|
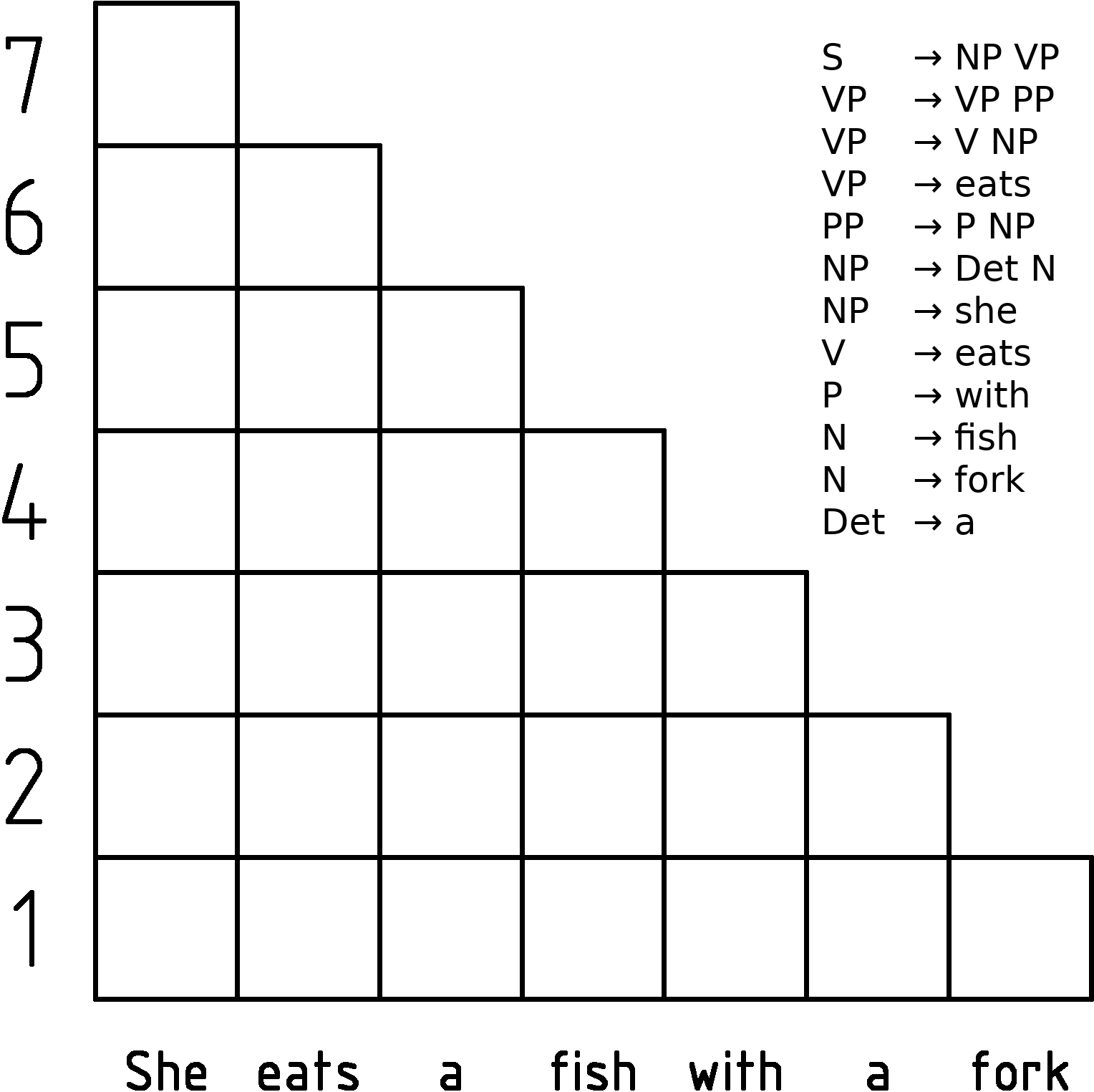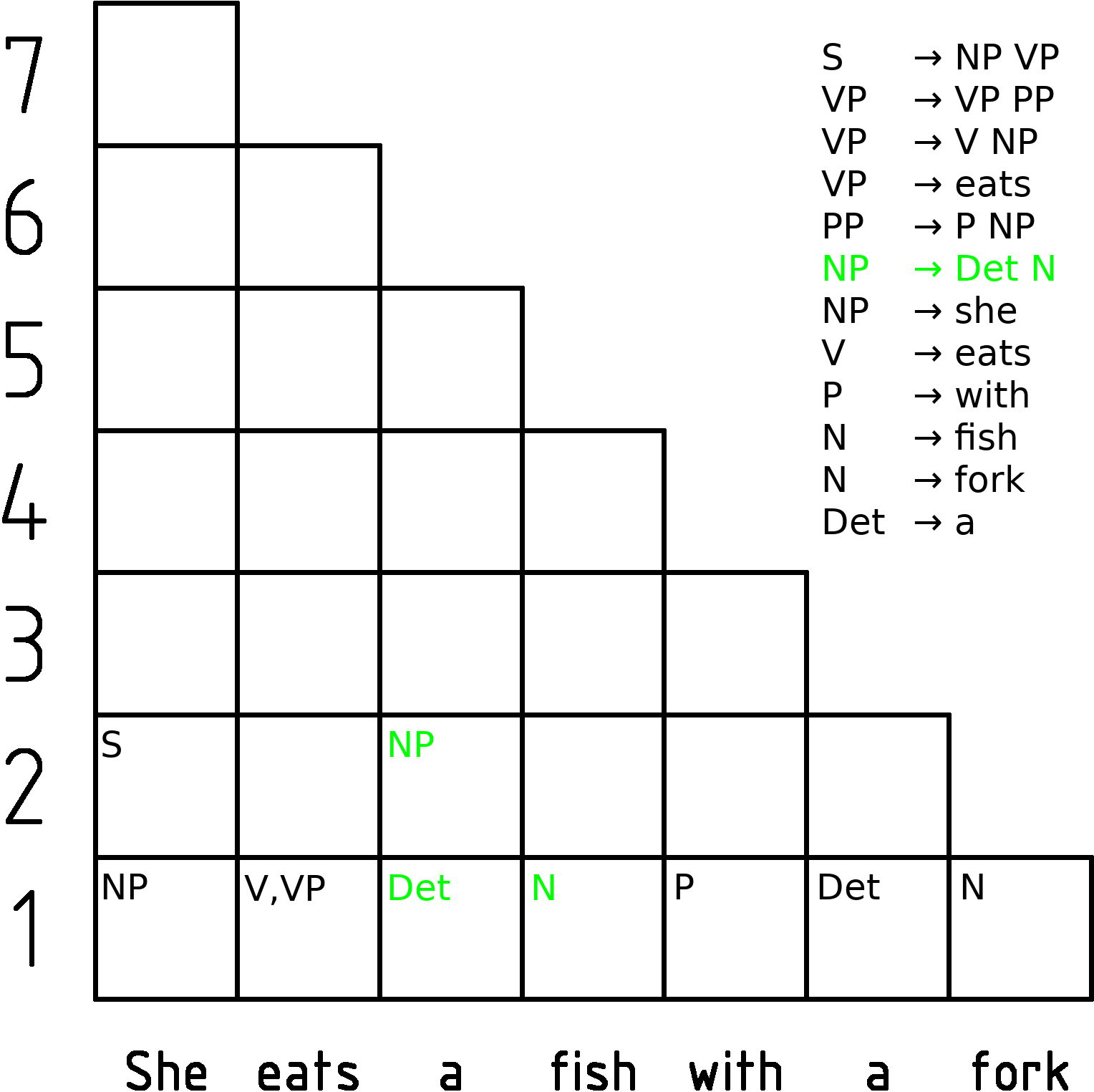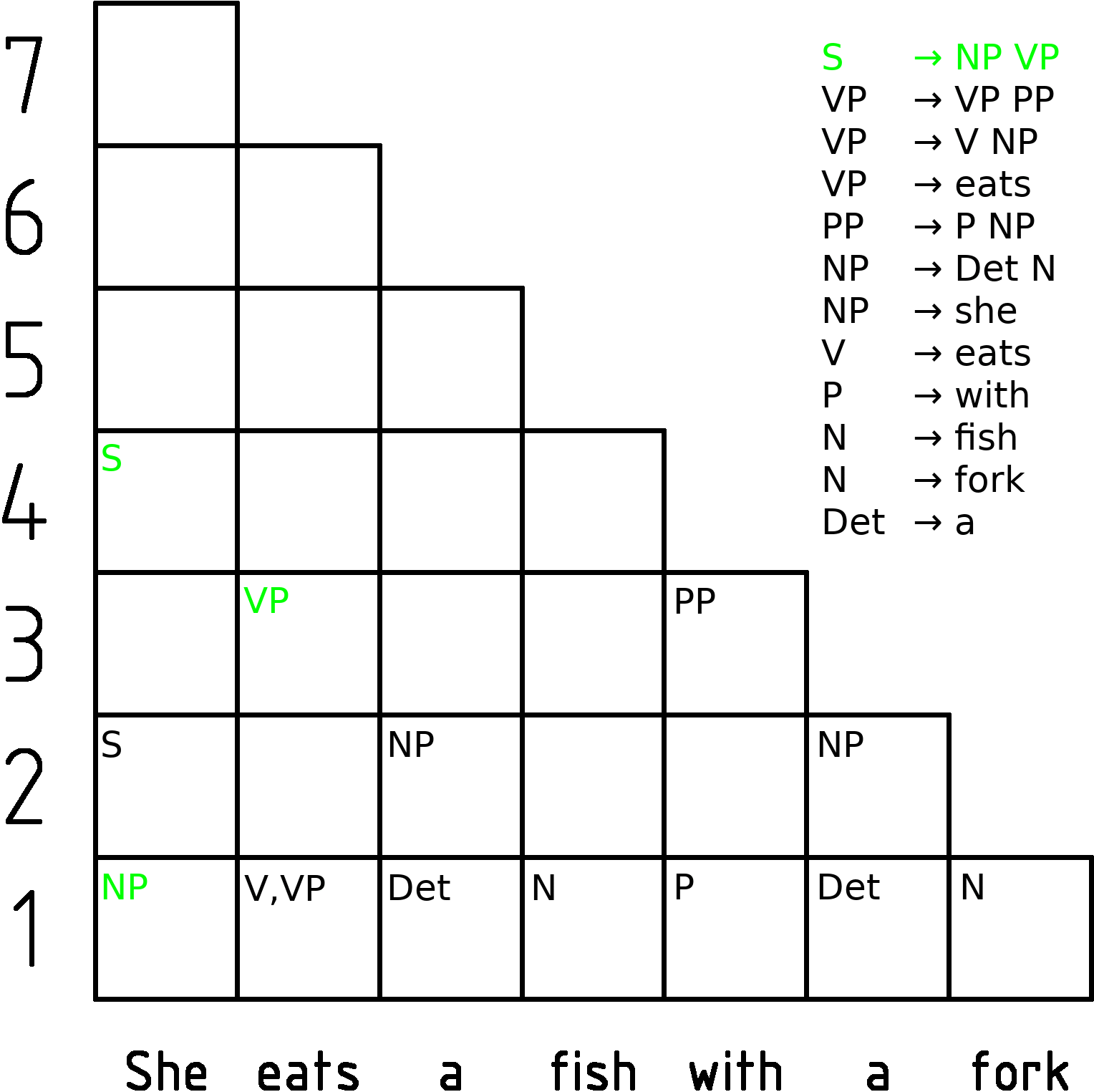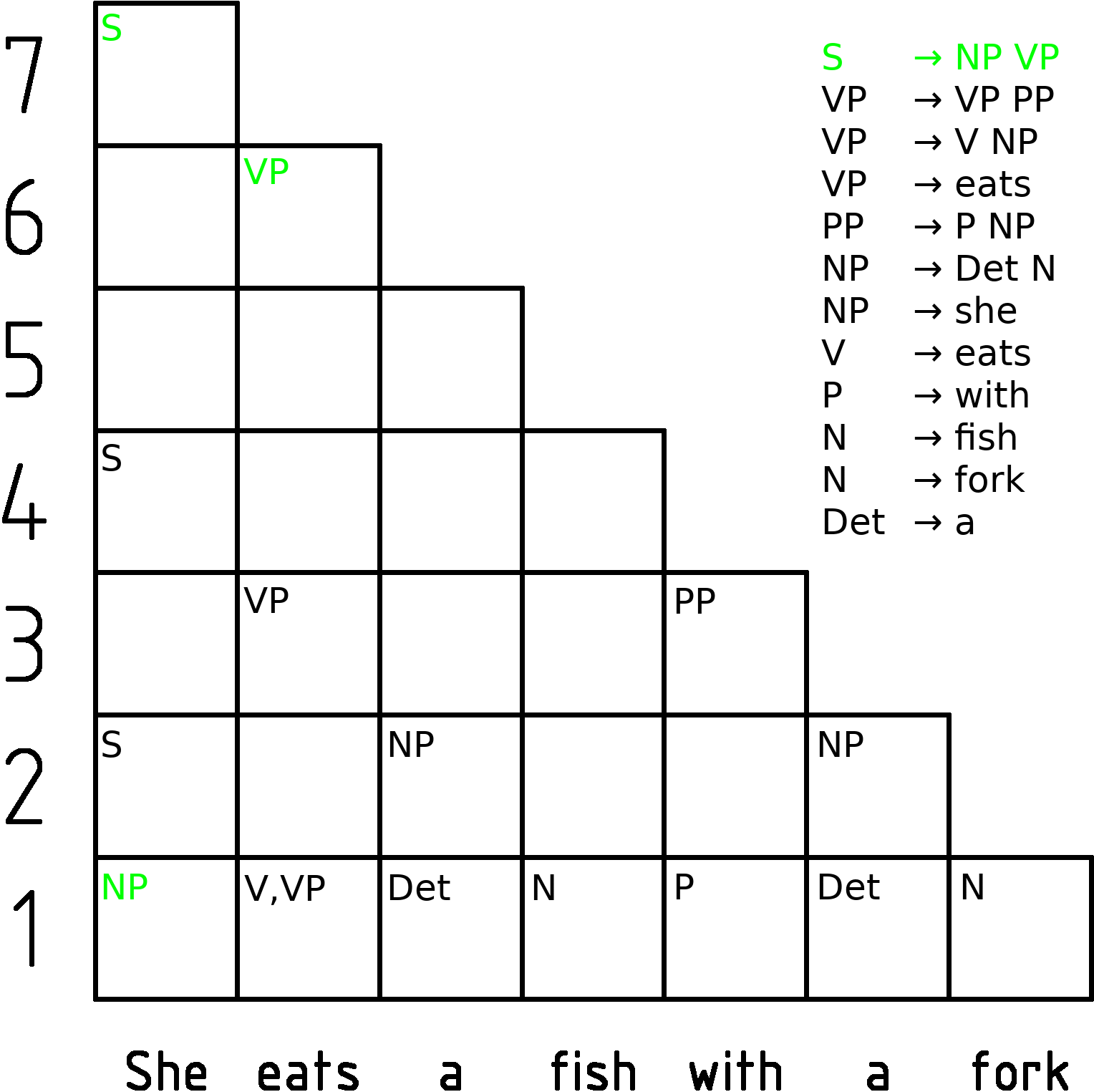
Chart Parsing
In computer science, a chart parser is a type of parser suitable for ambiguous grammars (including grammars of natural languages). It uses the dynamic programming approach—partial hypothesized results are stored in a structure called a chart and can be re-used. This eliminates backtracking and prevents a combinatorial explosion. Chart parsing is generally credited to Martin Kay. Types of chart parsers A common approach is to use a variant of the Viterbi algorithm. The Earley parser is a type of chart parser mainly used for parsing in computational linguistics, named for its inventor. Another chart parsing algorithm is the Cocke-Younger-Kasami (CYK) algorithm. Chart parsers can also be used for parsing computer languages. Earley parsers in particular have been used in compiler-compilers where their ability to parse using arbitrary Context-free grammars eases the task of writing the grammar for a particular language. However their lower efficiency has led to people avoidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Parsing
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is the process of analyzing a string of symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar. The term ''parsing'' comes from Latin ''pars'' (''orationis''), meaning part (of speech). The term has slightly different meanings in different branches of linguistics and computer science. Traditional sentence parsing is often performed as a method of understanding the exact meaning of a sentence or word, sometimes with the aid of devices such as sentence diagrams. It usually emphasizes the importance of grammatical divisions such as subject and predicate. Within computational linguistics the term is used to refer to the formal analysis by a computer of a sentence or other string of words into its constituents, resulting in a parse tree showing their syntactic relation to each other, which may also contain semantic and other information ( p-values). Some parsing algor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsing
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is the process of analyzing a string of symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar. The term ''parsing'' comes from Latin ''pars'' (''orationis''), meaning part (of speech). The term has slightly different meanings in different branches of linguistics and computer science. Traditional sentence parsing is often performed as a method of understanding the exact meaning of a sentence or word, sometimes with the aid of devices such as sentence diagrams. It usually emphasizes the importance of grammatical divisions such as subject and predicate. Within computational linguistics the term is used to refer to the formal analysis by a computer of a sentence or other string of words into its constituents, resulting in a parse tree showing their syntactic relation to each other, which may also contain semantic and other information ( p-values). Some parsing algo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brute-force Search
In computer science, brute-force search or exhaustive search, also known as generate and test, is a very general problem-solving technique and algorithmic paradigm that consists of systematically enumerating all possible candidates for the solution and checking whether each candidate satisfies the problem's statement. A brute-force algorithm that finds the divisors of a natural number ''n'' would enumerate all integers from 1 to n, and check whether each of them divides ''n'' without remainder. A brute-force approach for the eight queens puzzle would examine all possible arrangements of 8 pieces on the 64-square chessboard and for each arrangement, check whether each (queen) piece can attack any other. While a brute-force search is simple to implement and will always find a solution if it exists, implementation costs are proportional to the number of candidate solutionswhich in many practical problems tends to grow very quickly as the size of the problem increases ( §Combinator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottom-up Parsing
In computer science, parsing reveals the grammatical structure of linear input text, as a first step in working out its meaning. Bottom-up parsing recognizes the text's lowest-level small details first, before its mid-level structures, and leaving the highest-level overall structure to last. Bottom-up Versus Top-down The bottom-up name comes from the concept of a parse tree, in which the most detailed parts are at the bottom of the upside-down tree, and larger structures composed from them are in successively higher layers, until at the top or "root" of the tree a single unit describes the entire input stream. A bottom-up parse discovers and processes that tree starting from the bottom left end, and incrementally works its way upwards and rightwards. Compilers: Principles, Techniques, and Tools (2nd Edition), by Alfred Aho, Monica Lam, Ravi Sethi, and Jeffrey Ullman, Prentice Hall 2006. A parser may act on the structure hierarchy's low, mid, and highest levels without ever c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Top-down Parsing
Top-down parsing in computer science is a parsing strategy where one first looks at the highest level of the parse tree and works down the parse tree by using the rewriting rules of a formal grammar. LL parsers are a type of parser that uses a top-down parsing strategy. Top-down parsing is a strategy of analyzing unknown data relationships by hypothesizing general parse tree structures and then considering whether the known fundamental structures are compatible with the hypothesis. It occurs in the analysis of both natural languages and computer languages. Top-down parsing can be viewed as an attempt to find left-most derivations of an input-stream by searching for parse-trees using a top-down expansion of the given formal grammar rules. Inclusive choice is used to accommodate ambiguity by expanding all alternative right-hand-sides of grammar rules. Simple implementations of top-down parsing do not terminate for left-recursive grammars, and top-down parsing with backtrackin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Context-free Grammars
In formal language theory, a context-free grammar (CFG) is a formal grammar whose production rules are of the form :A\ \to\ \alpha with A a ''single'' nonterminal symbol, and \alpha a string of terminals and/or nonterminals (\alpha can be empty). A formal grammar is "context-free" if its production rules can be applied regardless of the context of a nonterminal. No matter which symbols surround it, the single nonterminal on the left hand side can always be replaced by the right hand side. This is what distinguishes it from a context-sensitive grammar. A formal grammar is essentially a set of production rules that describe all possible strings in a given formal language. Production rules are simple replacements. For example, the first rule in the picture, :\langle\text\rangle \to \langle\text\rangle = \langle\text\rangle ; replaces \langle\text\rangle with \langle\text\rangle = \langle\text\rangle ;. There can be multiple replacement rules for a given nonterminal symbol. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compiler-compiler
In computer science, a compiler-compiler or compiler generator is a programming tool that creates a parser, interpreter, or compiler from some form of formal description of a programming language and machine. The most common type of compiler-compiler is more precisely called a parser generator. It only handles syntactic analysis. The input of a parser generator is a grammar file, typically written in Backus–Naur form (BNF) or extended Backus–Naur form (EBNF) that defines the syntax of a target programming language. The output is the source code of a parser for the programming language. The output of the (compiled) parser source code is a parser. It may be either standalone or embedded. This parser takes as an input the source code of the target programming language source and performs some action or outputs an abstract syntax tree (AST). Parser generators do not handle the semantics of the AST, or the generation of machine code for the target machine."A Syntax Direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocke-Younger-Kasami Algorithm
In computer science, the Cocke–Younger–Kasami algorithm (alternatively called CYK, or CKY) is a parsing algorithm for context-free grammars published by Itiroo Sakai in 1961. The algorithm is named after some of its rediscoverers: John Cocke, Daniel Younger, Tadao Kasami, and Jacob T. Schwartz. It employs bottom-up parsing and dynamic programming. The standard version of CYK operates only on context-free grammars given in Chomsky normal form (CNF). However any context-free grammar may be transformed (after convention) to a CNF grammar expressing the same language . The importance of the CYK algorithm stems from its high efficiency in certain situations. Using big ''O'' notation, the worst case running time of CYK is \mathcal\left( n^3 \cdot \left, G \ \right), where n is the length of the parsed string and \left, G \ is the size of the CNF grammar G . This makes it one of the most efficient parsing algorithms in terms of worst-case asymptotic complexity, although other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Linguistics
Computational linguistics is an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary field concerned with the computational modelling of natural language, as well as the study of appropriate computational approaches to linguistic questions. In general, computational linguistics draws upon linguistics, computer science, artificial intelligence, mathematics, logic, philosophy, cognitive science, cognitive psychology, psycholinguistics, anthropology and neuroscience, among others. Sub-fields and related areas Traditionally, computational linguistics emerged as an area of artificial intelligence performed by computer scientists who had specialized in the application of computers to the processing of a natural language. With the formation of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL) and the establishment of independent conference series, the field consolidated during the 1970s and 1980s. The Association for Computational Linguistics defines computational linguistics as: The term "comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to practical disciplines (including the design and implementation of hardware and software). Computer science is generally considered an area of academic research and distinct from computer programming. Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and for preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of repositories ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
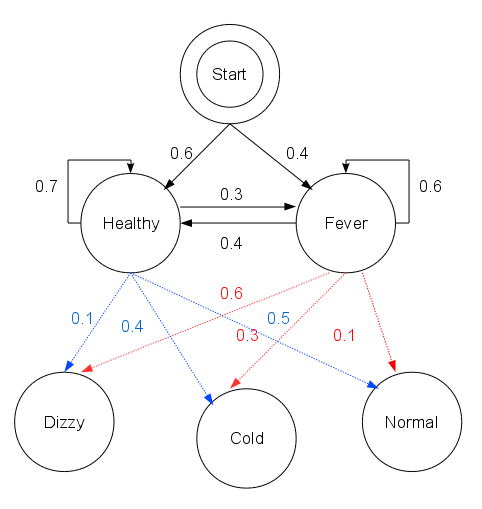
Viterbi Algorithm
The Viterbi algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm for obtaining the maximum a posteriori probability estimate of the most likely sequence of hidden states—called the Viterbi path—that results in a sequence of observed events, especially in the context of Markov information sources and hidden Markov models (HMM). The algorithm has found universal application in decoding the convolutional codes used in both CDMA and GSM digital cellular, dial-up modems, satellite, deep-space communications, and 802.11 wireless LANs. It is now also commonly used in speech recognition, speech synthesis, diarization, keyword spotting, computational linguistics, and bioinformatics. For example, in speech-to-text (speech recognition), the acoustic signal is treated as the observed sequence of events, and a string of text is considered to be the "hidden cause" of the acoustic signal. The Viterbi algorithm finds the most likely string of text given the acoustic signal. History The Viterb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Kay
Martin Kay (1935 – 8 August 2021) was a computer scientist, known especially for his work in computational linguistics. Born and raised in the United Kingdom, he received his M.A. from Trinity College, Cambridge, in 1961. In 1958 he started to work at the Cambridge Language Research Unit, one of the earliest centres for research in what is now known as Computational Linguistics. In 1961, he moved to the Rand Corporation in Santa Monica, California, US, where he eventually became head of research in linguistics and machine translation. He left Rand in 1972 to become Chair of the Department of Computer Science at the University of California, Irvine. In 1974, he moved to the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center as a Research Fellow. In 1985, while retaining his position at Xerox PARC, he joined the faculty of Stanford University half-time. He was most recently Professor of Linguistics at Stanford University and Honorary Professor of Computational Linguistics at Saarland Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |