|
Chardal
Hardal (also spelled Chardal; he, חרד״ל, acronym for , , plural ) usually refers to the portion of the Religious Zionist Jewish community in Israel which inclines significantly toward Haredi ideology (whether in terms of outlook on the secular world, or in their stringent '' khumra'' approach to ''Halakha''). Hardal Jews are also known as ''Torani'' (lit., "Torah-oriented") or ''Torani-Leumi''. Description On yeshiva.org.il, "Chardal" is described as, "The people who classify themselves as 'Charedi Leumi', or 'Chardal', try to keep the Mitzvot strictly, ''Kalah Kechamurah'' ight and weighty matters alike while being involved in the national life in the state, and in the settling of Eretz Yisrael." It has also been explained as the "Anglo Orthodox religious sector who follow a Charedi lifestyle, yet may also serve in the army in religious units, attend a Hesder yeshiva, and pursue a work career". Yet another explanation is, "those connected to the seriousness of Torah lear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustard (condiment)
Mustard is a condiment made from the mustard seed, seeds of a mustard plant (white/yellow mustard, ''white mustard, Sinapis alba''; brown mustard, ''Brassica juncea''; or black mustard, ''Brassica nigra''). The whole, ground, cracked, or bruised mustard seeds are mixed with water, vinegar, lemon juice, wine, or other liquids, salt, and often other flavorings and spices, to create a paste or sauce ranging in color from bright yellow to dark brown. The seed itself has a strong, pungent, and somewhat bitter taste. The taste of mustard condiments ranges from sweet to spicy. Mustard is commonly paired with meats, vegetables and cheeses, especially as a condiment for sandwiches, hamburgers, and hot dogs. It is also used as an ingredient in many salad dressing, dressings, Glaze (cooking technique), glazes, sauces, soups, and marinades. As a cream or as individual seeds, mustard is used as a condiment in the cuisine of Indian cuisine, India and Bangladeshi cuisine, Bangladesh, the Medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bnei Akiva
Bnei Akiva ( he, בְּנֵי עֲקִיבָא, , "Children of Akiva") is the largest religious Zionist youth movement in the world, with over 125,000 members in 42 countries. It was first established in Mandatory Palestine in 1929. History Bnei Akiva was established on Lag BaOmer 1929 as the youth wing of the Mizrachi movement. Concurrent with the establishment of the movement in pre-independence Israel, organizations of religious youth operated in the Diaspora. In 1958, the Israeli and Diaspora groups merged to form the modern World Bnei Akiva, which operates both in and out of Israel for Diaspora youth, along with Bnei Akiva Israel, which operates in Israel for Israeli youth. Ideology Bnei Akiva's objectives are to educate Jewish youth with values of Torah and work, to provide stimulating experiential and informal opportunities for encountering Judaism, and to encourage Jewish continuity and leadership. Bnei Akiva's twin ideals of ''Torah'' and ''Avodah'' translate to reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payot
''Pe'ot'', anglicized as payot ( he, פֵּאוֹת, pēʾōt, "corners") or payes (), is the Hebrew term for sidelocks or sideburns. Payot are worn by some men and boys in the Orthodox Jewish community based on an interpretation of the Tanakh's injunction against shaving the "sides" of one's head. Literally, ''pe'a'' means "corner, side, edge". There are different styles of payot among Haredi or Hasidic, Yemenite, and Chardal Jews. Yemenite Jews call their sidelocks ''simanim'' (), literally, "signs", because their long-curled sidelocks served as a distinguishing feature in the Yemenite society (differentiating them from their non-Jewish neighbors). Rabbinic interpretation Reason According to Maimonides, shaving the sidelocks was a heathen practice. Specifics The Torah says, "you shall not round off the ''pe'a'' of your head ()". The word ''pe'a'' was taken to mean the hair in front of the ears extending to beneath the cheekbone, on a level with the nose (Talmud – Makkot 20a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
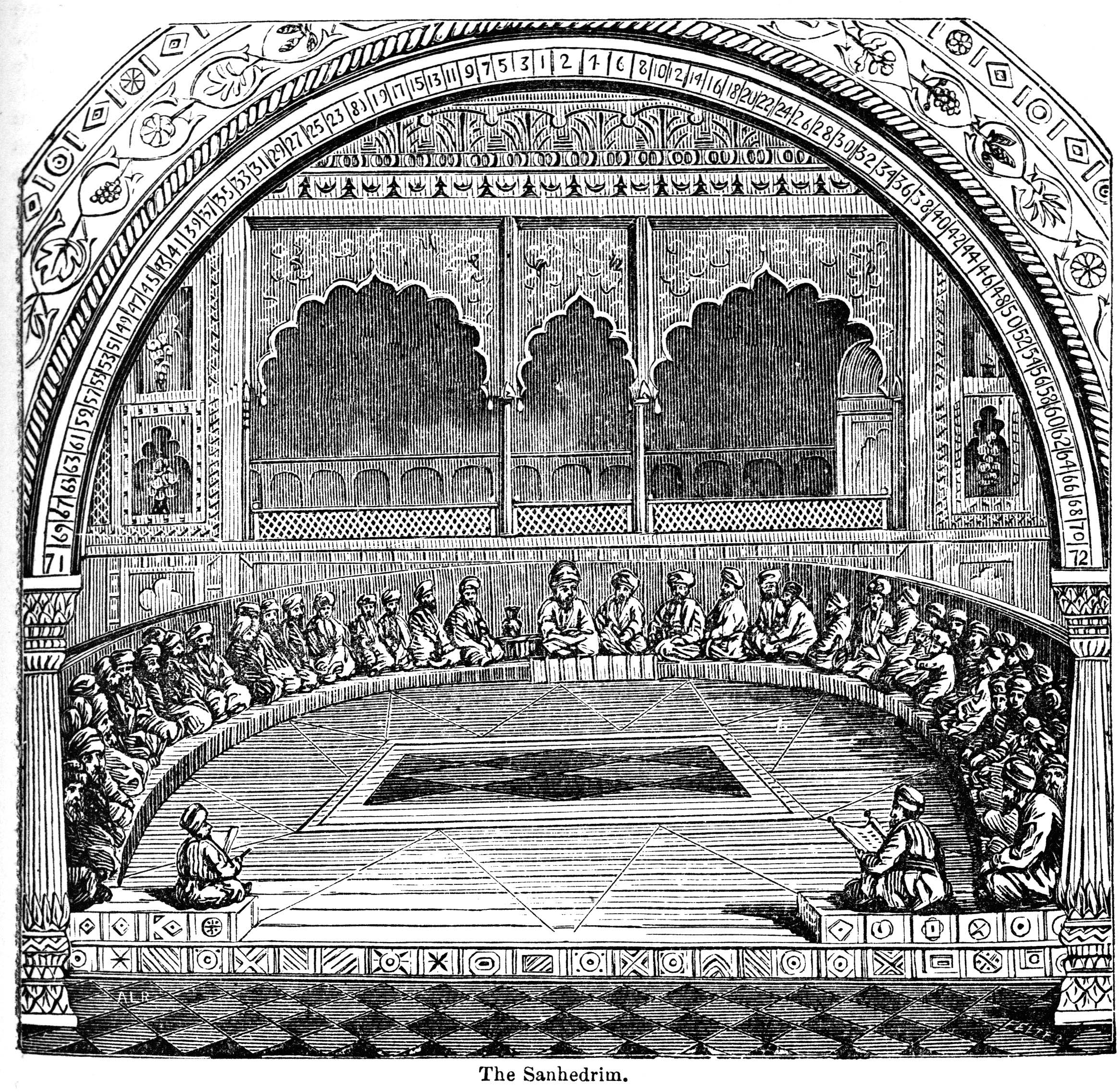
Da'as Torah
Rabbinic authority in Judaism relates to the theological and communal authority attributed to rabbis and their pronouncements in matters of Jewish law. The extent of rabbinic authority differs by various Jewish groups and denominations throughout history. The origins of rabbinic authority in Judaism is understood as originally linked to the High Court of ancient Israel and Judah, known as the Sanhedrin. Scholars understand that the extent of rabbinic authority, historically, would have related to areas of Jewish civil, criminal, and ritual law, while rabbinic positions that relate to non-legal matters, such as Jewish philosophy would have been viewed as non-binding.Turkel, E. (1993). The nature and limitations of rabbinic authority. Tradition: A Journal of Orthodox Jewish Thought, 27(4), 80-99. Rabbinic authority also distinguished the practice of Judaism by the Pharisees (i.e., Rabbinic Judaism) to the religious practice of the Sadducees and the Qumran sect. This concept is linked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip (;The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory under the control of the Palestinian National Authority and Hamas, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza...". ar, قِطَاعُ غَزَّةَ ' , he, רצועת עזה, ), or simply Gaza, is a State of Palestine, Palestinian Enclave and exclave, exclave on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. The smaller of the two Palestinian territories, it borders Egypt on the southwest for and Israel on the east and north along a border. Together, the Gaza Strip and the West Bank make up the State of Palestine, while being under Israeli-occupied territories, Israeli military occupation since 1967. The territories of Gaza and the West Bank are separated from each other by Israeli territory. Both fell under the jurisdiction of the Palestinian National Authority, Palestinian Authority, but the Strip is governed by Hamas, a militant, fundamentali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messianic Age
In Abrahamic religions, the Messianic Age is the future period of time on Earth in which the messiah will reign and bring universal peace and brotherhood, without any evil. Many believe that there will be such an age; some refer to it as the consummate "kingdom of God" or the "world to come". Jews believe that such a figure is yet to come, while Christians and Muslims believe that this figure will be Jesus. Judaism According to Jewish tradition, the Messianic Era will be one of global peace and harmony; an era free of strife and hardship, conducive to the furtherment of the knowledge of the Creator. The theme of the Messiah ushering in an era of global peace is encapsulated in two of the most famous scriptural passages from the Book of Isaiah: In his Mishneh Torah, Maimonides describes the Messianic Era: :"And at that time there will be no hunger or war, no jealousy or rivalry. For the good will be plentiful, and all delicacies available as dust. :The entire occupation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitzvah
In its primary meaning, the Hebrew word (; he, מִצְוָה, ''mīṣvā'' , plural ''mīṣvōt'' ; "commandment") refers to a commandment commanded by God to be performed as a religious duty. Jewish law () in large part consists of discussion of these commandments. According to religious tradition, there are 613 such commandments. In its secondary meaning, the word ''mitzvah'' refers to a deed performed in order to fulfill such a commandment. As such, the term ''mitzvah'' has also come to express an individual act of human kindness in keeping with the law. The expression includes a sense of heartfelt sentiment beyond mere legal duty, as "you shall love your neighbor as yourself" (Leviticus 19:18). The opinions of the Talmudic rabbis are divided between those who seek the purpose of the ''mitzvot'' and those who do not question them. The latter argue that if the reason for each ''mitzvah'' could be determined, people might try to achieve what they see as the purpose of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kippah
A , , or , plural ), also called ''yarmulke'' (, ; yi, יאַרמלקע, link=no, , german: Jarmulke, pl, Jarmułka or ''koppel'' ( yi, קאפל ) is a brimless cap, usually made of cloth, traditionally worn by Jewish males to fulfill the customary requirement that the head be covered. It is worn by all men in Orthodox Jewish communities during prayers and by most Orthodox Jewish men at all other times. Among non-Orthodox Jewish communities, those who wear them customarily do so only during prayer, while attending a synagogue, or in other rituals, and often women may also wear them in those communities. Etymology The term ( he, כיפה) literally means "dome", as the kippah is worn on the head like a dome. The Yiddish term might be derived from the Polish or the Ukrainian , perhaps ultimately from Medieval Latin ("cowl, hood"). It may also be of Turkic origin (akin to , meaning "rainwear"); the word is often associated with the phrase (), formed from the Aramaic wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzitzit
''Tzitzit'' ( he, ''ṣīṣīṯ'', ; plural ''ṣīṣiyyōṯ'', Ashkenazi Hebrew, Ashkenazi: '; and Samaritan Hebrew, Samaritan: ') are specially knotted ritual Fringe (trim), fringes, or tassels, worn in antiquity by Israelites and today by observant Jews and Samaritans. are usually attached to the four corners of the ''tallit gadol'' (prayer shawl), usually referred to simply as a or ; and ''tallit katan'' (everyday undergarment). Through synecdoche, a may be referred to as . Etymology The word may derive from the semitic root, Hebrew root [n-ts-h]. shares this root with the Hebrew for 'lock of hair', or 'dreadlock'. For example, in the Book of Ezekiel an angel grabs the prophet "by the of [his] head;" he could be said to be "dragged by his hair." A popular etymological interpretation of derives from another word which shares this root. ( 'budding flower') may once have referred to floral ornamentation on clothing. One can hear distinct similarities with cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew (notably Mishnaic) and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages.Aram Yardumian"A Tale of Two Hypotheses: Genetics and the Ethnogenesis of Ashkenazi Jewry".University of Pennsylvania. 2013. Yiddish is primarily written in the Hebrew alphabet. Prior to World War II, its worldwide peak was 11 million, with the number of speakers in the United States and Canada then totaling 150,000. Eighty-five percent of the approximately six million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust were Yiddish speakers,Solomon Birnbaum, ''Grammatik der jiddischen Sprache'' (4., erg. Aufl., Hambu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singular: , Modern Hebrew: are a Jewish diaspora population who coalesced in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. Their traditional diaspora language is Yiddish (a West Germanic language with Jewish linguistic elements, including the Hebrew alphabet), which developed during the Middle Ages after they had moved from Germany and France into Northern Europe and Eastern Europe. For centuries, Ashkenazim in Europe used Hebrew only as a sacred language until the revival of Hebrew as a common language in 20th-century Israel. Throughout their numerous centuries living in Europe, Ashkenazim have made many important contributions to its philosophy, scholarship, literature, art, music, and science. The rabbinical term ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Har Hamor
Yeshivat Har Hamor (); is a Religious Zionist yeshiva in Har Homa, Jerusalem, founded in 1997 as an offshoot of Yeshivat Mercaz HaRav. The president of the yeshiva is Rabbi Zvi Thau, and its other heads are Rabbis Amiel Sternberg and Mordechai Sternberg. There are currently around 450 students. Many of the students are married ("avrechim"), and the average student age is higher than at most Religious Zionist yeshivas. The name means "mountain of myrrh", based on Song of Songs 4:6, a phrase which in the Jewish tradition refers to the Temple Mount. The word "Hamor" is also an acronym for "''Hemshech'' continuation ofMercaz HaRav". History The Yeshiva was founded when a group of rabbis, led by Rabbi Zvi Thau, broke off from Mercaz Harav. The broader cause of the separation was a disagreement between Rabbi Avraham Shapira, head of Mercaz HaRav, and Rabbi Thau about the best approach for Torah education. The immediate cause was Rabbi Thau's opposition to the establishment of a tea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |