|
Charles Alexander McMahon
Lieutenant-General Charles Alexander McMahon FRS FGS (23 March 1830 – 21 February 1904) was an Anglo-Irish soldier, geologist, and administrator in British India. In 1899 he was awarded the Lyell Medal by the Geological Society of London. McMahon died in February 1904, aged 73, and an obituary in the ''Geological Magazine'' described him as an excellent geologist and petrologist and a prominent member of the Geological Society of London, noting that he had had no early scientific training. He was the father of Henry McMahon (born 1862), who followed his father into a career in India."McMahon, Arthur Henry, b. Nov. 28, 1862, son of Lieut.-Col. McMahon, 6, Regent's Park, Heavitree, Exeter" in Lionel Sumner Milford, ''Haileybury Register, 1862-1891'' (Haileybury College, 1891), p. 149 Honours McMahon was elected as a Fellow of the Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, a Fellow of the Geological Society of London, and a Fellow of the University of Lahore The Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom)
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen), formerly more commonly lieutenant-general, is a senior rank in the British Army and the Royal Marines. It is the equivalent of a multinational three-star rank; some British lieutenant generals sometimes wear three-star insignia, in addition to their standard insignia, when on multinational operations. Lieutenant general is a superior rank to Major-general (United Kingdom), major general, but subordinate to a General (United Kingdom), (full) general. The rank has a NATO rank code of OF-8, equivalent to a Vice-Admiral (Royal Navy), vice-admiral in the Royal Navy and an air marshal in the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the air forces of many Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth countries. The rank insignia for both the Army and the Royal Marines is a crown over a crossed sabre and baton. Since the coronation of Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom, Queen Elizabeth II, the St Edward's Crown, commonly known as the Queen's Crown, has been depicted. Before 1953 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ballynahinch
The battle of Ballynahinch was a military engagement of the Irish Rebellion of 1798 between a force of roughly 4,000 United Irishmen rebels led by Henry Munro and approximately 2,000 government troops under the command of George Nugent. After rebel forces had occupied Newtownards on 9 June, they gathered the next day in the surrounding countryside and elected Munro as their leader, who occupied Ballyhinch on 11 June. Nugent led a column of government troops in 12 June which recaptured the town and bombarded rebel positions. On the next day, the rebels attacked Ballyhinch, but were driven back and defeated. Background In County Down, the Irish Rebellion of 1798 by the Society of United Irishmen had faltered after the arrest of William Steel Dickson on 5 June 1798. Several rebel commanders, many of whom were Presbyterian, managed to briefly revive the rebellion's momentum. A rebel force led by David Bailie Warden attacked Newtownards on 9 June, which was garrisoned by a det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahore Division
Lahore Division is an administrative division of Punjab Province, Pakistan. It comprises four Districts - Kasur, Lahore, Nankana Sahib and Sheikhupura. The Lahore Division is commanded by a Commissioner to manage the division. Under the Commissioner there are four Additional Commissioners. For each district there is a Deputy Commissioner. Under the reforms of 2000, this tier of government was abolished, but in 2008 divisions were restored. History Lahore Division was originally an administrative division of the Punjab Province of British India. It extended along the right bank of the Sutlej River from the Himalaya to Multan, and comprised the six districts of Sialkot, Gujranwala, Lahore, Amritsar, Gurdaspur and Gujrat. The total area of the division was and the population according to the 1901 census of India was 5,598,463. The commissioner for the division also exercised political control over the hill state of Chamba. The Commissioner's headquarters were at Lahore and Dalh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commissioner
A commissioner (commonly abbreviated as Comm'r) is, in principle, a member of a commission or an individual who has been given a commission (official charge or authority to do something). In practice, the title of commissioner has evolved to include a variety of senior officials, often sitting on a specific commission. In particular, the commissioner frequently refers to senior police or government officials. A high commissioner is equivalent to an ambassador, originally between the United Kingdom and the Dominions and now between all Commonwealth states, whether Commonwealth realms, republics or countries having a monarch other than that of the realms. The title is sometimes given to senior officials in the private sector; for instance, many North American sports leagues. There is some confusion between commissioners and commissaries because other European languages use the same word for both. Therefore titles such as ''commissaire'' in French, ''Kommissar'' in German and ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjab Commission
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. Punjab's capital and largest city and historical and cultural centre is Lahore. The other major cities include Faisalabad, Rawalpindi, Gujranwala, Multan, Ludhiana, Amritsar, Sialkot, Chandigarh, Jalandhar, and Bahawalpur. Punjab grew out of the settlements along the five rivers, which served as an important route to the Near East as early as the ancient Indus Valley civilization, dating back to 3000 BCE, and had numerous migrations by the Indo-Aryan peoples. Agriculture has been the major economic feature of the Punjab and has therefore formed the foundation of Punjabi culture, with one's social status being determined by land ownership. The Punjab emerged as an important agricultural r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madras Army
The Madras Army was the army of the Presidency of Madras, one of the three presidencies of British India within the British Empire. The presidency armies, like the presidencies themselves, belonged to the East India Company until the Government of India Act 1858 (passed in the aftermath of the Indian Rebellion of 1857) transferred all three presidencies to the direct authority of the British Crown. In 1895 all three presidency armies were merged into the British Indian Army. Establishment and early history The Madras Army of the Honourable East India Company came into being through the need to protect the Company's commercial interests. These were mostly untrained guards, with only some bearing arms. The French attack and capture of Madras in 1746 forced the British hand. In 1757, the East India Company decided to raise well-trained military units to conduct operations, conquer territory, and demand allegiance from local rulers. The loosely organised military units were lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
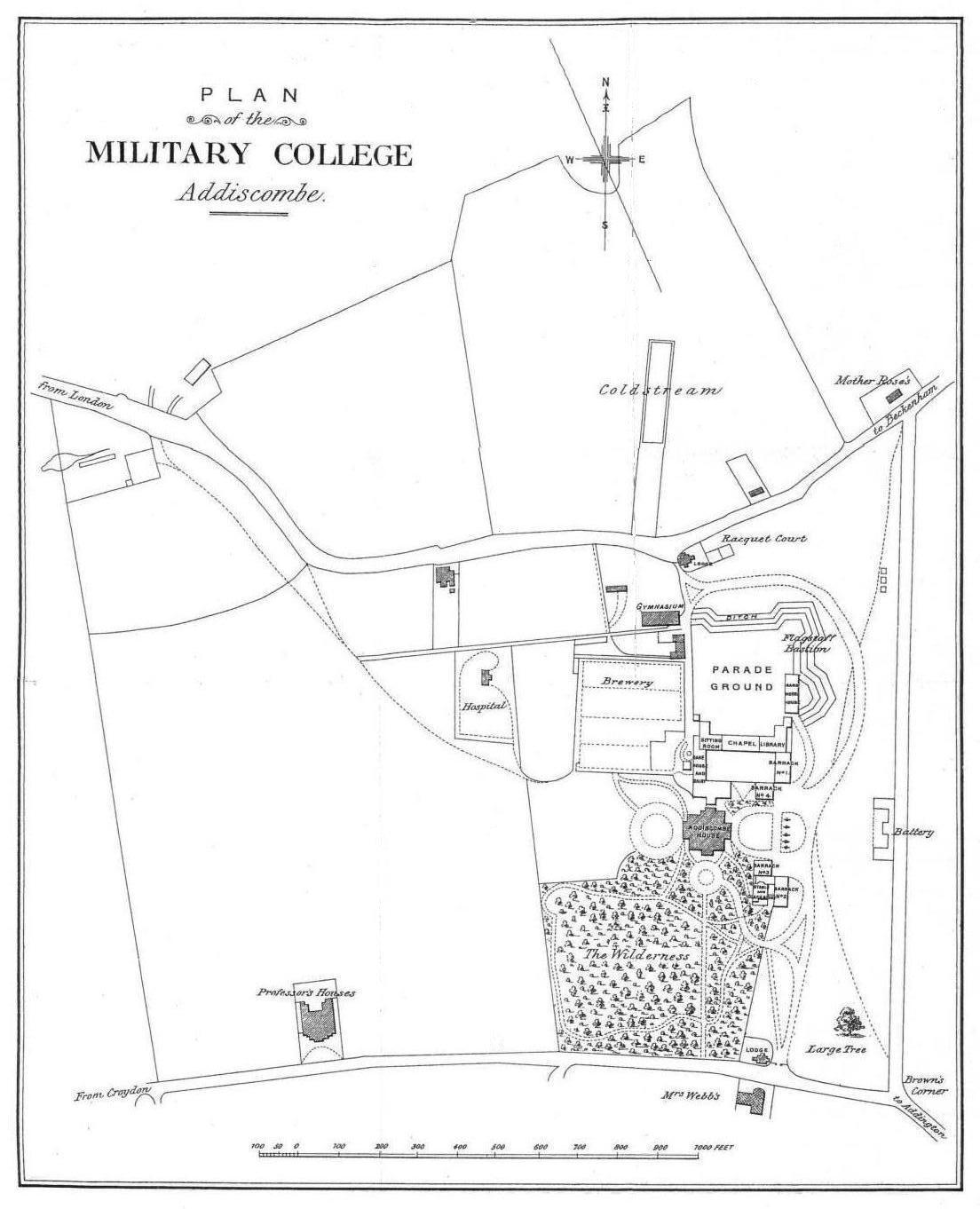
Addiscombe Military Seminary
The East India Company Military Seminary was a British military academy at Addiscombe, Surrey, in what is now the London Borough of Croydon. It opened in 1809 and closed in 1861. Its purpose was to train young officers to serve in the East India Company's own army in India. The institution was formally known as the East India Company Military Seminary (a name the cadets always disliked) until 1855, when the name was changed to the East India Company Military College.Bourne 1979, p. 206. In 1858, when the college was taken over by the government, it was renamed the Royal India Military College. Colloquially, it was known as Addiscombe Seminary, Addiscombe College, or Addiscombe Military Academy. The Seminary was a sister institution to the East India Company College in Hertfordshire, which trained civilian "writers" (clerks). In military terms it was a counterpart to the Royal Military Academy at Woolwich and the Royal Military College at Sandhurst. History Addiscombe Plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1881 United Kingdom Census
The United Kingdom Census of 1881 recorded the people residing in every household on the night of Sunday 3 April 1881, and was the fifth of the UK censuses to include details of household members. Data recorded Details collected include: address, name, relationship to the head of the family, marital status, age at last birthday, gender, occupation, and place of birth. As with earlier censuses, the form asked whether any "lunatics", "imbeciles" or "idiots" lived in the household, causing the Registrar General to observe that: "It is against human nature to expect a mother to admit her young child to be an idiot, however much she may fear this to be true. To acknowledge the fact is to abandon all hope." The total population of England, Wales and Scotland was recorded as 29,707,207. Notable respondents included Winston Churchill, Karl Marx and Charles Darwin. Indexing The 1881 census was the first UK census to be indexed in its entirety. In the 1980s, in a project that has been ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanwell
Hanwell () is a town in the London Borough of Ealing, in the historic County of Middlesex, England. It is about 1.5 miles west of Ealing Broadway and had a population of 28,768 as of 2011. It is the westernmost location of the London post town. Hanwell is mentioned in the Domesday Book. St Mary's Church was established in the tenth century and has been rebuilt three times since, the present church dating to 1842. Schools were established around this time in Hanwell; notably Central London District School which Charlie Chaplin attended. By the end of the 19th century there were over one thousand houses in Hanwell. The Great Western Railway came in 1838 and Hanwell railway station opened. Later the trams of London United Tramways came on the Uxbridge Road in 1904, running from Chiswick to Southall. From 1894 it was its own urban district of Middlesex until being absorbed into Ealing Urban District in 1926. To its west flows the River Brent, which marks Hanwell's boundary wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal India Asylum
The Royal India Asylum was a lunatic asylum operated by the Secretary of State for India at Hanwell between 1870 and 1892. The asylum occupied Elm Grove House in Church Road, Hanwell, a large property standing in extensive grounds which had first been turned into an asylum by Susan Wood. Her husband was the brother of the wife of William Ellis, the first superintendent of the Hanwell Asylum.Andrew RobertThe Lunacy Commission(1981 Middlesex University web, accessed 11 September 2008. In March 1870, the Secretary of State for India bought the Elm Grove House estate from the Perceval family for £24,500. Sir Matthew Digby Wyatt then oversaw the conversion of the property into a lunatic asylum for patients sent home from British India. The new Royal Indian Asylum opened in August 1870, Margaret Makepeace, Lead Curator, East India Company Records“The Royal Indian Asylum and the building of the railway at Ealing” 9 January 2013. Text was copied from this source, which is available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armies of the Seventh Coalition. One of these was a British-led coalition consisting of units from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover, Duchy of Brunswick, Brunswick, and Duchy of Nassau, Nassau, under the command of the Duke of Wellington (referred to by many authors as ''the Anglo-allied army'' or ''Wellington's army''). The other was composed of three corps of the Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian army under the command of Field Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, von Blücher (the fourth corps of this army fought at the Battle of Wavre on the same day). The battle marked the end of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle was contemporaneously known as the Battle of Mont Saint-J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |