|
Chamber Of Senators (Bolivia)
The Chamber of Senators ( es, Cámara de Senadores) is the upper house of the Plurinational Legislative Assembly of Bolivia. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in the Political Constitution of the State and others determined by Bolivian laws. The Senate is the legislative body of the country, where each Senator represents the interests of their Departments. The session room is located in the Legislative Palace building in Plaza Murillo. The Senate has 36 seats. Each of the country's nine departments returns four senators elected by proportional representation (using the D'Hondt method The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is a method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in party-list proportional representation systems. It belongs to the class of highe ...). (From 1985 to 2009, the Senate had 27 seats: three seats per department: two from the party or formula that receives the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of The Senate Of Bolivia
The president of the Chamber of Senators of Bolivia is the presiding officer of the upper chamber of the Plurinational Legislative Assembly. The president is currently elected for a one-year term. Below is a list of office-holders.:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Salvador_Romero_Ballivian/publication/324569555_Diccionario_biografico_de_parlamentarios_1979_-_2019/links/5ad5f31e458515c60f552793/Diccionario-biografico-de-parlamentarios-1979-2019.pdf Presidents 1831 to 1868 Presidents after 1878 See also * President of the Chamber of Deputies of Bolivia References {{reflist * Senate, President of the Bolivia , image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ... 1831 establishments in Bolivia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Bolivia
The current Constitution of Bolivia ( es, Constitución Política del Estado; literally, the ''Political Constitution of the State'') came into effect on 7 February 2009 when it was promulgated by President Evo Morales, after being approved in a referendum with 90.24% participation. The referendum was held on 25 January 2009, with the constitution being approved by 61.43% of voters. It is the 17th constitution in the country's history; previous constitutions were enacted in 1826, 1831, 1834, 1839, 1843, 1851, 1861, 1868, 1871, 1878, 1880, 1938, 1945, 1947, 1961, and 1967. The 2009 Constitution defines Bolivia as a unitary plurinational, and secular (rather than a Catholic, as before) state, formally known as the Plurinational State of Bolivia. It calls for a mixed economy of state, private, and communal ownership; restricts private land ownership to a maximum of 5,000 hectares (12,400 acres); and recognizes a variety of autonomies at the local and departmental level. It eleva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Bolivia
The politics of Bolivia takes place in a tree of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the president is head of state, head of government and head of a diverse multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of parliament. Both the Judiciary and the electoral branch are independent of the executive and the legislature. After the 2015 election, 53.3% of the seats in national parliament were held by women, a higher proportion of women than that of the population. History The civil war between the Conservatives and the Liberals ended in 1912 with the latter's victory; a liberal era began that lasted until 1927. A system of public education developed, accompanied by moderate anticlericalism: Catholicism lost its status as the only religion recognized by the State in 1906 and civil marriage was adopted in 1969. Bolivian liberalism, however, is clearly losing its progres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Upper Houses
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900-1924 * National Supermarkets, a defunct American grocery store chain * National String Instrument Corporation, a guitar company formed to manufacture the first reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D'Hondt Method
The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is a method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in party-list proportional representation systems. It belongs to the class of highest-averages methods. The method was first described in 1792 by future U.S. president Thomas Jefferson. It was re-invented independently in 1878 by Belgian mathematician Victor D'Hondt, which is the reason for its two different names. Motivation Proportional representation systems aim to allocate seats to parties approximately in proportion to the number of votes received. For example, if a party wins one-third of the votes then it should gain about one-third of the seats. In general, exact proportionality is not possible because these divisions produce fractional numbers of seats. As a result, several methods, of which the D'Hondt method is one, have been devised which ensure that the parties' seat allocations, which are of whole numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportional Representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divisions (Political party, political parties) of the electorate. The essence of such systems is that all votes cast - or almost all votes cast - contribute to the result and are actually used to help elect someone—not just a Plurality (voting), plurality, or a bare majority—and that the system produces mixed, balanced representation reflecting how votes are cast. "Proportional" electoral systems mean proportional to ''vote share'' and ''not'' proportional to population size. For example, the United States House of Representatives, US House of Representatives has 435 districts which are drawn so roughly equal or "proportional" numbers of people live within each district, yet members of the House are elected in first-past-the-post e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate Of Bolivia
The Chamber of Senators ( es, Cámara de Senadores) is the upper house of the Plurinational Legislative Assembly of Bolivia. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in the Political Constitution of the State and others determined by Bolivian laws. The Senate is the legislative body of the country, where each Senator represents the interests of their Departments. The session room is located in the Legislative Palace building in Plaza Murillo. The Senate has 36 seats. Each of the country's nine departments returns four senators elected by proportional representation (using the D'Hondt method The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is a method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in party-list proportional representation systems. It belongs to the class of highe ...). (From 1985 to 2009, the Senate had 27 seats: three seats per department: two from the party or formula that receives t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
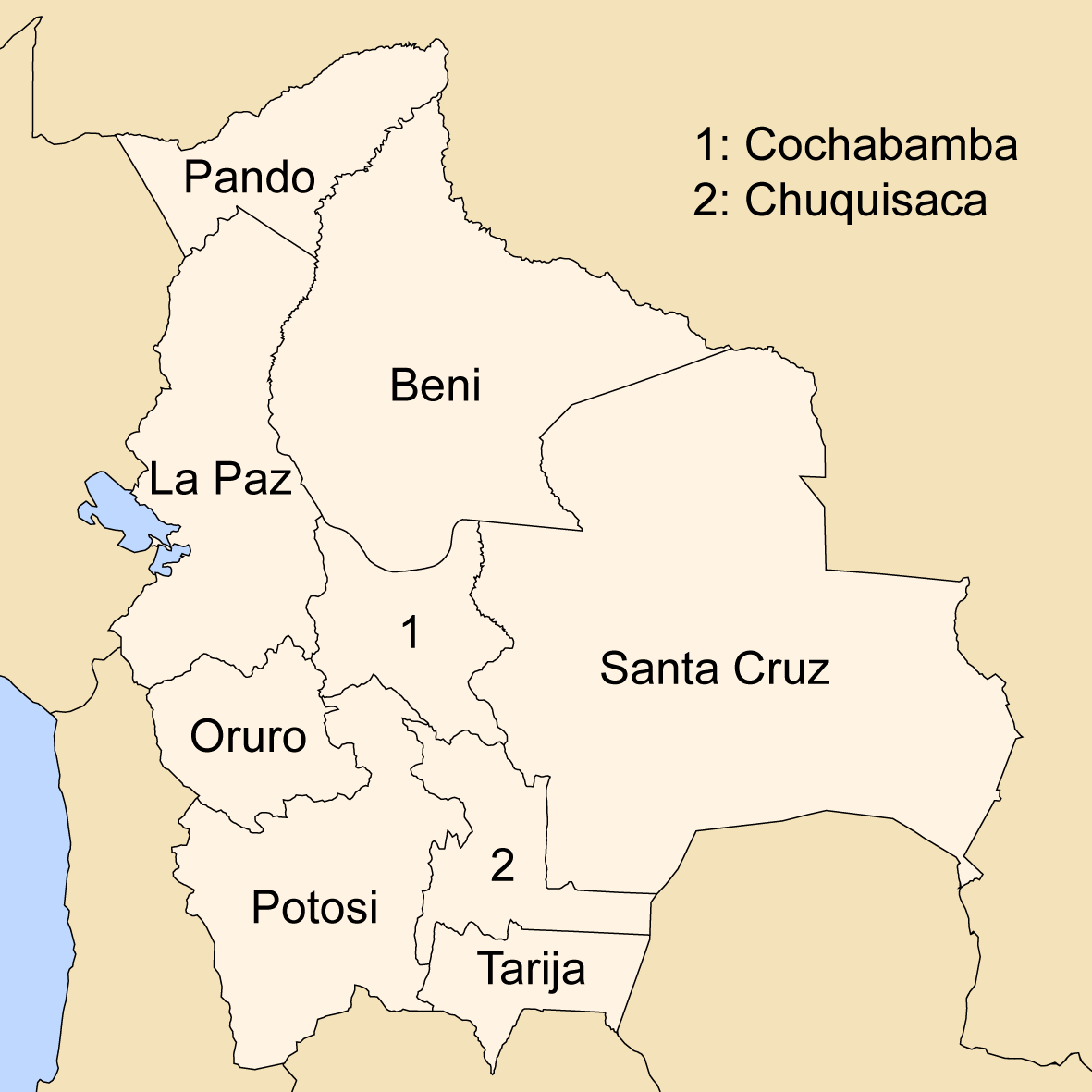
Departments Of Bolivia
Bolivia is a unitary state consisting of nine departments ( es, departamentos). Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia, and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly—a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Each department is represented by four Senators, while Deputies are awarded to each department in proportion to their total population. Out of the nine departments, La Paz was originally the most populous, with 2,706,351 inhabitants as of 2012 but the far eastern department of Santa Cruz has since surpassed it by 2020; Santa Cruz also claims the title as the largest, encompassing . Pando is the least populated, with a population of 110,436. The smallest in area is Tarija, encompassing . Departments Former Departments By population Notes See also * ISO 3166-2:BO, the ISO codes for the departments of Bolivia. * Boliv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Bolivia
The law of Bolivia includes a constitution and a number of codes. Constitution Bolivia has had seventeen constitutions. Sources By 1840, sources of the law of Bolivia included: (1) Acts of the Peru-Bolivian Confederation, prior to the revolution of Bolivia. (2) Acts of the legislature of the Republic. Among these Acts there was a general code of laws, entitled Codigo Santa Cruz. This title is evidently in imitation of the title of Code Napoleon; for Santa Cruz is the name of the general who was elected president of the Republic in 1828; and under his presidency, the Codigo was published. (3) Decisions of the Bolivian courts. (4) Spanish law. (5) Roman civil law. (6) The ancient Peruvian law, or the customs and usages of the country. Legislation The legislature has been called the Congreso Nacional. The gazette is called Gaceta Oficial de Bolivia. List of legislation *Spanish Criminal Code of 1822 *Penal Code of 1834 *Mining Law of 13 October 1880 *Rules for the application o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square patchwork with the (top left to bottom right) diagonals forming colored stripes (green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, white, green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, from top right to bottom left) , other_symbol = , other_symbol_type = Dual flag: , image_coat = Escudo de Bolivia.svg , national_anthem = " National Anthem of Bolivia" , image_map = BOL orthographic.svg , map_width = 220px , alt_map = , image_map2 = , alt_map2 = , map_caption = , capital = La Paz Sucre , largest_city = , official_languages = Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrónico Rodríguez
Andrónico Rodríguez Ledezma (born 11 November 1988) is a Bolivian ''cocalero'' activist, political scientist, politician, and trade unionist serving as president of the Senate since 2020. A member of the Movement for Socialism, he serves as senator for Cochabamba. Rodríguez's lengthy career in the ''cocalero'' union hierarchy saw him serve as general secretary of the 21 September Workers' Center from 2015 to 2016 and as executive of the Mamoré Bulo Bulo Federation from 2016 to 2018, in addition to a multitude of other minor positions. He has served as vice president of the Coordination Committee of the Six Federations of the Tropic of Cochabamba since 2018 and held office as president of the organization from 2019 to 2020 in the absence of the body's longtime leader, Evo Morales. Early life and career Of Quechua descent, Andrónico Rodríguez was born on 11 November 1988 in Sacaba, Cochabamba, the second-youngest of four children born to Carlos Rodríguez and Sinforosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plurinational Legislative Assembly
The Plurinational Legislative Assembly ( es, Asamblea Legislativa Plurinacional) is the national legislature of Bolivia , image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ..., placed in La Paz, the country's seat of government. The assembly is Bicameralism, bicameral, consisting of a lower house (the Chamber of Deputies (Bolivia), Chamber of Deputies or ''Cámara de Diputados)'' and an upper house (the Chamber of Senators (Bolivia), Chamber of Senators, or ''Cámara de Senadores)''. The Vice President of Bolivia also serves as the ''ex officio'' President of the Plurinational Legislative Assembly. Each house elects its own directorate: a President, first and second Vice Presidents, and three or four Secretaries (for the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies, respectively). Each party is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |