|
Charlestown Of Aberlour
Aberlour ( gd, Obar Lobhair) is a village in Moray, Scotland, south of Elgin on the road to Grantown. The Lour burn is a tributary of the River Spey, and it and the surrounding parish are both named Aberlour, but the name is more commonly used in reference to the village which straddles the stream and flanks the Spey – although the full name of the village is Charlestown of Aberlour. Etymology Aberlour, recorded in 1226 as ''Aberlower'', means 'confluence of the Lour burn'. The first element is the Pictish word ''aber'' 'river mouth, confluence'. The name of the Lour burn is from Gaelic ''labhar'' 'loud, noisy'. This probably replaced an earlier Pictish cognate word. Charlestown refers to Charles Grant of Elchies. History A site noted as Abirlaur is shown in this location on maps in Joan Blaeu's Atlas of Scotland, from 1654. The current village, Charlestown of Aberlour, was "founded by Charles Grant of Elchies in 1812 – with the name of Charlestown of Aberlour af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moray
Moray () gd, Moireibh or ') is one of the 32 local government council areas of Scotland. It lies in the north-east of the country, with a coastline on the Moray Firth, and borders the council areas of Aberdeenshire and Highland. Between 1975 and 1996 Moray, with similar boundaries, was a district of the then Grampian Region. History The name, first attested around 970 as ', and in Latinised form by 1124 as ', derives from the earlier Celtic forms *''mori'' 'sea' and *''treb'' 'settlement' (c.f. Welsh ''môr-tref''). During the Middle Ages, the Province of Moray was much larger than the modern council area, also covering much of what is now Highland and Aberdeenshire. During this period Moray may for a time have been either an independent kingdom or a highly autonomous vassal of Alba. In the early 12th century, Moray was defeated by David I of Scotland following a conflict with Óengus of Moray, and rule over the area was passed to William fitz Duncan. After that the title be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Macpherson Grant
Margaret Macpherson Grant (27 April 183414 April 1877) was a Scottish heiress and philanthropist. Born in Aberlour parish to a local surgeon, she was educated in Hampshire, and was left an only child when her elder brother died in India in 1852. Two years later, she inherited a large fortune from her uncle, Alexander Grant, an Aberlour-born planter and merchant who had become rich in Jamaica. Macpherson Grant took up residence in Aberlour House, which had been built for her uncle by William Robertson. She lived unconventionally for a woman of her time, dressing in a manner one newspaper called "manly", and entering into what was described as a form of marriage with a female companion, Charlotte Temple, whom she had met in London in 1864. Macpherson Grant donated generously to charitable enterprises, especially those associated with the Scottish Episcopal Church, establishing an orphanage (now the Aberlour Child Care Trust) and founding St Margaret's Episcopal Church in Aberl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Cameron Sim
Alexander Cameron Sim (28 August 1840 – 28 November 1900) was a British-born pharmacist and entrepreneur active in Japan during the Meiji period. He was also the founder of the Kobe Regatta & Athletic Club. Biography Sim was born in Aberlour, Scotland in 1840. He relocated to London in his youth, and received a post as a pharmacist at the Royal London Hospital in 1862. In 1866, he volunteered for an overseas assignment, and was sent to the Royal Naval Hospital in Hong Kong, where he spent the next 3.5 years. In late 1869, he moved to Nagasaki, Japan, where he resided in the treaty port, but moved to Kobe in 1870, where he initially worked as a pharmacist for the foreign firm ''Llewellyn Shōkai''. However, he began his own company, ''AC Sim Shōkai'', later the same year. Sim's company specialized in the import and distribution of medicines and medical supplies. In 1884, Sim introduced a carbonated beverage based on lemonade to the Kobe foreign settlement. This drink, called " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
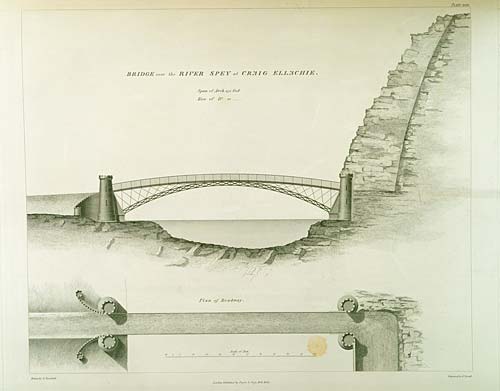
Craigellachie Bridge
Craigellachie Bridge is a cast iron arch bridge across the River Spey at Craigellachie, Moray, Craigellachie, near to the village of Aberlour in Moray, Scotland. It was designed by the renowned civil engineer Thomas Telford and built from 1812 to 1814. It is a Category A listed structure. Construction The bridge has a single Span (architecture), span of approximately and was revolutionary for its time, in that it used an extremely slender arch which was not possible using traditional masonry construction. The ironwork was cast at the Plas Kynaston iron foundry at Cefn Mawr, near Ruabon in Denbighshire (historic), Denbighshire by William Hazledine, who cast a number of Telford bridges. The ironwork was transported from the foundry through the Ellesmere Canal and Pontcysyllte Aqueduct then by sea to Speymouth, where it was loaded onto wagons and taken to the site. Testing in the 1960s revealed that the cast-iron had an unusually high tensile strength. This was probably specified b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Engineer
A civil engineer is a person who practices civil engineering – the application of planning, designing, constructing, maintaining, and operating infrastructure while protecting the public and environmental health, as well as improving existing infrastructure that may have been neglected. Civil engineering is one of the oldest engineering disciplines because it deals with constructed environment including planning, designing, and overseeing construction and maintenance of building structures, and facilities, such as roads, railroads, airports, bridges, harbors, channels, dams, irrigation projects, pipelines, power plants, and water and sewage systems. The term "civil engineer" was established by John Smeaton in 1750 to contrast engineers working on civil projects with the military engineers, who worked on armaments and defenses. Over time, various sub-disciplines of civil engineering have become recognized and much of military engineering has been absorbed by civil engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Telford
Thomas Telford FRS, FRSE, (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire, he designed numerous infrastructure projects in his native Scotland, as well as harbours and tunnels. Such was his reputation as a prolific designer of highways and related bridges, he was dubbed ''The Colossus of Roads'' (a pun on the Colossus of Rhodes), and, reflecting his command of all types of civil engineering in the early 19th century, he was elected as the first President of the Institution of Civil Engineers, a post he held for 14 years until his death. The town of Telford in Shropshire was named after him. Early career Telford was born on 9 August 1757, at Glendinning, a hill farm east of Eskdalemuir Kirk, in the rural parish of Westerkirk, in Eskdale, Dumfriesshire. His father John Telford, a shepherd, died soon after Thomas was born. Thomas was raised in poverty by his mother Janet Jac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordonstoun
Gordonstoun School is a co-educational independent school for boarding and day pupils in Moray, Scotland. It is named after the estate owned by Sir Robert Gordon in the 17th century; the school now uses this estate as its campus. It is located in Duffus to the north-west of Elgin. Pupils are accepted subject to an interview plus references and exam results. It is one of the last remaining full boarding schools in the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1934 as the British Salem School by German-Jewish educator Kurt Hahn based on the model of Schule Schloss Salem, that he had founded in Germany in 1919. Gordonstoun has an enrollment of around 500 full boarders as well as about 100 day pupils between the ages of 6 and 18. With the number of teaching staff exceeding 100, there is a low student-teacher ratio compared to the average in the United Kingdom. There are eight boarding houses (formerly nine prior to the closure of Altyre house in summer 2016) including two 17th-century bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preparatory School (UK)
A preparatory school (or, shortened: prep school) in the United Kingdom is a fee-charging independent primary school that caters for children up to approximately the age of 13. The term "preparatory school" is used as it ''prepares'' the children for the Common Entrance Examination in order to secure a place at an independent secondary school, typically one of the English public schools. They are also preferred by some parents in the hope of getting their child into a state selective grammar school. Most prep schools are inspected by the Independent Schools Inspectorate, which is overseen by Ofsted on behalf of the Department for Education. Overview Boys' prep schools are generally for 8-13 year-olds, who are prepared for the Common Entrance Examination, the key to entry into many secondary independent schools. Before the age of 7 or 8, the term "pre-prep school" is used. Girls' independent schools in England tend to follow the age ranges of state schools more closely than th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberlour House (school)
Aberlour House is the junior school of Gordonstoun School, and is now fully merged with it. It educated pupils from age 6 to 13. The links between Aberlour House and Gordonstoun were very close. They shared the same school song and school flag (purple and white). Furthermore, they shared the same school motto – "''plus est en vous''", a contraction of "''plus est en vous que vous pensez''" meaning, "there is more in you than you think". They were both founded by the German educationalist Dr Kurt Hahn. His bust was prominently displayed in Aberlour House's front hall for many years. The prep school was founded at Wester Elchies in 1936 – three years after Gordonstoun. Wester Elchies expanded such that in 1947 a modest stately home – Aberlour House – was bought. Charles Brereton was appointed headmaster by Kurt Hahn. Aberlour House had been occupied by the Army during the Second World War and is three miles from Wester Elchies. The younger boys attended Wester Elchies unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberlour House (building)
Aberlour House is a country house near Aberlour in Moray, Scotland. It was built in 1838 by William Robertson for Alexander Grant, planter and merchant from Aberlour, after his return to the UK. His niece, Margaret Macpherson Grant, lived in it after Grant died, and it was later home to John Ritchie Findlay of ''The Scotsman'' newspaper and his descendants. It was requisitioned for military use during the Second World War, and after the war was sold for use as a preparatory school for Gordonstoun. The school was later moved into Gordonstoun's estate, and the building was sold to Walkers Shortbread, who restored and renovated it, and now use it as their head office. It has been designated a Category A listed building. Description Aberlour House, the only country house that William Robertson built from scratch, has been described by Charles McKean and Walker and Woodworth as his "masterpiece". Its main block presents a two-storey, five bay north-facing frontage, with a por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortbread
Shortbread or shortie is a traditional Scottish biscuit usually made from one part white sugar, two parts butter, and three to four parts plain wheat flour. Unlike many other biscuits and baked goods, shortbread does not contain any leavening, such as baking powder or baking soda. Shortbread is widely associated with Christmas and Hogmanay festivities in Scotland, and some Scottish brands are exported around the world. History Shortbread originated in Scotland. Although it was prepared during much of the 12th century, and probably benefited from cultural exchange with French pastry chefs during the Auld Alliance between France and Scotland, the refinement of shortbread is popularly credited to Mary, Queen of Scots in the 16th century. This type of shortbread was baked, cut into triangular wedges, and flavoured with caraway seeds. The triangular wedges became known as "petticoat tails" in Scots and this form of shortbread has become particularly associated with Mary, Queen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walkers Shortbread
Walker's Shortbread is a Scottish manufacturer of shortbread, biscuits, cookies and crackers. The company's well-known shortbread is baked in the Moray village of Aberlour, following a recipe developed by Joseph Walker in 1898. Walkers Shortbread operates four factories in Aberlour, where the company is also headquartered, and two in nearby Elgin, Scotland. The company is Scotland's biggest exporter of food and employs over 4,000 people in 15 locations. It is sold in tartan packaging all over the world. History The business was founded by Joseph Walker in the village of Torphins, Aberdeenshire, in 1898. In 1992, Walkers Shortbread started producing oaten biscuits for Duchy Originals, having been approached the previous year. In 2006, Walkers announced that the bakery in Aberlour would be closing and turning into a research facility for the company. The company has received the Queen's Award for Export Achievement three times. Walkers Shortbread is also still owned and manag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



