|
Charles Dare
Admiral Sir Charles Holcombe Dare Knight Commander of the Order of St Michael and St George, KCMG Companion of The Most Honourable Order of the Bath, CB Member of the Royal Victorian Order, MVO (9 November 1854 – 6 August 1924) was an English Royal Navy officer. He commanded several ships and shore establishments before and during World War I, and was knighted by King George V. Family Dare was born on 9 November 1854 to Charles William Dare, a lawyer with a practice in London, and Anne Agnes (née Mew, from Newport, Isle of Wight) in North Curry, Somerset, one of four brothers and a sister. Dare's grandfather, also Charles Holcombe Dare, was a Land Tax Commissioner for North Curry. The family had connections in London and the Isle of Wight. Dare married Emily Agnes Harper, a railway guard's daughter who, unusually for the time, brought an illegitimate daughter, Maud, to the marriage. Naval career Early career Dare enlisted in the Royal Navy as an officer cadet, first serving a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear-Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star "admiral" rank. It is often regarded as a two-star rank with a NATO code of OF-7. The term originated in the days of naval sailing squadrons and can trace its origins to the Royal Navy. Each naval squadron was assigned an admiral as its head, who commanded from the centre vessel and directed the squadron's activities. The admiral would in turn be assisted by a vice admiral, who commanded the lead ships that bore the brunt of a battle. In the rear of the squadron, a third admiral commanded the remaining ships and, as this section was considered to be in the least danger, the admiral in command of it was typically the most junior. This has continued into the modern age, with rear admiral the most junior admiralty of many navies. In most European navies, the equivalent rank is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Monarch (1868)
HMS ''Monarch'' was the first seagoing British warship to carry her guns in turrets, and the first British warship to carry guns of calibre. Design She was designed by Sir Edward Reed, at a time when the basic configuration of battleship design was undergoing major change simultaneously in many aspects. Sail was gradually giving way to steam, wooden hulls had just been superseded by iron, smoothbore artillery firing round-shot had been overtaken by rifled shell-firing cannon, increasingly heavier armour was being mounted, and there was mounting agitation in naval design circles to abandon broadside armament in favour of that mounted in turrets. In this melting-pot, any battleship design was fated to be a compromise, and the design of ''Monarch'' proved to be so. Having determined that ''Monarch'' would carry her main artillery in turrets, the Board of Admiralty then stipulated that, as she was destined for overseas service, and steam engines were not at that time wholly re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Berwick (1902)
HMS ''Berwick'' was one of 10 armoured cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. She was assigned to the 2nd Cruiser Squadron of the Channel Fleet upon completion in 1903 and was transferred to the Home Fleet in 1906. She accidentally rammed and sank a British destroyer in 1908. ''Berwick'' was refitted in 1908–09 before she was transferred to the 4th Cruiser Squadron on the North America and West Indies Station later that year. She captured a German merchant ship shortly after World War I began. The ship patrolled for German commerce raiders and escorted convoys for the war. ''Berwick'' was assigned to the 8th Light Cruiser Squadron in 1919 before she was paid off and sold for scrap in 1920. Design and description The ''Monmouth''s were intended to protect British merchant shipping from fast cruisers like the French , or the . The ships were designed to displace . They had an overall length of , a beam of and a deep draught of . The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoured Cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast enough to outrun any battleship it encountered. For many decades, naval technology had not advanced far enough for designers to produce a cruiser which combined an armored belt with the long range and high speed required to fulfill its mission. For this reason, beginning in the 1880s and 1890s, many navies preferred to build protected cruisers, which only relied on a light armored deck to protect the vital parts of the ship. However, by the late 1880s, the development of modern rapid-fire breech-loading cannon and high-explosive shells made the reintroduction of side armor a necessity. The invention of face-hardened armor in the mid-1890s offered effective protection with less weight than previously. Varying in size, the armored cruiser was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Assistance (1900)
Eleven ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Assistance'': * was a 50-gun ship launched in 1650, rebuilt in 1699, 1712 and 1725, and sunk in 1746 as a breakwater. * was a 50-gun fourth rate launched in 1747 and sold in 1773. * was a transport launched in 1771 and sold in 1802. * was a 50-gun fourth rate launched in 1781 and wrecked in 1802. * HMS ''Assistance'' was a prison hulk, launched in 1769 as the 74-gun third rate . She became a prison hulk in 1796, was renamed HMS ''Assistance'' in 1805 and was broken up in 1815. * was a storeship launched in 1809 at Deptford and sold in 1821. * was a discovery vessel, formerly the merchant vessel ''Baboo''. She was purchased in 1850 and abandoned in the Arctic in 1854. * was a screw storeship purchased in 1855 and wrecked in 1860. * was an iron screw storeship launched in 1874 and sold in 1897. * was a repair ship purchased in 1900 and handed over to Ward shipbreakers in part payment for in 1937. * was a repair ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Bellona (1890)
Eight ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Bellona'' after Bellona, the goddess of war in Roman mythology: * was a 30-gun sixth rate, formerly the French privateer ''Bellone''. She was captured in 1747, and sold in 1749. * was a 74-gun third rate, launched in 1760 and broken up in 1814. * ''Bellona'', possibly a hired armed vessel or armed ship, was lost at the mouth of the Elbe circa December 1779. She had been escorting a convoy from Hull to Hamburg. Several of the merchantmen in the convoy were lost too. * was a 3-gun vessel purchased in 1794. She was used as a mud boat from 1799 and was broken up in 1805. * was a 28-gun sixth rate, formerly the French privateer . She was captured in 1806, renamed HMS ''Blanche'' in 1809, and was broken up in 1814. * HMS ''Bellona'' was a 74-gun third rate launched in 1812 as . She was renamed HMS ''Bellona'' in 1818, used for harbour service from 1840 and was broken up in 1868. * was a third-class cruiser launched in 1890 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles. The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hundred years, has changed its meaning over time. During the Age of Sail, the term ''cruising'' referred to certain kinds of missions—independent scouting, commerce protection, or raiding—fulfilled by frigates or sloops-of-war, which functioned as the ''cruising warships'' of a fleet. In the middle of the 19th century, ''cruiser'' came to be a classification of the ships intended for cruising distant waters, for commerce raiding, and for scouting for the battle fleet. Cruisers came in a wide variety of sizes, from the medium-sized protected cruiser to large armored cruisers that were nearly as big (although not as powerful or as well-armored) as a pre-dreadnought battleship. With the advent of the dreadnought battleship before World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain (naval)
Captain is the name most often given in English-speaking navies to the rank corresponding to command of the largest ships. The rank is equal to the army rank of colonel and air force rank of group captain. Equivalent ranks worldwide include ship-of-the-line captain (e.g. France, Argentina, Spain), captain of sea and war (e.g. Brazil, Portugal), captain at sea (e.g. Germany, Netherlands) and " captain of the first rank" (Russia). The NATO rank code is OF-5, although the United States of America uses the code O-6 for the equivalent rank (as it does for all OF-5 ranks). Four of the uniformed services of the United States — the United States Navy, United States Coast Guard, United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Officer Corps — use the rank. Etiquette Any naval officer who commands a ship is addressed by naval custom as "captain" while aboard in command, regardless of their actual rank, even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Archer (1885)
HMS ''Archer'' was an torpedo cruiser of the British Royal Navy which built by the Glasgow shipbuilder J & G Thomson between 1885 and 1888. She served on overseas stations, including operations off Africa, China and Australia. She was sold for scrap in 1905. Construction ''Archer'' was laid down at J & G Thomson's Clydebank shipyard on 2 March 1885 as the lead ship of her class of torpedo cruisers, was launched on 23 December that year and completed by Commander John Ferris on 11 December 1888 in Devonport.Chesneau and Kolesnik p. 81. Torpedo cruisers were small, relatively fast, ships intended to defend the fleet against attacks by hostile torpedo boats, while themselves being capable of attacking hostile fleets with torpedoes. The ''Archer'' class were enlarged derivatives of the earlier , and carried a heavier armament than the previous class.Chesneau and Kolesnik pp. 80–81. ''Archer'' was long overall and between perpendiculars, with a beam of and a draught of . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redbreast-class Gunboat
The ''Redbreast'' class comprised nine first-class screw-driven composite gunboats built for the Royal Navy in 1889, mounting six guns. Construction Design The ''Redbreast'' class were designed by Sir William Henry White, the Royal Navy Director of Naval Construction in 1888. The hull was of composite construction, that is, iron keel, frames, stem and stern posts with wooden planking. These were the last class of composite-hulled gunboats built for the Royal Navy - the next class of gunboat, the ''Bramble''-class gunboat of 1898, was of steel construction. Propulsion The class was fitted with a triple-expansion reciprocating steam engine developing 1,200 indicated horsepower, sufficient to propel them at through a single screw. Sail plan The class was given a barquentine A barquentine or schooner barque (alternatively "barkentine" or "schooner bark") is a sailing vessel with three or more masts; with a square rigged foremast and fore-and-aft rigged main, mizzen and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
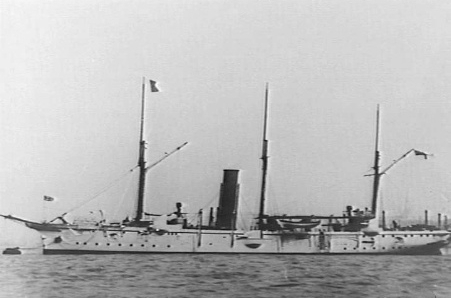
HMS Lapwing (1889)
Eight ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Lapwing'', after the northern lapwing, a species of bird: * was a 10-gun cutter launched in 1764 and lost in 1765. * was a 28-gun sixth rate launched in 1785. She was used on harbour service from 1813 and was broken up in 1828. * was a 6-gun packet brig launched in 1825, used as a breakwater from 1845, and sold in 1861. * was a wooden screw gunvessel launched in 1856 and sold in 1864. * was a wooden screw gunvessel launched in 1867 and sold in 1885. * was a composite screw gunboat launched in 1889 and sold in 1910. * was an launched in 1911 and sold for scrapping in 1921. * was a sloop launched in 1943 and sunk by a U-boat U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare role ... in 1945. {{DEFAULTSORT:Lapwing, Hms Royal N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_William_Frederick_Mitchell.jpg)