|
Chandrayaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 (, ; ) is a planned third lunar exploration mission by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Following Chandrayaan-2, where a last-minute glitch in the Soft landing (aeronautics), soft landing guidance software led to the failure of the lander's soft landing attempt after a successful orbital insertion, another lunar mission for demonstrating soft landing was proposed. Chandrayaan-3 will be a mission repeat of Chandrayaan-2 but will only include a lander and rover similar to that of Chandrayaan-2. It will not have an orbiter, but its propulsion module will behave like a communications relay satellite. The spacecraft is scheduled to be launched in June 2023. Background In the second phase of the Chandrayaan programme to demonstrate soft landing on the Moon, ISRO launched Chandrayaan-2 onboard a LVM 3 , Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM 3) launch vehicle consisting of an orbiter, a lander and a rover. The lander was scheduled to touchdown on the lunar surface i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrayaan-2
Chandrayaan-2 (, ; ) is the second lunar exploration mission developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), after Chandrayaan-1. It consists of a lunar orbiter, and also included the ''Vikram'' lander, and the ''Pragyan'' lunar rover, all of which were developed in India. The main scientific objective is to map and study the variations in lunar surface composition, as well as the location and abundance of lunar water. The spacecraft was launched on its mission to the Moon from the second launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Andhra Pradesh on 22 July 2019 at 09:13:12 UTC by a GSLV Mark III-M1. The craft reached the Moon's orbit on 20 August 2019 and began orbital positioning manoeuvres for the landing of the ''Vikram'' lander. The lander and the rover were scheduled to land on the near side of the Moon, in the south polar region at a latitude of about 70° south on 6 September 2019 and conduct scientific experiments for one lunar day, which approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikram (spacecraft)
Chandrayaan-2 (, ; ) is the second lunar exploration mission developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), after Chandrayaan-1. It consists of a lunar orbiter, and also included the ''Vikram'' lander, and the ''Pragyan'' lunar rover, all of which were developed in India. The main scientific objective is to map and study the variations in lunar surface composition, as well as the location and abundance of lunar water. The spacecraft was launched on its mission to the Moon from the second launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Andhra Pradesh on 22 July 2019 at 09:13:12 UTC by a GSLV Mark III-M1. The craft reached the Moon's orbit on 20 August 2019 and began orbital positioning manoeuvres for the landing of the ''Vikram'' lander. The lander and the rover were scheduled to land on the near side of the Moon, in the south polar region at a latitude of about 70° south on 6 September 2019 and conduct scientific experiments for one lunar day, which approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrayaan Programme
The Chandrayaan programme (), also known as the Indian Lunar Exploration Programme is an ongoing series of outer space missions by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The programme incorporates lunar orbiter, impactor, soft lander and rover spacecraft. The name of the programme is from Sanskrit ' (). Programme structure The Chandrayaan (Indian Lunar Exploration Programme) programme is a multiple mission programme. , one orbiter with an impactor probe has been sent to the Moon, using ISRO's workhorse PSLV rocket. The second spacecraft consisting of orbiter, soft lander and rover was launched on 22 July 2019, by using a GSLV Mk III rocket. In a podcast from AT, VSSC director S. Somanath stated that there will be a Chandrayaan-3 and more follow up missions in Chandrayaan Program. The Chandrayaan-3 mission is expected to launch in 2023. Phase I: Orbiter and Impactor Chandrayaan-1 Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee announced the Chandrayaan project on course in his In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Polar Exploration Mission
The Lunar Polar Exploration mission (LUPEX), also known as Chandrayaan-4, is a robotic lunar mission concept by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) that would send a lunar rover and lander to explore the south pole region of the Moon no earlier than 2025. JAXA is likely to provide the under-development H3 launch vehicle and the rover, while ISRO would be responsible for the lander. The mission concept is currently in conceptual phase. History ISRO signed an Implementation Arrangement (IA) in December 2017 for pre-phase A, phase A study and completed the feasibility report in March 2018 with Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to explore the polar regions of Moon for water with a joint Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX) that would be launched no earlier than 2025. ISRO and JAXA held the Joint Mission Definition Review (JMDR) in December 2018. By the end of 2019, JAXA concluded its internal Project Readiness Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrayaan-4
The Lunar Polar Exploration mission (LUPEX), also known as Chandrayaan-4, is a robotic lunar mission concept by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) that would send a lunar rover and lander to explore the south pole region of the Moon no earlier than 2025. JAXA is likely to provide the under-development H3 launch vehicle and the rover, while ISRO would be responsible for the lander. The mission concept is currently in conceptual phase. History ISRO signed an Implementation Arrangement (IA) in December 2017 for pre-phase A, phase A study and completed the feasibility report in March 2018 with Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to explore the polar regions of Moon for water with a joint Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX) that would be launched no earlier than 2025. ISRO and JAXA held the Joint Mission Definition Review (JMDR) in December 2018. By the end of 2019, JAXA concluded its internal Project Readiness Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Rovers
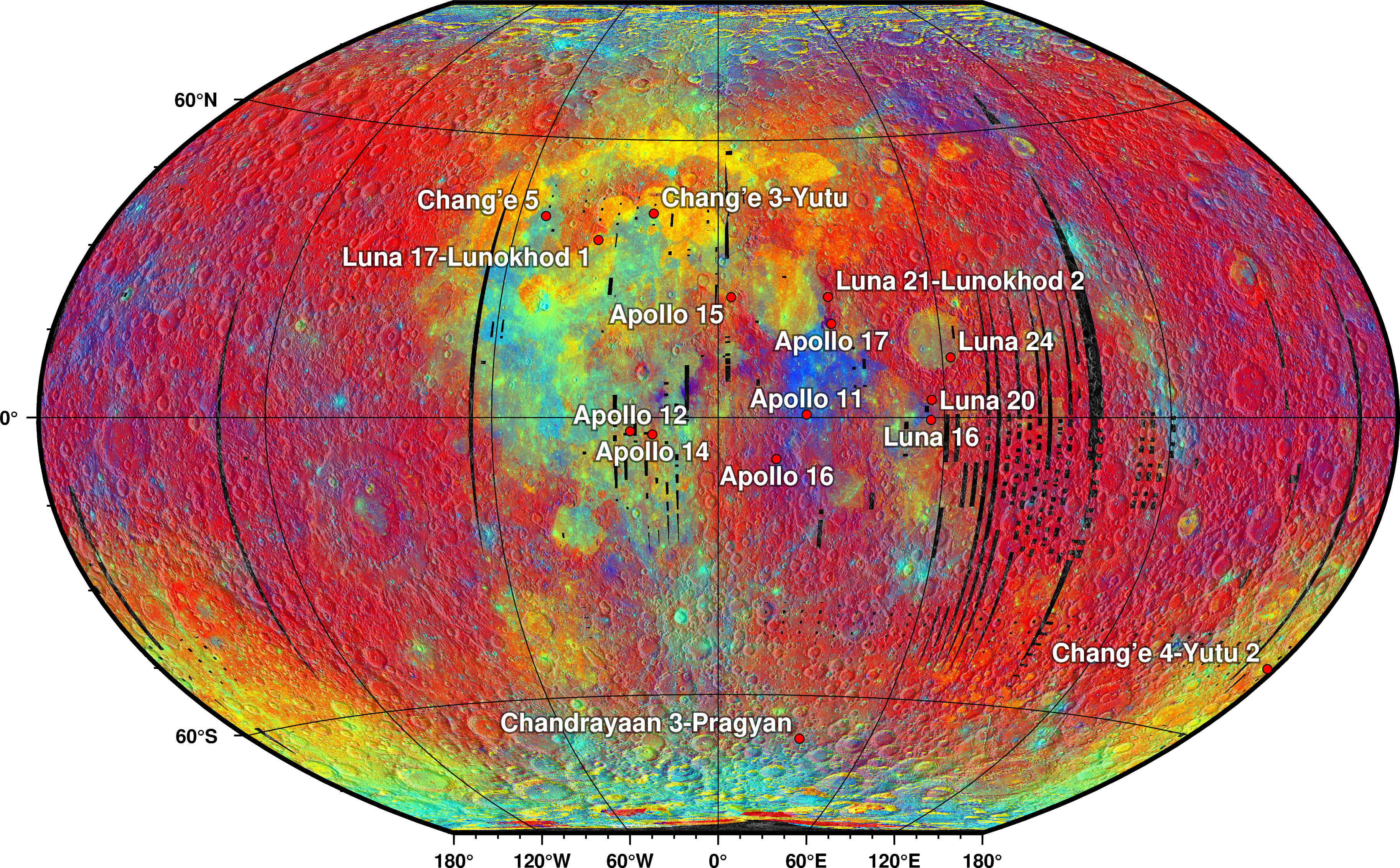
A lunar rover or Moon rover is a space exploration Rover (space exploration), vehicle designed to move across the surface of the Moon. The Apollo Program's Lunar Roving Vehicle was driven on the Moon by members of three American crews, Apollo 15, Apollo 16, 16, and Apollo 17, 17. Other rovers have been partially or fully autonomous robots, such as the Soviet Union's Lunokhods and the Chinese ''Yutu (rover), Yutus''. Three countries have had operating rovers on the Moon: the Soviet Union, the United States and China. An Indian mission failed while Japan and Greece currently have planned missions. Past missions Lunokhod 1 Lunokhod 1 (Луноход) was the first of two polycrystalline-panel-powered robotic lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod program after a previous unsuccessful attempt of a launch probe with Lunokhod programme#Lunokhod 201, Lunokhod 0 (No.201) in 1969. The spacecraft which carried Lunokhod 1 was named Luna 17. The spacec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Space Research Organisation
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman of ISRO acts as the executive of DOS as well. ISRO is India's primary agency for performing tasks related to space-based applications, space exploration and the development of related technologies. It is one of six government space agencies in the world which possess full launch capabilities, deploy cryogenic engines, launch extraterrestrial missions and operate large fleets of artificial satellites. The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by Jawaharlal Nehru under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962, on the urging of scientist Vikram Sarabhai, recognising the need in space research. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969, within DAE. In 1972, the government of India set up a Space Commissi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Rover
A lunar rover or Moon rover is a space exploration vehicle designed to move across the surface of the Moon. The Apollo Program's Lunar Roving Vehicle was driven on the Moon by members of three American crews, Apollo 15, 16, and 17. Other rovers have been partially or fully autonomous robots, such as the Soviet Union's Lunokhods and the Chinese '' Yutus''. Three countries have had operating rovers on the Moon: the Soviet Union, the United States and China. An Indian mission failed while Japan and Greece currently have planned missions. Past missions Lunokhod 1 Lunokhod 1 (Луноход) was the first of two polycrystalline-panel-powered robotic lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod program after a previous unsuccessful attempt of a launch probe with Lunokhod 0 (No.201) in 1969. The spacecraft which carried Lunokhod 1 was named Luna 17. The spacecraft soft-landed on the Moon in the Sea of Rains on November 1970. Lunokhod was the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon Landing
A Moon landing is the arrival of a spacecraft on the surface of the Moon. This includes both crewed and robotic missions. The first human-made object to touch the Moon was the Soviet Union's Luna 2, on 13 September 1959. The United States' Apollo 11 was the first crewed mission to land on the Moon, on 20 July 1969. There were six crewed U.S. landings between 1969 and 1972, and numerous uncrewed landings, with no soft landings happening between 22 August 1976 and 14 December 2013. The United States is the only country to have successfully conducted crewed missions to the Moon, with the last departing the lunar surface in December 1972. All soft landings took place on the near side of the Moon until 3 January 2019, when the Chinese Chang'e 4 spacecraft made the first landing on the far side of the Moon. Uncrewed landings After the unsuccessful attempt by Luna 1 to land on the Moon in 1959, the Soviet Union performed the first hard Moon landing – "hard" meaning the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missions To The Moon
As part of human exploration of the Moon, numerous space missions have been undertaken to study Earth's natural satellite. Of the Moon landings, Luna 2 of the Soviet Union was the first spacecraft to reach its surface successfully, intentionally impacting the Moon on 13 September 1959. In 1966, Luna 9 became the first spacecraft to achieve a controlled soft landing, while Luna 10 became the first mission to enter orbit. Between 1968 and 1972, crewed missions to the Moon were conducted by the United States as part of the Apollo program. Apollo 8 was the first crewed mission to enter orbit in December 1968, and it was followed by Apollo 10 in May 1969. Six missions landed humans on the Moon, beginning with Apollo 11 in July 1969, during which Neil Armstrong became the first person to walk on the Moon. Apollo 13 was intended to land; however, it was restricted to a flyby due to a malfunction aboard the spacecraft. All nine crewed missions returned safely to the Earth. While the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rover (space Exploration)
A rover (or sometimes planetary rover) is a planetary surface exploration device designed to move across the solid surface on a planet or other planetary mass celestial bodies. Some rovers have been designed as land vehicles to transport members of a human spaceflight crew; others have been partially or fully autonomous robots. Rovers are typically created to land on another planet (other than Earth) via a lander (spacecraft), lander-style spacecraft, tasked to collect information about the terrain, and to take crust (geology), crust samples such as dust, soil, rocks, and even liquids. They are essential tools in space exploration. Features Rovers arrive on spacecraft and are used in conditions very distinct from those on the Earth, which makes some demands on their design. Reliability Rovers have to withstand high levels of acceleration, high and low temperatures, pressure, dust, corrosion, cosmic rays, remaining functional without repair for a needed period of time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar South Pole
The lunar south pole is the southernmost point on the Moon, at 90°S. It is of special interest to scientists because of the occurrence of water ice in permanently shadowed areas around it. The lunar south pole region features craters that are unique in that the near-constant sunlight does not reach their interior. Such craters are cold traps that contain a fossil record of hydrogen, water ice, and other volatiles dating from the early Solar System. In contrast, the lunar north pole region exhibits a much lower quantity of similarly sheltered craters. Geography The lunar south pole is located on the center of the polar Antarctic Circle (80°S to 90°S).Lunar South Pole. NASA. 2017. Accessed on 16 July 2019. The lunar south pole has shifted 5 degrees from its original position billions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)

