|
Charles Philippe De Bosset
Charles Philippe de Bosset (29 July 1773 - 15 March 1845) was a Swiss engineer, who as an officer of the British army, became governor of Cephalonia. The de Bosset Bridge in Cephalonia is named after him. Life Born in Neuenberg, Switzerland, de Bosset was a member of the so-called Swiss Regiment and rose to the rank of colonel. From 1810 to 1813, he was governor of the island of Cephalonia, and oversaw numerous infrastructure developments, including the expansion of the road network and the construction of today's De Bosset Bridge over the Gulf of Argostoli. To increase financial leeway, he introduced taxes, e.g. on street lighting, and had illegal annexes on the main Lithostroto road demolished. In recognition of his services, de Bosset was made a Knight of the Order of Guelph in 1816.William Arthur Shaw: The Knights of England. Band 1, Sherratt and Hughes, London 1906, S. 463 (archive.org). From 1816 to 1818 he served as Inspector of the Ionian Islands. On his retirement, he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalonia
Kefalonia or Cephalonia ( el, Κεφαλονιά), formerly also known as Kefallinia or Kephallenia (), is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece and the 6th largest island in Greece after Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes and Chios. It is also a separate regional units of Greece, regional unit of the Ionian Islands (region), Ionian Islands region. It was a former Latin Catholic diocese Roman Catholic Diocese of Cephalonia and Zakynthos, Kefalonia–Zakynthos (Cefalonia–Zante) and short-lived titular see as just Kefalonia. The capital city of Cephalonia is Argostoli. History Antiquity Legend An ''Aitiology, aition'' explaining the name of Cephallenia and reinforcing its cultural connections with Athens associates the island with the mythological figure of Cephalus, who helped Amphitryon of Mycenae in a war against the Taphians and Teleboans. He was rewarded with the island of Same (ancient Greece), Same, which thereafter came to be known as Kefallinia, Cephallenia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bosset Bridge
The De Bosset Bridge (formerly Drapano Bridge) is a stone bridge built in 1813 over the bay of Argostoli in Kefalonia. At 689.9 meters, it is the longest stone bridge over the sea in the world. History When the Republic of the Ionian Islands was under British patronage, part of the burden of occupation was reimbursed in the form of infrastructure projects. The Swiss engineer Charles de Bosset became island governor in 1810 and put the emphasis of his activity on the road and bridge construction. Numerous connections were shortened with bridges over ravines. The biggest project, however, was the bridge over the Bay of Argostoli to Drapano, which shortened the way to Lixouri and the north of the island. It separates the Koutavos lagoon from the bay. In 1812 De Bosset presented his idea of a bridge to the island council, which had to confirm the construction. Counterargument was that the bridge could give robbers a slight escape route, since its northern end is (then as today) un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
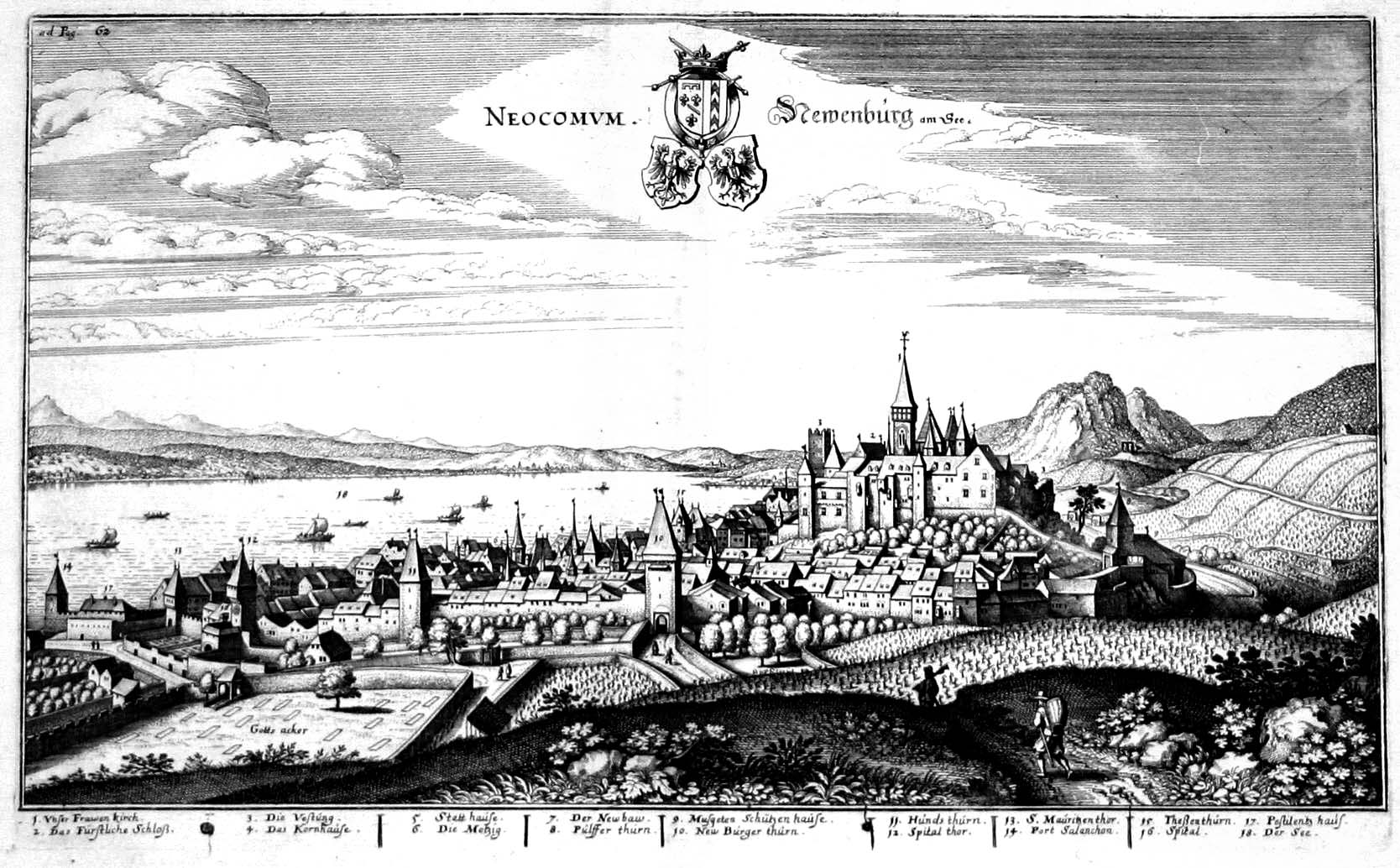
Neuchâtel
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier, Boudry, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier , twintowns = Aarau (Switzerland), Besançon (France), Sansepolcro (Italy) Neuchâtel (, , ; german: Neuenburg) is the capital of the Swiss canton of Neuchâtel, situated on the shoreline of Lake Neuchâtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of Neuchâtel, Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 45,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". It was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, then part of the Holy Roman Empire and later under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1802 to 1814. In 1848, Neuchâtel became a republic and a canton of Switzerland. Neuch� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Argostoli
The Gulf of Argostoli ( el, Κόλπος Αργοστολίου) is a gulf of the Ionian Sea on the island of Cephalonia, western Greece. It separates the Paliki peninsula from mainland Cephalonia, and opens toward the Ionian Sea in the south. The gulf is long (north to south) and wide. Lixouri, the second-largest town of Cephalonia, is situated on its western shore, and the capital Argostoli is situated on a bay in the eastern shore. The shores of the gulf are mountainous, especially in the east. The main settlements on the shore of the gulf are, from the southwest and clockwise: Lixouri, Agios Dimitrios, Kouvalata, Kontogourata, Farsa, Drapano and Argostoli. The Gulf of Argostoli is navigable, and the ports of Argostoli and Lixouri are served by ferries. Concerns have risen about the environmental effects of fish farming upright=1.3, Salmon farming in the sea (mariculture) at Loch Ainort, Isle of Skye">mariculture.html" ;"title="Salmon farming in the sea (mariculture">Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionian Islands (region)
The Ionian Islands Region ( el, Περιφέρεια Ιονίων Νήσων, translit=Periféria Ioníon Níson, ) is the smallest by area of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece located in the Ionian Sea. It comprises all the Ionian Islands except Kythera, which, although historically part of the island group, was separated and integrated to the Attica Region. Demographics The population of the Ionian Islands in 2011 was 207,855, decreased by 1.5% compared to the population in 2001. Nevertheless, the region remains the third by population density with 90.1/km2 nationwide, well above the national of 81.96/km2. The most populous of the major islands is Corfu with a population of 104,371, followed by Zante (40,759), Cephalonia (35,801), Leucas (23,693) and Ithaca (3,231). In 2001, the foreign-born population was 19,360 or 9.3%, the majority of which was concentrated in Corfu and Zante. Most of them originate from Albania (13,536). The fertility rate for 2011 according t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre-Louis Guinand
Markree Observatory was an astronomical observatory in County Sligo, Ireland. The asteroid 9 Metis was discovered from this observatory in 1848 by Cooper's assistant Andrew Graham using a comet seeker telescope. (Signed 29 April 1848; the discovery was first announced on 27 April) The observatory was also home to the largest refractor of the early 1830s, which had a aperture Cauchoix of Paris lens; the largest in the world at that time. The observatory also housed a number of instruments and was operated to varying degrees throughout the 19th century. The observatory is noted for its discovery of the asteroid 9 Metis in 1848 as well as a 60,000 item star catalogue of the 1850s. In the later 1800s it was operated again after a brief hiatus, and gained note for its meteorological observations and research on double stars. History In 1830, Colonel Edward Joshua Cooper MP (1798–1863) eldest son of Edward Synge Cooper MP, and Ann, daughter of Henry Vansittart, Governor of Bengal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleurier
Fleurier was a municipality in the district of Val-de-Travers in the canton of Neuchâtel in Switzerland. On 1 January 2009, the former municipalities of Boveresse, Buttes, Couvet, Fleurier, Les Bayards, Môtiers, Noiraigue, Saint-Sulpice and Travers merged to form the administrative district of Val-de-Travers.Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office accessed 14 January 2010 The Nobel laureates, physicist and pharmacologist |
Ithaca (island)
Ithaca, Ithaki or Ithaka (; Greek language, Greek: Ιθάκη, ''Ithaki'' ; Ancient Greek: Ἰθάκη, ''Ithakē'' ) is a Greek island located in the Ionian Sea, off the northeast coast of Kefalonia and to the west of continental Greece. Ithaca's main island has an area of and had a population in 2011 of 3,231. It is the second-smallest of seven main Ionian Islands, after Paxi. Ithaca is a separate regional units of Greece, regional unit of the Ionian Islands (region), Ionian Islands region, and the only Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality of the regional unit. The capital is Vathy, Ithaca, Vathy (or Vathi). Modern Ithaca is generally identified with Homer's Ithaca, the home of Odysseus, whose delayed return to the island is the plot of the classical Greek poem the ''Odyssey''. Alternative names Although the name Ithaca has remained unchanged since ancient times, written documents of different periods also refer to the island by other names, such as: *Val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.Among the national museums in London, sculpture and decorative and applied art are in the Victoria and Albert Museum; the British Museum houses earlier art, non-Western art, prints and drawings. The National Gallery holds the national collection of Western European art to about 1900, while art of the 20th century on is at Tate Modern. Tate Britain holds British Art from 1500 onwards. Books, manuscripts and many works on paper are in the British Library. There are significant overlaps between the coverage of the various collections. The British Museum was the first public national museum to cover all fields of knowledge. The museum was established in 1753, largely b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; grc, Μυκῆναι or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos; and south of Corinth. The site is inland from the Saronic Gulf and built upon a hill rising above sea level. In the second millennium BC, Mycenae was one of the major centres of Greek civilization, a military stronghold which dominated much of southern Greece, Crete, the Cyclades and parts of southwest Anatolia. The period of Greek history from about 1600 BC to about 1100 BC is called Mycenaean in reference to Mycenae. At its peak in 1350 BC, the citadel and lower town had a population of 30,000 and an area of 32 hectares. The first correct identification of Mycenae in modern literature was during a survey conducted by Francesco Grimani, commissioned by the Provveditore Generale of the Kingdom of the Morea in 1700, who used Pausanias's description of the Lio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1773 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – The hymn that becomes known as ''Amazing Grace'', at this time titled "1 Chronicles 17:16–17", is first used to accompany a sermon led by curate John Newton in the town of Olney, Buckinghamshire, England. * January 12 – The first museum in the American colonies is established in Charleston, South Carolina; in 1915, it is formally incorporated as the Charleston Museum. * January 17 – Second voyage of James Cook: Captain Cook in HMS Resolution (1771) becomes the first European explorer to cross the Antarctic Circle. * January 18 – The first opera performance in the Swedish language, ''Thetis and Phelée'', performed by Carl Stenborg and Elisabeth Olin in Bollhuset in Stockholm, Sweden, marks the establishment of the Royal Swedish Opera. * February 8 – The Grand Council of Poland meets in Warsaw, summoned by a circular letter from King Stanisław August Poniatowski to respond to the Kingdom's threate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
.jpg)