|
Chapter 7, Title 11, United States Code
Chapter 7 of Title 11 U.S. Code is the bankruptcy code that governs the process of liquidation under the bankruptcy laws of the U.S. In contrast to bankruptcy under Chapter 11 and Chapter 13, which govern the process of ''reorganization'' of a debtor, Chapter 7 bankruptcy is the most common form of bankruptcy in the U.S. For businesses When a financially troubled business is unable to pay creditors, the business may file (or be compelled by creditors to file) for bankruptcy in a federal court under Chapter 7, which means that the business ceases operations unless those operations are continued by the Chapter 7 trustee. In a Chapter 7 bankruptcy, the trustee is appointed almost immediately, with broad powers to examine the finances of the business in bankruptcy; generally, the trustee sells the assets and distributes the money to the creditors. The investors who took the least amount of risk prior to the bankruptcy are generally paid first. For example, secured creditors w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Title 11 Of The United States Code
Title 11 of the United States Code, also known as the United States Bankruptcy Code, is the source of bankruptcy law in the United States Code. Chapters Title 11 is subdivided into nine chapters. It used to include more chapters, but some of them have since been repealed in their entirety. The nine chapters are: *Chapter 1: General Provisions *Chapter 3: Case Administration *Chapter 5: Creditors, the Debtor and the Estate * Chapter 7: Liquidation * Chapter 9 : Adjustment of Debts of a Municipality *Chapter 11: Reorganization *Chapter 12: Adjustment of Debts of a Family Farmer or Fisherman with Regular Annual Income *Chapter 13: Adjustment of Debts of an Individual with Regular Income * Chapter 15: Ancillary and Other Cross-Border Cases References Further reading External linksUnited States Bankruptcy Codevia usbankruptcycode.orgU.S. Code Title 11 via United States Government Publishing OfficeU.S. Code Title 11 via Cornell University Cornell University is a private stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bankruptcy Discharge
A discharge in United States bankruptcy law, when referring to a debtor's discharge, is a statutory injunction against the commencement or continuation of an action (or the employment of process, or an act) to collect, recover or offset a debt as a personal liability of the debtor. The discharge is one of the primary benefits afforded by relief under the Bankruptcy Code and is essential to the "fresh start" of debtors following bankruptcy that is a central principle under federal bankruptcy law. Discharge is also believed to play an important role in credit markets by encouraging lenders, who may be more sophisticated and have better information than debtors, to monitor debtors and limit risk-taking.Michael SimkovicRisk-Based Student Loans(2012) A discharge of debts is granted to debtors but can be denied or revoked by the court based on certain misconduct of debtors, including fraudulent actions or failure of a debtor to disclose all assets during a bankruptcy case. Some debt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
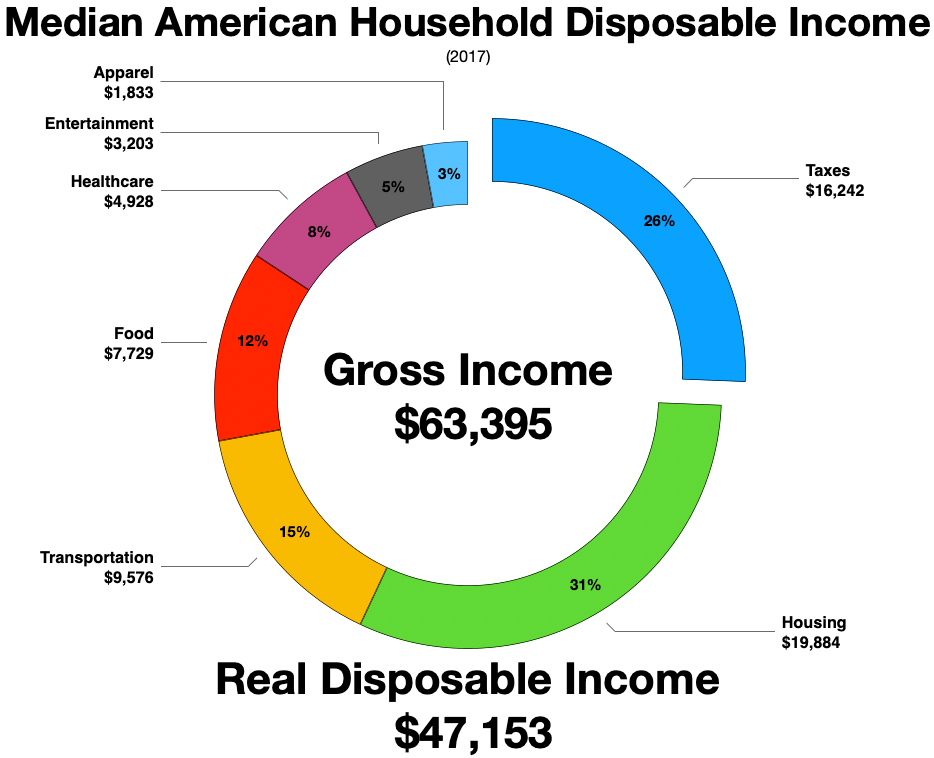
Disposable Income
Disposable income is total personal income minus current income taxes. In national accounts definitions, personal income minus personal current taxes equals disposable personal income. Subtracting personal outlays (which includes the major category of personal r privateconsumption expenditure) yields personal (or, private) savings, hence the income left after paying away all the taxes is referred to as disposable income. Restated, consumption expenditure plus savings equals disposable income after accounting for transfers such as payments to children in school or elderly parents’ living and care arrangements. The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is the fraction of a change in disposable income that is consumed. For example, if disposable income rises by $100, and $65 of that $100 is consumed, the MPC is 65%. Restated, the marginal propensity to save is 35%. For the purposes of calculating the amount of income subject to garnishments, United States' federal law defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Trustee Program
The United States Trustee Program is a component of the United States Department of Justice that is responsible for overseeing the administration of bankruptcy cases and private trustees. The applicable federal law is found at and , et seq. In addition to the twenty-one United States Trustees, the program is administered by the Executive Office for U.S. Trustees (EOUST), located in Washington, D.C., and 95 field offices. The United States Trustee is the federal official charged with enforcing civil bankruptcy laws in the United States. Overview The United States Attorney General generally appoints a separate United States Trustee for each of twenty-one geographical regions for a five-year term. Each United States Trustee is removable from office by and works under the general supervision of the Attorney General (see and ). Each United States Trustee, an officer of the Department of Justice, is responsible for maintaining and supervising a panel of private trustees for Chapte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alimony
Alimony, also called aliment (Scotland), maintenance (England, Ireland, Northern Ireland, Wales, Canada, New Zealand), spousal support (U.S., Canada) and spouse maintenance (Australia), is a legal obligation on a person to provide financial support to their spouse before or after marital separation or divorce. The obligation arises from the divorce law or family law of each country. In most jurisdictions, it is distinct from child support, where, after divorce, one parent is required to contribute to the support of their children by paying money to the child's other parent or guardian. Etymology The term alimony comes from the Latin word '' alimōnia'' ("nourishment, sustenance", from ''alere,'' "to nourish"), from which the terms alimentary (of, or relating to food, nutrition, or digestion), and aliment (a Scots Law rule regarding sustenance to assure the wife's lodging, food, clothing, and other necessities after divorce) are also derived. History The Code of Hammurabi (1754 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crime
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a State (polity), state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definitions of", in Cane and Conoghan (editors), ''The New Oxford Companion to Law'', Oxford University Press, 2008 (), p. 263Google Books). though statutory definitions have been provided for certain purposes. The most popular view is that crime is a Category of being, category created by law; in other words, something is a crime if declared as such by the relevant and applicable law. One proposed definition is that a crime or offence (or criminal offence) is an act harmful not only to some individual but also to a community, society, or the state ("a public wrong"). Such acts are forbidden and punishable by law. The notion that acts such as murder, rape, and theft are to be prohibited exists worldwide. What precisely is a criminal offence is de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restitution
The law of restitution is the law of gains-based recovery, in which a court orders the defendant to ''give up'' their gains to the claimant. It should be contrasted with the law of compensation, the law of loss-based recovery, in which a court orders the defendant to ''pay'' the claimant for their loss. Evolving Meaning ''American Jurisprudence'' 2d edition notes: Legal vs Equitable Remedy Restitution may be either a legal remedy or an equitable remedy, "depend ngupon the basis for the plaintiff's claim and the nature of the underlying remedies sought". Generally, restitution and equitable tracing is an equitable remedy when the money or property wrongfully in the possession of defendant is traceable (i.e., can be tied to "particular funds or property"). In such a case, restitution comes in the form of a constructive trust or equitable lien. Where the particular property at issue cannot be particularly identified, restitution is a legal remedy. This occurs, for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine (penalty)
A fine or mulct (the latter synonym typically used in civil law) is a penalty of money that a court of law or other authority decides has to be paid as punishment for a crime or other offense. The amount of a fine can be determined case by case, but it is often announced in advance. The most usual use of the term is for financial punishments for the commission of crimes, especially minor crimes, or as the settlement of a claim. One common example of a fine is money paid for violations of traffic laws. Currently in English common law, relatively small fines are used either in place of or alongside community service orders for low-level criminal offences. Larger fines are also given independently or alongside shorter prison sentences when the judge or magistrate considers a considerable amount of retribution is necessary, but there is unlikely to be significant danger to the public. For instance, fraud is often punished by very large fines since fraudsters are typically ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adversary Proceeding
An adversary proceeding in bankruptcy is a type of lawsuit in the American legal system. It is distinguished from other suits by being filed a United States bankruptcy court in connection with a larger bankruptcy proceeding. Procedure Adversary proceedings are governed by certain court rules found in Part VII of the Federal Rules of Bankruptcy Procedure and, in part, by the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure. A bankruptcy case may contain one or more adversary proceedings or (most commonly) none at all. Other than their connection to a bankruptcy proceeding, adversary proceedings are largely similar to a standard lawsuit in federal district court. The suit is opened by a complaint filed with the Bankruptcy Court, and proceeds through the same stages of litigation, including discovery and trial (including jury trial in appropriate cases). The adversary proceeding may address claims to do with federal or state law, or in rare cases other law, as well. The only limitation is that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
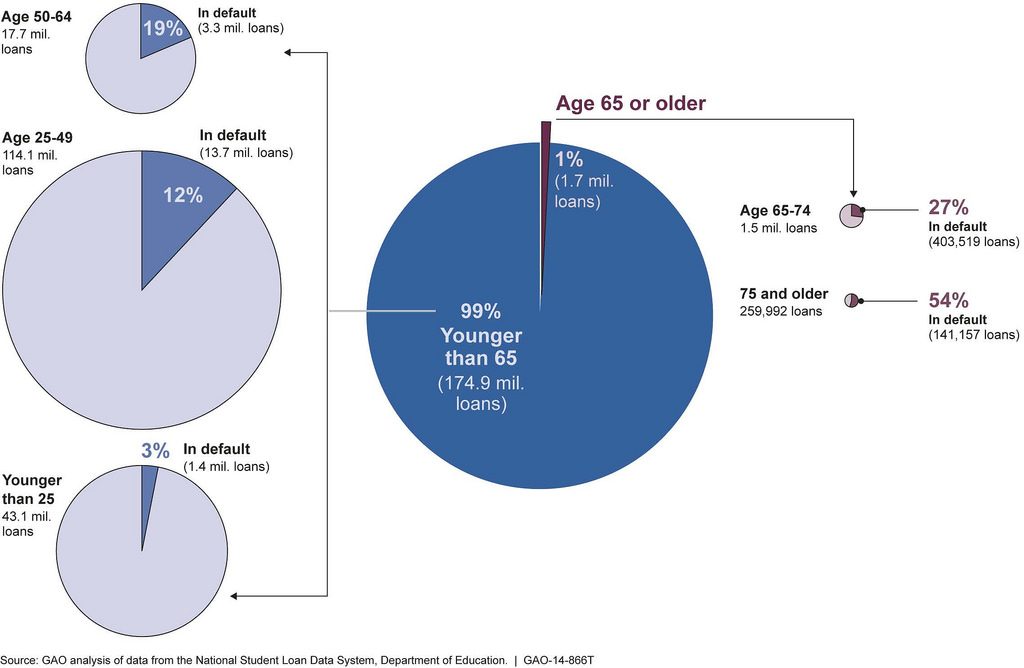
Student Loans
A student loan is a type of loan designed to help students pay for post-secondary education and the associated fees, such as tuition, books and supplies, and living expenses. It may differ from other types of loans in the fact that the interest rate may be substantially lower and the repayment schedule may be deferred while the student is still in school. It also differs in many countries in the strict laws regulating renegotiating and bankruptcy. This article highlights the differences of the student loan system in several major countries. Australia Tertiary student places in Australia are usually funded through the HECS-HELP scheme. This funding is in the form of loans that are not normal debts. They are repaid over time via a supplementary tax, using a sliding scale based on taxable income. As a consequence, loan repayments are only made when the former student has income to support the repayments. Discounts are available for early repayment. The scheme is available to cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Property Taxes
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inheritance or gift and taxes on financial and capital transactions" (see: ), but this article only covers taxes on realty. The tax is levied by the governing authority of the jurisdiction in which the property is located. This can be a national government, a federated state, a county or geographical region or a municipality. Multiple jurisdictions may tax the same property. Often a property tax is levied on real estate. It may be imposed annually or at the time of a real estate transaction, such as in real estate transfer tax. This tax can be contrasted to a rent tax, which is based on rental income or imputed rent, and a land value tax, which is a levy on the value of land, excluding the value of buildings and other improvements. Under a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Support
Child support (or child maintenance) is an ongoing, periodic payment made by a parent for the financial benefit of a child (or parent, caregiver, guardian) following the end of a marriage or other similar relationship. Child maintenance is paid directly or indirectly by an ''obligor'' to an ''obligee'' for the care and support of children of a relationship that has been terminated, or in some cases never existed. Often the obligor is a non-custodial parent. The obligee is typically a custodial parent, a caregiver, a Legal guardian, guardian. Depending on the jurisdiction, a custodial parent may pay child support to a non-custodial parent. Typically one has the same duty to pay child support irrespective of sex, so a mother is required to pay support to a father just as a father must pay a mother. In some jurisdictions where there is joint custody, the child is considered to have two custodial parents and no non-custodial parents, and a custodial parent with a higher income (obligo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |