|
Chants
A chant (from French ', from Latin ', "to sing") is the iterative speaking or singing of words or sounds, often primarily on one or two main pitches called reciting tones. Chants may range from a simple melody involving a limited set of notes to highly complex musical structures, often including a great deal of repetition of musical subphrases, such as Great Responsories and Offertories of Gregorian chant. Chant may be considered speech, music, or a heightened or stylized form of speech. In the Late Middle Ages, some religious chant evolved into song (forming one of the roots of later Western music). Chant as a spiritual practice Chanting (e.g., mantra, sacred text, the name of God/Spirit, etc.) is a commonly used spiritual practice. Like prayer, chanting may be a component of either personal or group practice. Diverse spiritual traditions consider chant a route to spiritual development. Some examples include chant in African, Hawaiian, Native American, Assyrian a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregorian Chant
Gregorian chant is the central tradition of Western plainsong, plainchant, a form of monophony, monophonic, unaccompanied sacred song in Latin (and occasionally Greek language, Greek) of the Roman Catholic Church. Gregorian chant developed mainly in western and central Europe during the 9th and 10th centuries, with later additions and redactions. Although popular legend credits Pope Gregory I with inventing Gregorian chant, scholars believe that he only ordered a compilation of melodies throughout the whole Christian world, after having instructed his emissaries in the Schola cantorum, where the Neume, neumatical notation was perfected, with the result of most of those melodies being a later Carolingian synthesis of the Old Roman chant and Gallican chant. Gregorian chants were organized initially into four, then eight, and finally 12 mode (music), modes. Typical melodic features include a characteristic Ambitus (music), ambitus, and also characteristic intervallic patterns relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Responsory
A responsory or respond is a type of chant in western Christian liturgies. Definition The most general definition of a responsory is any psalm, canticle, or other sacred musical work sung responsorially, that is, with a cantor or small group singing verses while the whole choir or congregation respond with a refrain. However, this article focuses on those chants of the western Christian tradition that have traditionally been designated by the term responsory. In the Roman Rite and rites strongly influenced by it, such as the pre-reformation English rite and the monastic rite of the Rule of St. Benedict, these chants ordinarily follow readings at services of the Divine Office (also called the Liturgy of the Hours); however, they have also been used as processional chants. Structure and performance A responsory has two parts: a respond (or refrain), and a verse. Methods of performance vary, but typically the respond will be begun by the cantor then taken up by the entire choir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantra
A mantra ( ; Pali: ''mantra'') or mantram (Devanagari: मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words (most often in an Indo-Iranian language like Sanskrit or Avestan) believed by practitioners to have religious, magical or spiritual powers. Feuerstein, Georg (2003), ''The Deeper Dimension of Yoga''. Shambala Publications, Boston, MA Some mantras have a syntactic structure and a literal meaning, while others do not. ꣽ, ॐ (Aum, Om) serves as an important mantra in various Indian religions. Specifically, it is an example of a seed syllable mantra ( bijamantra). It is believed to be the first sound in Hinduism and as the sonic essence of the absolute divine reality. Longer mantras are phrases with several syllables, names and words. These phrases may have spiritual interpretations such as a name of a deity, a longing for truth, reality, light, immortality, peace, love, knowledge, and action. Examples of lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics. Hawaii consists of 137 volcanic islands that comprise almost the entire Hawaiian Islands, Hawaiian archipelago (the exception, which is outside the state, is Midway Atoll). Spanning , the state is Physical geography, physiographically and Ethnology, ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania. Hawaii's ocean coastline is consequently the List of U.S. states and territories by coastline, fourth-longest in the U.S., at about . The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niihau, Niihau, Kauai, Kauai, Oahu, Oahu, Molokai, Molokai, Lanai, Lānai, Kahoʻolawe, Kahoolawe, Maui, and Hawaii (island), Hawaii, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans (also called American Indians, First Americans, or Indigenous Americans) are the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of the United States, particularly of the Contiguous United States, lower 48 states and Alaska. They may also include any Americans whose origins lie in any of the indigenous peoples of North or South America. The United States Census Bureau publishes data about "American Indians and Alaska Natives", whom it defines as anyone "having origins in any of the original peoples of North and South America ... and who maintains tribal affiliation or community attachment". The census does not, however, enumerate "Native Americans" as such, noting that the latter term can encompass a broader set of groups, e.g. Native Hawaiians, which it tabulates separately. The European colonization of the Americas from 1492 resulted in a Population history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, precipitous decline in the size of the Native American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perception, perceptual property that allows sounds to be ordered on a frequency-related scale (music), scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melody, melodies. Pitch is a major auditory system, auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration (music), duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective Psychoacoustics, psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their percep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With nearly billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Demographics of Africa, Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including Geography of Africa, geography, Climate of Africa, climate, corruption, Scramble for Africa, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renaissance). Around 1350, centuries of prosperity and growth in Europe came to a halt. A series of famines and Plague (disease), plagues, including the Great Famine of 1315–1317 and the Black Death, reduced the population to around half of what it had been before the calamities. Along with depopulation came social unrest and endemic warfare. Kingdom of France, France and Kingdom of England, England experienced serious peasant uprisings, such as the Jacquerie and the Peasants' Revolt, as well as over a century of intermittent conflict, the Hundred Years' War. To add to the many problems of the period, the unity of the Catholic Church was temporarily shattered by the Western Schism. Collectively, those events ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qiraʼat
In Islam, (pl. ; ) refers to the ways or fashions that the Quran, the holy book of Islam, is recited. More technically, the term designates the different linguistic, lexical, phonetic, morphological and syntactical forms permitted with reciting the Quran. Differences between include varying rules regarding the prolongation, intonation, and pronunciation of words, but also differences in stops, vowels, consonants (leading to different pronouns and verb forms), entire words and even different meanings. However, the variations don't change the overall message or doctrinal meanings of the Qur'an, as the differences are often subtle and contextually equivalent. also refers to the branch of Islamic studies that deals with these modes of recitation. There are ten recognised schools of , each one deriving its name from a noted Quran reciter or "reader" ( pl. or ), such as Nafi‘ al-Madani, Ibn Kathir al-Makki, Abu Amr of Basra, Ibn Amir ad-Dimashqi, Aasim ibn Abi al-Najud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedic Chant
The oral tradition of the Vedas () consists of several pathas, "recitations" or ways of chanting the Vedic mantras. Such traditions of Vedic chant are often considered the oldest unbroken oral tradition in existence, the fixation of the Vedic texts ( samhitas) as preserved dating to roughly the time of Homer (early Iron Age or 800 BC).Scharfe, Ch. 13: "Memorising the Veda", p. 240 ff. UNESCO proclaimed the tradition of Vedic chant a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity on November 7, 2008. Tones Vedic chantings use 4 tones – (middle tone), (lower tone), (higher tone) and (high tone extended). These are usually marked with intuitive marks – an underline for (), a small vertical line above the letter for () and two vertical lines for (). Pathas The various pathas or recitation styles are designed to allow the complete and perfect memorization of the text and its pronunciation, including the Vedic pitch accent. Eleven such ways of reciting th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian People
Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group Indigenous peoples, indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians Assyrian continuity, share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from other Mesopotamian groups, such as the Babylonians, they share in the broader cultural heritage of the Mesopotamian region. Modern Assyrians may culturally self-identify as Terms for Syriac Christians#Syriac identity, Syriacs, Chaldean Catholics, Chaldeans, or Terms for Syriac Christians#Aramean identity, Arameans for religious, geographic, and tribal identification. Assyrians speak various dialects of Neo-Aramaic, specifically those known as Suret and Turoyo, which are among the oldest continuously spoken and written languages in the world. Aramaic was the lingua franca of West Asia for centuries and was the language spoken by historical Jesus, Jesus. It has influenced other languages such as Hebrew an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
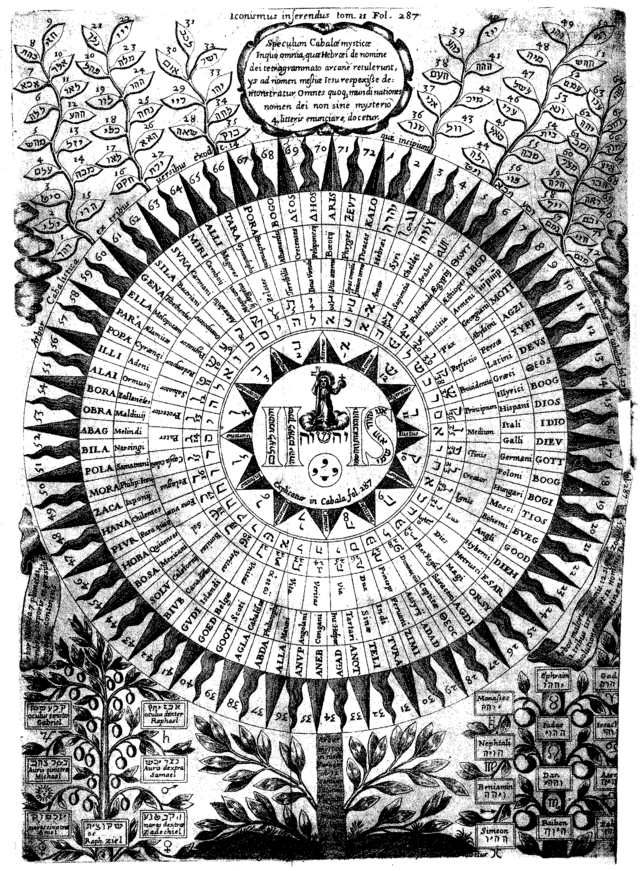
Names Of God
There are various names of God, many of which enumerate the various Quality (philosophy), qualities of a Supreme Being. The English word ''God (word), god'' (and its equivalent in other languages) is used by multiple religions as a noun to refer to different deities, or specifically to the Supreme Being, as denoted in English by the capitalized and uncapitalized terms ''God'' and ''deity, god''. Ancient cognate equivalents for the biblical Hebrew ''Elohim'', one of the most common Names of God in Judaism, names of God in the Bible, include Proto-Semitic language, proto-Semitic ''El (deity), El'', biblical Aramaic ''Names of God in Judaism#Elah, Elah'', and Arabic ''ilah''. The personal or proper name for God in many of these languages may either be distinguished from such property (philosophy), attributes, or homonymic. For example, in Judaism the tetragrammaton is sometimes related to the ancient Hebrew ''Names of God in Judaism#Ehyeh, ehyeh'' ("I Am that I Am, I will be"). It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |