the Back Bay district, urging this plan for years before his views were carried out by the state. Here Gridley James Fox Bryant was his colleague. Commonwealth Avenue, now one of the finest streets in the world, is due almost entirely to his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Torrey Harris
William Torrey Harris (September 10, 1835 – November 5, 1909) was an American educator, philosopher, and lexicographer. He worked for nearly a quarter century in St. Louis, Missouri, where he taught school and served as Superintendent of Schools for twelve years. With Susan Blow, in 1873 he established the first permanent, public kindergarten in the country. He is also known for establishing high school as an integral part of public education. Increasingly interested in Hegelian philosophy, he was cofounder of ''Journal of Speculative Philosophy'' (1867), the first philosophical journal in the US. He also worked with Amos Bronson Alcott's Concord School of Philosophy. In 1889 Harris was appointed as US Commissioner of Education, and served in that role, under four presidents, until 1906. Biography Born in 1835 in North Killingly, Connecticut, he attended Phillips Academy in Andover, Massachusetts. He completed two years at Yale College, then moved West. Beginning at age 22, H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hjalmar Hjorth Boyesen
Hjalmar Hjorth Boyesen (23 September 1848 – 4 October 1895) was a Norwegian-American author and college professor. He is best remembered for his novel ''Gunnar: A Tale of Norse Life'', which is generally considered to have been the first novel by a Norwegian immigrant in America. Biography He was born at the Norwegian naval base Fredriksvern, near the village of Stavern in Vestfold County, Norway. Boyesen grew up in Fredriksvern, then in Kongsberg, and, from 1854, at Systrand in Sogn. From 1860, he went to Drammen Latin School, and, after his final exams, he took another exam at the university in 1868. Boyesen was well-schooled in both German and Scandinavian literature, graduating from the University of Leipzig and the University of Oslo. Career Boyesen migrated to the United States during 1869 and initially became assistant editor of '' Fremad'', a Norwegian language weekly published in Chicago. The multi-lingual Boyesen subsequently taught Greek and Latin classes at Urbana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Burroughs
John Burroughs (April 3, 1837 – March 29, 1921) was an American naturalist and nature essayist, active in the conservation movement in the United States. The first of his essay collections was ''Wake-Robin'' in 1871. In the words of his biographer Edward Renehan, Burroughs' special identity was less that of a scientific naturalist than that of "a literary naturalist with a duty to record his own unique perceptions of the natural world." The result was a body of work whose resonance with the tone of its cultural moment explains both its popularity at that time, and its relative obscurity since. Early life and marriage Burroughs was the seventh of Chauncy and Amy Kelly Burroughs' ten children. He was born on the family farm in the Catskill Mountains, near Roxbury in Delaware County, New York. As a child he spent many hours on the slopes of Old Clump Mountain, looking off to the east and the higher peaks of the Catskills, especially Slide Mountain, which he would later writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Pentland Mahaffy
Sir John Pentland Mahaffy (26 February 183930 April 1919) was an Irish classicist and polymathic scholar. Education and Academic career He was born near Vevey in Switzerland on 26 February 1839 to Irish parents, Nathaniel Brindley Mahaffy and the former Elizabeth Pentland, receiving his early education privately in Switzerland and Germany, and later and more formally at Trinity College Dublin. As an undergraduate, he became President of the University Philosophical Society. He was elected a scholar in 1857, graduated in classics and philosophy in 1859, and was elected a fellow in 1864. Mahaffy held a chair in Ancient History at Trinity from 1871, and eventually became Provost in 1914, at the age of 75. He was a distinguished classicist and papyrologist as well as a Doctor of Music. He wrote the music for the Grace in chapel. Mahaffy, a man of great versatility, published numerous works across a range of subjects, some of which, especially those dealing with the 'Silver Age' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)