|
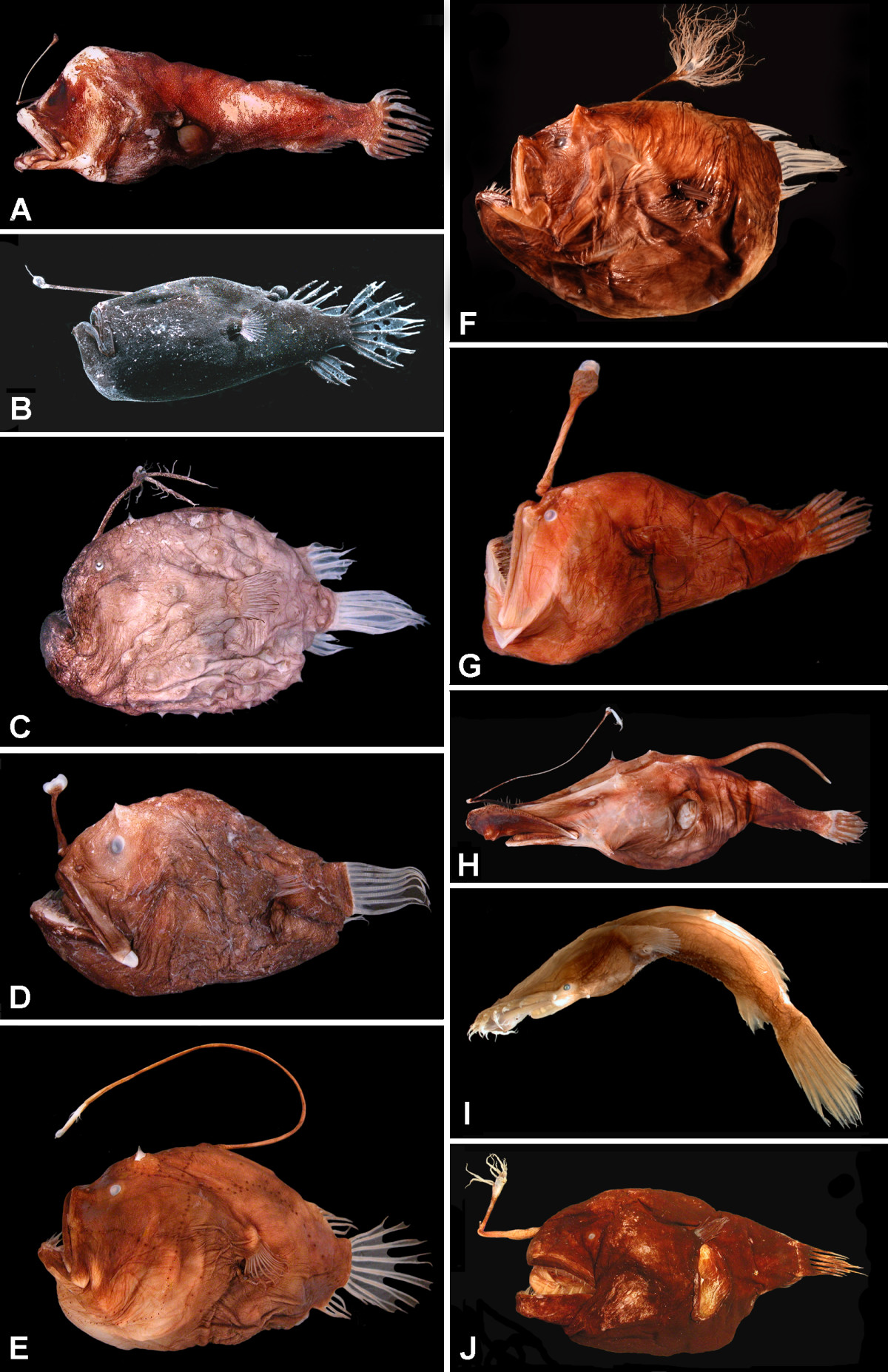
Chaunax Endeavouri
The coffinfish or furry coffinfish (''Chaunax endeavouri'') is a species of sea toad of the family Chaunacidae. It is found in salty temperate waters of southwestern Pacific, off east coast of Australia. The coffinfish was first discovered around February 1997 in Sicily, Italy by the skipper of the ''Libra'', which was a trawler who was harbored in Mazara at the time. It can be also found in depths of . Deep sea crab fishermen off the east coast of Florida pull them up from depth ranging from 5,000–8,000 feet about 54–68 miles off the coast. They have a globose and spiny body that grows to a maximum length of (SL male/unsexed) and a black mouth lining and an illicium on the snout that can be lowered into a groove. Distribution Endemic to the temperate waters of the southwestern Pacific, off east coast of Australia. Habitat Benthic, muddy bottom of the ocean, Australian continental shelf and upper slope in the deep ocean, usually 200m–2500m. The Indian Ocean also has two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert Percy Whitley
Gilbert Percy Whitley (9 June 1903 – 18 July 1975) was a British-born Australian ichthyologist and malacologist who was Curator of Fishes at the Australian Museum in Sydney for about 40 years. He was born at Swaythling, Southampton, England, and was educated at King Edward VI School, Southampton and the Royal Naval College, Osborne. Whitley migrated with his family to Sydney in 1921 and he joined the staff of the Australian Museum in 1922 while studying zoology at Sydney Technical College and the University of Sydney. In 1925 he was formally appointed Ichthyologist (later Curator of Fishes) at the Museum, a position he held until retirement in 1964. During his term of office he doubled the size of the ichthyological collection to 37,000 specimens through many collecting expeditions. Whitley was also a major force in the Royal Zoological Society of New South Wales, of which he was made a Fellow in 1934 and where he served as president during 1940–41, 1959–60 and 1973–74. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterolateral
{{disambig ...
Anterolateral may refer to: * Anterolateral central arteries * Anterolateral ligament * Anterolateral ganglionic branches * Anterolateral sulcus of medulla * Anterolateral sulcus of spinal cord * Anterolateral system The spinothalamic tract is a part of the anterolateral system or the ventrolateral system, a sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Fauna Of Australia
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Fish Of Australia
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean. Marine or marines may refer to: Ocean * Maritime (other) * Marine art * Marine biology * Marine debris * Marine habitats * Marine life * Marine pollution Military * Marines, a naval-based infantry force ** United States Marine Corps ** Royal Marines of the UK ** Brazilian Marine Corps ** Spanish Marine Infantry ** Fusiliers marins (France) ** Indonesian Marine Corps ** Republic of China Marine Corps ** Republic of Korea Marine Corps ** Royal Thai Marine Corps *"Marine" also means "navy" in several languages: ** Austro-Hungarian Navy () ** Belgian Navy (, , ) ** Royal Canadian Navy () *** Provincial Marine (1796–1910), a predecessor to the Royal Canadian Navy ** Navy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo () ** Royal Danish Navy () ** Finnish Navy (, ) ** French Navy () ** Gabonese Navy () ** German Navy () ** Royal Moroccan Navy () ** Royal Netherlands Navy () ** Swedish Navy () Places * Marines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Pacific Ocean
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Most fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Indian Ocean
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthomysis Microps
''Acanthomysis microps'' is a species of mysid that was discovered during a study of the coastal waters of Maharashtra and South Gujarat that took place during 2008 and 2009. This species of mysid is different from others in the same genus because of its "combination of broadly rounded rostrum, narrower eyes and the spination of the uropodal endopod and telson The telson () is the posterior-most division of the body of an arthropod. Depending on the definition, the telson is either considered to be the final segment of the arthropod body, or an additional division that is not a true segment on accou ..." . References Mysida Crustaceans described in 2009 {{Malacostraca-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagic Zone
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients (such as iron, magnesium and calcium) all change. Marine life is affected by bathymetry (underwater topography) such as the seafloor, shoreline, or a submarine seamount, as well as by proximity to the boundary between the ocean and the atmosphere at the ocean surface, which brings light for photosynthesis, predation from above, and wind stirring up waves and setting currents in motion. The pelagic zone refers to the open, free waters away from the shore, where marine life can swim freely in any direction unhindered by topographical constraints. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraodontidae
Tetraodontidae is a family of primarily marine and estuarine fish of the order Tetraodontiformes. The family includes many familiar species variously called pufferfish, puffers, balloonfish, blowfish, blowies, bubblefish, globefish, swellfish, toadfish, toadies, toadle, honey toads, Haaris Anwar fish, sugar toads, and sea squab. They are morphologically similar to the closely related porcupinefish, which have large external spines (unlike the thinner, hidden spines of the Tetraodontidae, which are only visible when the fish have puffed up). The scientific name refers to the four large teeth, fused into an upper and lower plate, which are used for crushing the hard shells of crustaceans and mollusks, their natural prey. The majority of pufferfish species are toxic and some are among the most poisonous vertebrates in the world. In certain species, the internal organs, such as the liver, and sometimes the skin, contain tetrodotoxin, and are highly toxic to most animals when ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)