|
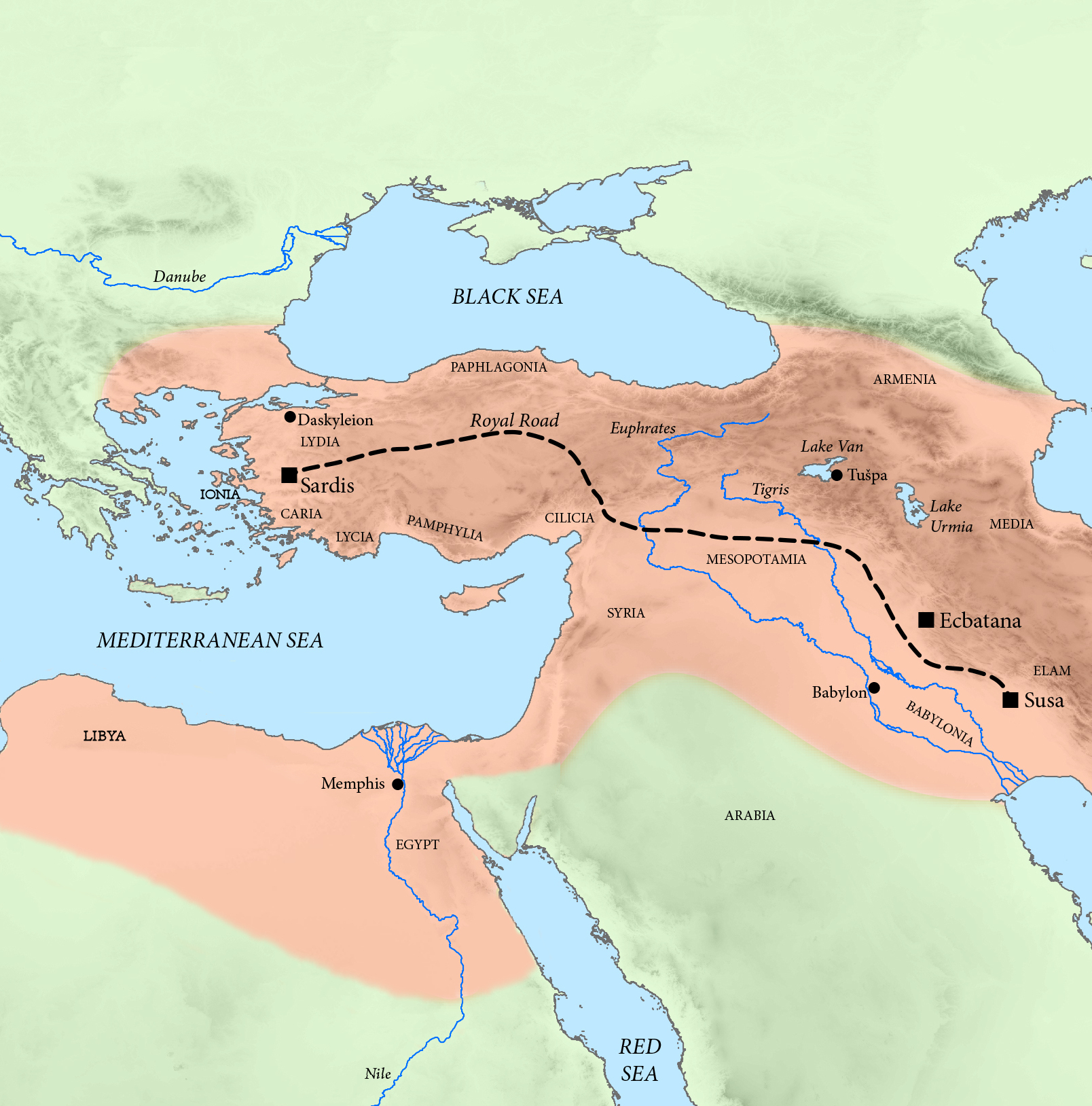
Chapar Khaneh
''Chapar Khaneh'' ( fa, چاپارخانه, , ) is the Persian-language term that refers to the postal service system used throughout the Achaemenid Empire. It was created by Cyrus the Great and later developed by Darius the Great as the royal method of communication throughout the empire. Each ''Chapar Khaneh'' was a station mainly located along the Royal Road, an ancient highway that was reorganized and rebuilt by Darius I, which stretched from Sardis in modern-day Turkey to Susa in modern-day Iran, connecting most of the major cities of the Achaemenid Empire. Herodotus' description of the Royal Road and the various ''Chapar Khanehs'' along it is as follows: :''"Now the true account of the road in question is the following: Royal stations exist along its whole length, and excellent caravanserais; and throughout, it traverses an inhabited tract, and is free from danger. In Lydia and Phrygia there are twenty stations within a distance Of 94½ parasangs. On leaving Phrygia the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mail
The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letter (message), letters, and parcel (package), parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid-19th century, national postal systems have generally been established as a government monopoly, with a fee on the article prepaid. Proof of payment is usually in the form of an adhesive postage stamp, but a postage meter is also used for bulk mailing. With the advent of email, the retronym "snail mail" was coined. Postal authorities often have functions aside from transporting letters. In some countries, a Postal Telegraph and Telephone, postal, telegraph and telephone (PTT) service oversees the postal system, in addition to telephone and telegraph systems. Some countries' postal systems allow for savings accounts and handle applications for passports. The Universal Postal Union (UPU), established in 1874, includes 192 member countries a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kızılırmak River
The Kızılırmak (, Turkish for "Red River"), once known as the Halys River ( grc, Ἅλυς) and Alis River ( hy, Ալիս), is the longest river flowing entirely within Turkey. It is a source of hydroelectric power and is not used for navigation. Geography The Kızılırmak flows for a total of , rising in Eastern Anatolia around , flowing first to the west and southwest until , then forming a wide arch, the "Halys bend", flowing first to the west, then to the northwest, passing to the northeast of Lake Tuz (''Tuz Gölü'' in Turkish), then to the north and northeast, where it is joined by its major tributary, the Delice River (once known in Greek as the Cappadox river) at . After zigzagging to the northwest to the confluence with the Devrez River at , and back to the northeast, it joins the Gökırmak (''Blue River'' in Turkish) before finally flowing via a wide delta into the Black Sea east of Samsun at . There are dams on the river at Boyabat, Altınkaya and Der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angarum
Angarum was the name of the royal riding post in the Persian Empire during the Achaemenid period. In book 8, paragraph 98 of The Persian Wars, the historian Herodotus talks about the couriers: "Nothing mortal travels so fast as these Persian messengers. The entire plan is a Persian invention; and this is the method of it. Along the whole line of road there are men (they say) stationed with horses, in number equal to the number of days which the journey takes, allowing a man and horse to each day; and these men will not be hindered from accomplishing at their best speed the distance which they have to go, either by snow, rain, heat, or by the darkness of night. The first rider delivers his despatch to the second and the second passes it to the third; and so it is borne from hand to hand along the whole line, like the light in the torch-race, which the Greeks celebrate to Vulcan. The Persians give the riding post in this manner, the name of ''Angarum''." (The angarum were called ''pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angarium
The Angarium (Latin; from Greek ) was the institution of the royal mounted couriers in ancient Persia. The messengers, called (), alternated in stations that had a day's ride distance along the Royal Road. The riders were exclusively in the service of the Great King and the network allowed for messages to be transported from Susa to Sardis (2699 km) in nine days; the journey took ninety days on foot. Herodotus, in about 440 BC, describes the Persian messenger system which had been perfected by Darius I about half a century earlier: "Now there is nothing mortal which accomplishes a journey with more speed than these messengers, so skillfully has this been invented by the Persians: for they say that according to the number of days of which the entire journey consists, so many horses and men are set at intervals, each man and horse appointed for a day's journey. These neither snow nor rain nor heat nor darkness of night prevents from accomplishing each one the task proposed to him, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karkheh River
The Karkheh or Karkhen کرخه (perhaps the river known as the Gihon—one of the four rivers of Eden/Paradise to the Bible and as the Choaspes in ancient times; also called Eulæus; Hebrew: אולי Ulai) is a river in Khūzestān Province, Iran (ancient Susiana) that rises in the Zagros Mountains, and passes west of Shush (ancient Susa), eventually falling in ancient times into the Tigris just below its confluence with the Euphrates very near to the Iran-Iraq border. In modern times, after approaching within of the Dez River, it turns to the southwest and then, northwest of Ahvaz, turns northwest and is absorbed by the Hawizeh Marshes that straddle the Iran–Iraq border. Its peculiarly sweet water was sacred to the use of the Persian kings. Ancient names for the Karkheh should be treated as conjectural because the bed of the river has changed in historic times, and because a nearby watercourse between the Karkheh and the Dez River, the Shaur, confuses the identifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cissia (area)
Cissia( grc, Κισσία, ''Kissia'') was a very fertile district of Susiana in the Persian Empire, on the Choaspes. According to Herodotus, the inhabitants, Cissii, were a 'wild', free people, resembling the Persians in their manners. Herodotus and other ancient Greek writers sometimes referred to the region around Susa as "Cissia", a variant of the Kassite name. However, it is not clear if Kassites were actually living in that region so late. History In ancient times Cissia was subjugated by Tiglath-Pileser III. Once the Ionian Revolt was finally crushed by the Persian victory at the Battle of Lade, Darius began to plan to subjugate Greece. In 490 BC, he sent a naval task force under Datis and Artaphernes across the Aegean to subjugate the Cyclades, and then to make punitive attacks on Athens and Eretria. Reaching Euboea in mid-summer after a successful campaign in the Aegean, the Persians proceeded to put Eretria under siege. The siege lasted six days before a fifth col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matiene
Matiene was the name of a kingdom in northwestern Iran on the lands of the earlier kingdom of the Mannae. Ancient historians including Strabo, Ptolemy, Herodotus, Polybius, and Pliny mention names such as Mantiane, Martiane, Matiana, Matiani, Matiene, Martuni to designate a region located to the northwest of Media." Etymology The name Matiene may be related to Mitanni, the name of a state some 800 years earlier, which was founded by an Indo-Aryan ruling class governing the Hurrian population. The name Matiene was applied also to the neighboring Lake Matianus (Lake Urmia) located immediately to the east of the Matieni people. The Iranian root "Mati-" meaning "to tower, to stand out" (from the same Indo-European root that gives us the word "mountain") might explain the name. History The Mannaeans who probably spoke a Hurro-Urartian language, were subdued by the Scytho- Kimmerians during the seventh and eighth centuries BC and assimilated by Matienes. Matiene was ultimately c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the Persian Gulf. Geography The Tigris is 1,750 km (1,090 mi) long, rising in the Taurus Mountains of eastern Turkey about 25 km (16 mi) southeast of the city of Elazığ and about 30 km (20 mi) from the headwaters of the Euphrates. The river then flows for 400 km (250 mi) through Southeastern Turkey before becoming part of the Syria-Turkey border. This stretch of 44 km (27 mi) is the only part of the river that is located in Syria. Some of its affluences are Garzan, Anbarçayi, Batman, and the Great and the Little Zab. Close to its confluence with the Euphrates, the Tigris splits into several channels. First, the artificial Shatt al-Hayy branches off, to join the Euphrates near Nasiriya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab, which empties into the Persian Gulf. Etymology The Ancient Greek form ''Euphrátēs'' ( grc, Εὐφράτης, as if from Greek εὖ "good" and φράζω "I announce or declare") was adapted from Old Persian 𐎢𐎳𐎼𐎠𐎬𐎢 ''Ufrātu'', itself from Elamite 𒌑𒅁𒊏𒌅𒅖 ''ú-ip-ra-tu-iš''. The Elamite name is ultimately derived from a name spelt in cuneiform as 𒌓𒄒𒉣 , which read as Sumerian is "Buranuna" and read as Akkadian is "Purattu"; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean the same. In Akkadian the river was called ''Puratt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satrapy Of Armenia
The Satrapy of Armenia (Old Persian: 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴 or 𐎠𐎼𐎷𐎡𐎴𐎹 ), a region controlled by the Orontid dynasty (570–201 BC), was one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC that later became an independent kingdom. Its capitals were Tushpa and later Erebuni. History Origins After the collapse of the Kingdom of Urartu (Ararat), the region was placed under the administration of the Median Empire and the Scythians. Later the territory was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire, which incorporated it as a satrapy, and thus named it the land of "Armina" (in Old Persian; "''Harminuya''" in Elamite; "'' Urashtu''" in Babylonian). Orontid Dynasty The Orontid Dynasty, or known by their native name, Eruandid or Yervanduni, was an Iranian; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; hereditary dynasty that ruled the Armenian satrapy, the successor state to the Iron Age kingdom of Urartu (Ararat). It is suggested that it held dynastic familial linkages t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilicia (satrapy)
Cilicia was a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, with its capital being Tarsus. It was conquered sometime in the 540's BC by Cyrus the Great. Cilicia was a vassal, and although it had a vassal king it had to pay a tribute of 360 horses and 500 talents of silver, according to Herodotus. The fertile Cilician plains were the most important part of the satrapy. There were several sanctuaries that remained more or less independent from Persian rule. Some of these included Castabala, Mazaca, and Mallus. The last vassal king of Cilicia became involved in the civil war between Artaxerxes II and Cyrus the Younger. Having sided with Cyrus the Younger, who was defeated, the king was dethroned and Cilicia became an ordinary satrapy. The second to last satrap (governor) of Cilicia was the Babylonian Mazaios. Shortly afterwards, his successor was expelled by Alexander the Great. The region was later incorporated by the Roman Empire. See also *Cilicia * Çukurova *Adana *Cilician Gates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cappadocia (satrapy)
Cappadocia (from Old Persian 𐎣𐎫𐎱𐎬𐎢𐎣 ''Katpatuka'') was a satrapy (province) of the Achaemenid Empire located in Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). It was used by the Achaemenids to administer the regions beyond the Taurus Mountains and the Euphrates river. The Satrapy The Satrapy belonged to the third tax district and paid an estimated 360 talents a year in tribute. The first satrap (governor) known by name is Ariaramnes, who ruled sometime at the beginning of the reign of the Achaemenid king Darius the Great. His successors are unknown, although , the half brother of Xerxes, commanded the Cappadocians in 480 BCE. During the reign of Artaxerxes II, Cappadocia was divided, becoming Paphlagonia and Cappadocia Proper. Datames (abridged from Datamithra) then became the satrap of southern Cappadocia; he led a revolt and was later assassinated in 362 BCE. The last Achaemenid satrap of Cappadocia was Mithrobuzanes, who died in 334 BCE at the Battle of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)