|
Chapman Field (Miami)
Chapman Field (officially the Subtropical Horticulture Research Station) is a horticulture and agronomy research facility of the Agricultural Research Service, a division of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), located in Miami, Florida. Dating from 1898, it is one of the oldest entities in South Florida. The USDA also refers to it as the Miami Station. The introduction of economically useful plants into the US is a three-step process: (1) explorers find the plants in foreign countries; (2) the plants are sent back to a USDA introduction garden where they are evaluated; (3) successful plants are distributed to farmers and nurserymen. Chapman Field is the original introduction garden for tropical plants. Over 20,000 plant introductions have been registered at the Miami station since its establishment. Emphasis has been on rubber, cacao, coffee, mango, palm, avocado, lychee, and other plants. History Brickell Avenue The Miami station was started as a plant intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia are three of the leading rubber producers. Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers. Currently, rubber is harvested mainly in the form of the latex from the rubber tree (''Hevea brasiliensis'') or others. The latex is a sticky, milky and white colloid drawn off by making incisions in the bark and collecting the fluid in vessels in a process called "tapping". The latex then is refined into the rubber that is ready for commercial processing. In major areas, latex is allowed to coagulate in the collection cup. The coagulated lumps are collected and processed into dry forms for sale. Natural rubber is used extensively in many applications and products, either alone or in combination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Brickell
William Brickell (May 22, 1817(?) – January 14, 1908) joined Julia Tuttle as a co-founder of Miami, Florida. During the Civil War, Brickell and his wife Mary, whom he met and married in Australia, lived in the White House while he worked as an aide to President Abraham Lincoln. In 1868, the Brickells purchased two tracts of land, one of which stretched from Coconut Grove to the Miami River, which they purchased from Mrs. Harriet English and her brother Richard Fitzpatrick who had acquired it by grant from the King of Spain. The family moved to southern Florida from Cleveland, Ohio, arriving by ship in 1871. He and his family opened a trading post and post office in their home on the south bank of the Miami River, near the site of Fort Dallas. The Brickells' neighbor, Julia Tuttle, also originally from Cleveland, is credited with attracting the attention of Florida's east coast railroad and resort hotel magnate Henry M. Flagler to extend his interests to the area. Both Brickell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Areas Of Miami-Dade County, Florida
Protection is any measure taken to guard a thing against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights. Although the mechanisms for providing protection vary widely, the basic meaning of the term remains the same. This is illustrated by an explanation found in a manual on electrical wiring: Some kind of protection is a characteristic of all life, as living things have evolved at least some protective mechanisms to counter damaging environmental phenomena, such as ultraviolet light. Biological membranes such as bark on trees and skin on animals offer protection from various threats, with skin playing a key role in protecting organisms against pathogens and excessive water loss. Additional structures like scales and hair offer further protection from the elements and from predators, with some animals having features such as spines or camouflage s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
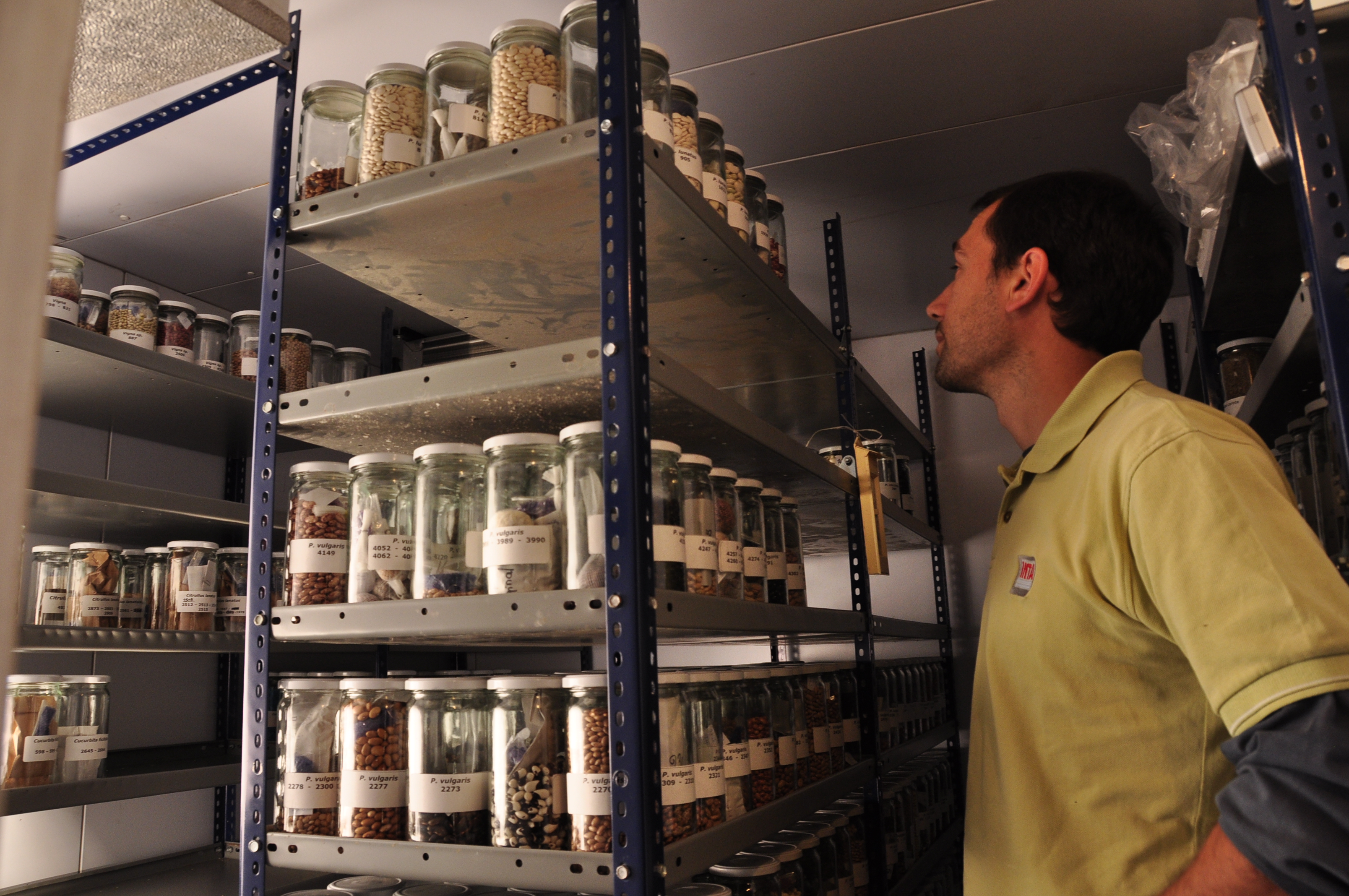
Germplasm
Germplasm are living genetic resources such as seeds or tissues that are maintained for the purpose of animal and plant breeding, preservation, and other research uses. These resources may take the form of seed collections stored in seed banks, trees growing in nurseries, animal breeding lines maintained in animal breeding programs or gene banks, etc. Germplasm collections can range from collections of wild species to elite, domesticated breeding lines that have undergone extensive human selection. Germplasm collection is important for the maintenance of biological diversity and food security. See also * Animal genetic resources for food and agriculture * Conservation biology * Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources * Forest genetic resources * International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture * Plant genetic resources * Seed saving References *Day-Rubenstein, K and Heisey, P. 2003. Plant Genetic Resources: New Rules for International Exchange' * 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Plant Germplasm System
The U.S. National Plant Germplasm System (NPGS) is a network of institutions and agencies (federal, state and private) led by the Agricultural Research Service (ARS) of the U.S. Department of Agriculture in the effort to conserve and facilitate the use of the genetic diversity of agriculturally important plants and their wild relatives. Introduction Tremendous genetic variability exists in the local varieties (landraces) of crops and their closely related wild plants (crop wild relatives). The NPGS assists plant breeders and other research scientists by acquiring, conserving, evaluating, documenting, and distributing germplasm (seeds and other propagative material) of these plants, as well as of improved cultivars and breeding lines. This diverse germplasm provides the genetic raw material needed by plant breeders to develop new varieties of crops that have desirable qualities and can withstand constantly changing biological and environmental stresses. Conservation and use of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embry–Riddle Aeronautical University
Embry–Riddle Aeronautical University (ERAU) is a private university focused on aviation and aerospace programs. Initially founded at Lunken Field in Cincinnati, Ohio in 1926, its main campuses are located in Daytona Beach, Florida, and Prescott, Arizona. It is the largest accredited university system specializing in aviation and aerospace. It has numerous online programs and academic programs offered at satellite locations. It began as a regional school for pilots and aircraft mechanics. With the expansion and development of aviation and related space programs, today the university enrolls more than 33,000 undergraduate and graduate students. History On December 17, 1925, Talton Higbee Embry and John Paul Riddle founded the Embry–Riddle Company at Lunken Airport in Cincinnati, Ohio. In spring 1926, the company opened the Embry–Riddle School of Aviation. Following a merge with the Aviation Corporation (AVCO), the Embry–Riddle flying school was closed in 1930. In 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Chapman
Victor Emmanuel Chapman (April 17, 1890 – June 24, 1916) was a French-American pilot remembered for his exploits during World War I. He was the first American pilot to die in the war. Growing up Chapman was born in New York City to essayist John Jay Chapman and Minna Timmins (who died in 1898). He and his father moved to France soon after. In France, Chapman obtained dual-citizen status as a French and US citizen. His father remarried, to Elizabeth Chanler, a sister of William A. Chanler from the Astor family, when Chapman was a teenager around 16 years old. Chapman returned to the United States in his late teens to attend Fay School (Class of 1903), St Paul's School, Concord, NH, and Harvard University. After graduating, Chapman returned to Europe, spending time in France and in Germany. Fighting in the war When World War I broke out, his father and stepmother moved to London, England. However, Chapman decided to stay in France, joining the French Foreign Legio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John W
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson Popenoe
Frederick Wilson Popenoe (March 9, 1892 – June 20, 1975) was an American Department of Agriculture employee and plant explorer. From 1916 to 1924, Popenoe explored Latin America to look for new strains of avocados. He reported his adventures to the ''National Geographic Society''. He went to work for the U.S. Department of Agriculture in 1913 and became the chief agronomist of the United Fruit Company in 1925. Career Popenoe attended Pomona College as a special student for one year. Afterwards, he worked for the United Fruit Company, where he became the first director of the Panamerican Agricultural School, Zamorano in Honduras. Popenoe won numerous awards and received three honorary doctorates, from: Universidad Mayor de San Marcos in Lima, Peru; Pomona College; and the University of Florida in Gainesville, Florida. Personal life Popenoe was married to the British archeologist Dorothy Popenoe, who was involved in excavation of the Playa de los Muertos in Hondura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Deering
Charles Deering (July 31, 1852 – February 5, 1927) was an American businessman, art collector, and philanthropist. He was an executive of the agricultural machinery company founded by his father that became International Harvester. Charles's successful stewardship of the family firm left him with the means and leisure to indulge his interests in the arts and natural sciences. His activities and benefactions in the US were centered on Chicago and Miami; he also aspired to found an art museum in Spain. Early life Deering was born July 31, 1852, in South Paris, Maine, the son of Abby Reed Barbour and William Deering. His father was a successful businessman then engaged in real estate speculation and the manufacture and sale of woolens. In 1856, Charles's mother died, and, the following year, his father married Clara Barbour Cummings Hamilton, a cousin of his late wife. The two children of this marriage were James Deering (1859–1925) and Abby Marion Deering (later Mrs Ric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Flagler
Henry Morrison Flagler (January 2, 1830 – May 20, 1913) was an American industrialist and a founder of Standard Oil, which was first based in Ohio. He was also a key figure in the development of the Atlantic coast of Florida and founder of the Florida East Coast Railway. He is also known as a founder of the cities of Miami and Palm Beach, Florida. Early life and education Flagler was born in Hopewell, New York. His father was Isaac Flagler, a Presbyterian minister and great-grandson of Zacharra Flegler, whose family had emigrated from the German Palatinate region to Holland in 1688. Zacharra worked in England for several years before moving to Dutchess County, New York, in 1710. His grandson Solomon changed the spelling of the surname to Flagler and passed it on to his 11 children. Flagler's mother was Elizabeth Caldwell Harkness Flagler, Isaac's third wife and a widow who had a stepson, Stephen V. Harkness, and a son, Daniel M. Harkness, from her marriage to decea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
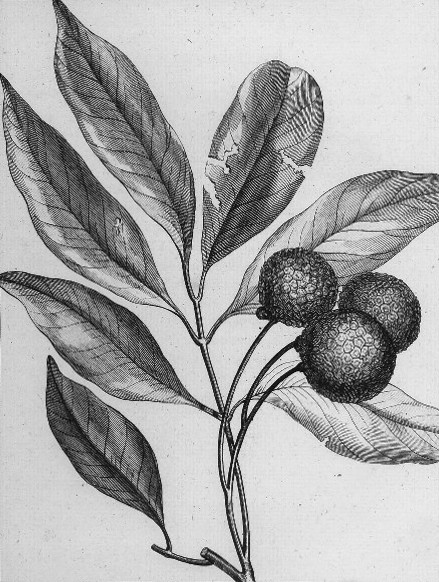
Lychee
Lychee (US: ; UK: ; ''Litchi chinensis''; ) is a monotypic taxon and the sole member in the genus ''Litchi'' in the soapberry family, ''Sapindaceae''. It is a tropical tree native to Southeast and Southwest China (the Guangdong, Fujian, Yunnan and Hainan provinces), Assam, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaya, Jawa, Borneo, Philippines and New Guinea. The tree is introduced into Cambodia, Andaman Islands, Bangladesh, East Himalaya, India, Mauritius and Réunion. The cultivation in China is documented from the 11th century. China is the main producer of lychees, followed by Vietnam, India, other countries in Southeast Asia, the Indian Subcontinent, Madagascar and South Africa. A tall evergreen tree, the lychee bears small fleshy fruits. The outside of the fruit is pink-red, roughly textured, and inedible, covering sweet flesh eaten in many different dessert dishes. Lychee seeds contain methylene cyclopropyl glycine which can cause hypoglycemia associated with outbreaks o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |