|
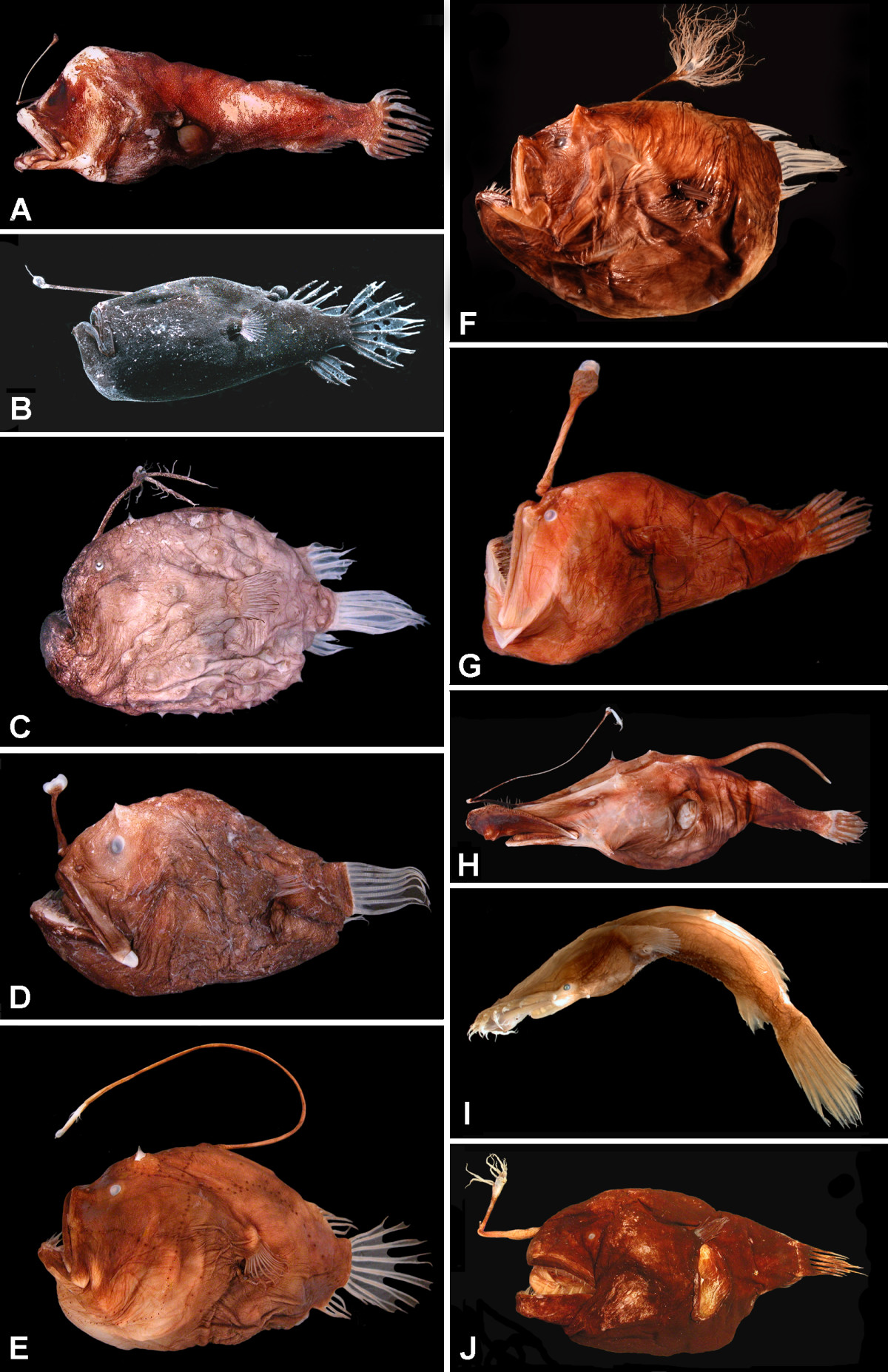
Chaunacops Roseus
''Chaunacops'' is a genus of lophiiform fish (anglerfish) in the family Chaunacidae. They are characterized as having globose heads, open sensory and lateral line canals, and loose skin covered by small spine-like scales. Colour, which has been noted as an important distinguishing characteristic, has generally been described as pink, reddish orange, or rose (Garman, 1899; Caruso, 1989b). However, recent work by Lundsten et al. (2012) suggests that juvenile ''Chaunacops coloratus'' may be blue and only adults are red or rose coloured. ''Chaunacops coloratus'' was first described in 1899 from a dead specimen collected during the US Albatross Expedition of 1891 at the Cocos Ridge collecting station. It is a deep-sea species of the order Lophiiformes (anglerfishes).This species is benthic, living at reported depths from 1789 to 3297 m in the east Indian and eastern Pacific oceans. It was first filmed alive at the seafloor at Davidson and Taney Seamounts in the northeast Pacific Ocea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davidson Seamount
Davidson Seamount is a seamount ( underwater volcano) located off the coast of Central California, southwest of Monterey and west of San Simeon. At long and wide, it is one of the largest known seamounts in the world. From base to crest, the seamount is tall, yet its summit is still below the sea surface. The seamount is biologically diverse, with 237 species and 27 types of deep-sea coral having been identified. Discovered during the mapping of California's coast in 1933, Davidson Seamount is named after geographer George Davidson of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey. Studied only sparsely for decades, NOAA expeditions to the seamount in 2002 and 2006 cast light upon its unique deep-sea coral ecosystem. Davidson Seamount is populated by a dense population of large, ancient corals, some of which are over 100 years of age. The data gathered during the studies fueled the making of Davidson Seamount into a part of the Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary in 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Garman
Samuel Walton Garman (June 5, 1843 – September 30, 1927), or "Garmann" as he sometimes styled himself, was a naturalist/zoologist from Pennsylvania. He became noted as an ichthyologist and herpetologist. Biography Garman was born in Indiana County, Pennsylvania, on 5 June 1843. In 1868 he joined an expedition to the American West with John Wesley Powell. He graduated from the Illinois State Normal University in 1870, and for the following year was principal of the Mississippi State Normal School. In 1871, he became professor of natural sciences in Ferry Hall Seminary, Lake Forest, Illinois, and a year later became a special pupil of Louis Agassiz. He was a friend and regular correspondent of the naturalist Edward Drinker Cope, and in 1872 accompanied him on a fossil hunting trip to Wyoming. In 1870 he became assistant director of herpetology and ichthyology at Harvard's Museum of Comparative Zoology. His work was mostly in the classification of fish, especially sharks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophiiform
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas the benth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial cells, known as hair cells, which respond to displacement caused by motion and transduce these signals into electrical impulses via excitatory synapses. Lateral lines serve an important role in schooling behavior, predation, and orientation. Fish can use their lateral line system to follow the vortices produced by fleeing prey. Lateral lines are usually visible as faint lines of pores running lengthwise down each side, from the vicinity of the gill covers to the base of the tail. In some species, the receptive organs of the lateral line have been modified to function as electroreceptors, which are organs used to detect electrical impulses, and as such, these systems remain closely linked. Most amphibian larvae and some fully aquatic adult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaunacops Coloratus
''Chaunacops'' is a genus of lophiiform fish (anglerfish) in the family Chaunacidae. They are characterized as having globose heads, open sensory and lateral line canals, and loose skin covered by small spine-like scales. Colour, which has been noted as an important distinguishing characteristic, has generally been described as pink, reddish orange, or rose (Garman, 1899; Caruso, 1989b). However, recent work by Lundsten et al. (2012) suggests that juvenile '' Chaunacops coloratus'' may be blue and only adults are red or rose coloured. '' Chaunacops coloratus'' was first described in 1899 from a dead specimen collected during the US Albatross Expedition of 1891 at the Cocos Ridge collecting station. It is a deep-sea species of the order Lophiiformes (anglerfishes).This species is benthic, living at reported depths from 1789 to 3297 m in the east Indian and eastern Pacific oceans. It was first filmed alive at the seafloor at Davidson and Taney Seamounts in the northeast Pacific Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaunacops Melanostomus
''Chaunacops'' is a genus of lophiiform fish (anglerfish) in the family Chaunacidae. They are characterized as having globose heads, open sensory and lateral line canals, and loose skin covered by small spine-like scales. Colour, which has been noted as an important distinguishing characteristic, has generally been described as pink, reddish orange, or rose (Garman, 1899; Caruso, 1989b). However, recent work by Lundsten et al. (2012) suggests that juvenile ''Chaunacops coloratus'' may be blue and only adults are red or rose coloured. ''Chaunacops coloratus'' was first described in 1899 from a dead specimen collected during the US Albatross Expedition of 1891 at the Cocos Ridge collecting station. It is a deep-sea species of the order Lophiiformes (anglerfishes).This species is benthic, living at reported depths from 1789 to 3297 m in the east Indian and eastern Pacific oceans. It was first filmed alive at the seafloor at Davidson and Taney Seamounts in the northeast Pacific Ocea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John H
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaunacops Roseus
''Chaunacops'' is a genus of lophiiform fish (anglerfish) in the family Chaunacidae. They are characterized as having globose heads, open sensory and lateral line canals, and loose skin covered by small spine-like scales. Colour, which has been noted as an important distinguishing characteristic, has generally been described as pink, reddish orange, or rose (Garman, 1899; Caruso, 1989b). However, recent work by Lundsten et al. (2012) suggests that juvenile ''Chaunacops coloratus'' may be blue and only adults are red or rose coloured. ''Chaunacops coloratus'' was first described in 1899 from a dead specimen collected during the US Albatross Expedition of 1891 at the Cocos Ridge collecting station. It is a deep-sea species of the order Lophiiformes (anglerfishes).This species is benthic, living at reported depths from 1789 to 3297 m in the east Indian and eastern Pacific oceans. It was first filmed alive at the seafloor at Davidson and Taney Seamounts in the northeast Pacific Ocea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Barbour
Thomas Barbour (August 19, 1884 – January 8, 1946) was an American herpetologist. From 1927 until 1946, he was director of the Harvard Museum of Comparative Zoology (MCZ) founded in 1859 by Louis Agassiz at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Life and career Barbour, the eldest of four brothers, was born in 1884 to Colonel William Barbour, and his wife, Julia Adelaide Sprague. Colonel Barbour was founder and president of The Linen Thread Company, Inc., a successful thread manufacturing enterprise having much business in the United States, Ireland, and Scotland. Although born on Martha's Vineyard, Massachusetts, where the family was spending the summer, Barbour grew up in Monmouth, New Jersey, where one of his younger brothers, William Warren Barbour, entered the political arena, eventually serving as U.S. Senator from New Jersey from 1931 to 1937 and again from 1938 to 1943. At age fifteen, Thomas Barbour was taken to visit Harvard University, which, entranced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaunacops Spinosus
''Chaunacops'' is a genus of lophiiform fish (anglerfish) in the family Chaunacidae. They are characterized as having globose heads, open sensory and lateral line canals, and loose skin covered by small spine-like scales. Colour, which has been noted as an important distinguishing characteristic, has generally been described as pink, reddish orange, or rose (Garman, 1899; Caruso, 1989b). However, recent work by Lundsten et al. (2012) suggests that juvenile ''Chaunacops coloratus'' may be blue and only adults are red or rose coloured. ''Chaunacops coloratus'' was first described in 1899 from a dead specimen collected during the US Albatross Expedition of 1891 at the Cocos Ridge collecting station. It is a deep-sea species of the order Lophiiformes (anglerfishes).This species is benthic, living at reported depths from 1789 to 3297 m in the east Indian and eastern Pacific oceans. It was first filmed alive at the seafloor at Davidson and Taney Seamounts in the northeast Pacific Ocea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |