|
Chainline
Chainline is the angle of a bicycle chain relative to the centerline of the bicycle frame. A bicycle is said to have perfect chainline if the chain is parallel to the centerline of the frame, which means that the rear sprocket is directly behind the front Crankset#Chainring, chainring. Chainline also refers to the distance between a sprocket and the centerline of the frame. Bicycles without a straight chainline are slightly less efficient due to frictional losses incurred by running the chain at an angle between the front chainring and rear sprocket. This is the main reason that a single-speed bicycle can be more efficient than a Derailleur, derailleur geared bicycle. Single-speed bicycles should have the straightest possible chainline. See also * Bicycle gearing References {{reflist Bicycle drivetrains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chainline (3621138368)
Chainline is the angle of a bicycle chain relative to the centerline of the bicycle frame. A bicycle is said to have perfect chainline if the chain is parallel to the centerline of the frame, which means that the rear sprocket is directly behind the front chainring. Chainline also refers to the distance between a sprocket and the centerline of the frame. Bicycles without a straight chainline are slightly less efficient due to frictional losses incurred by running the chain at an angle between the front chainring and rear sprocket. This is the main reason that a single-speed bicycle can be more efficient than a derailleur geared bicycle. Single-speed bicycles should have the straightest possible chainline. See also * Bicycle gearing Bicycle gearing is the aspect of a bicycle drivetrain that determines the relation between the cadence, the rate at which the rider pedals, and the rate at which the drive wheel turns. On some bicycles there is only one gear and, therefore, .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
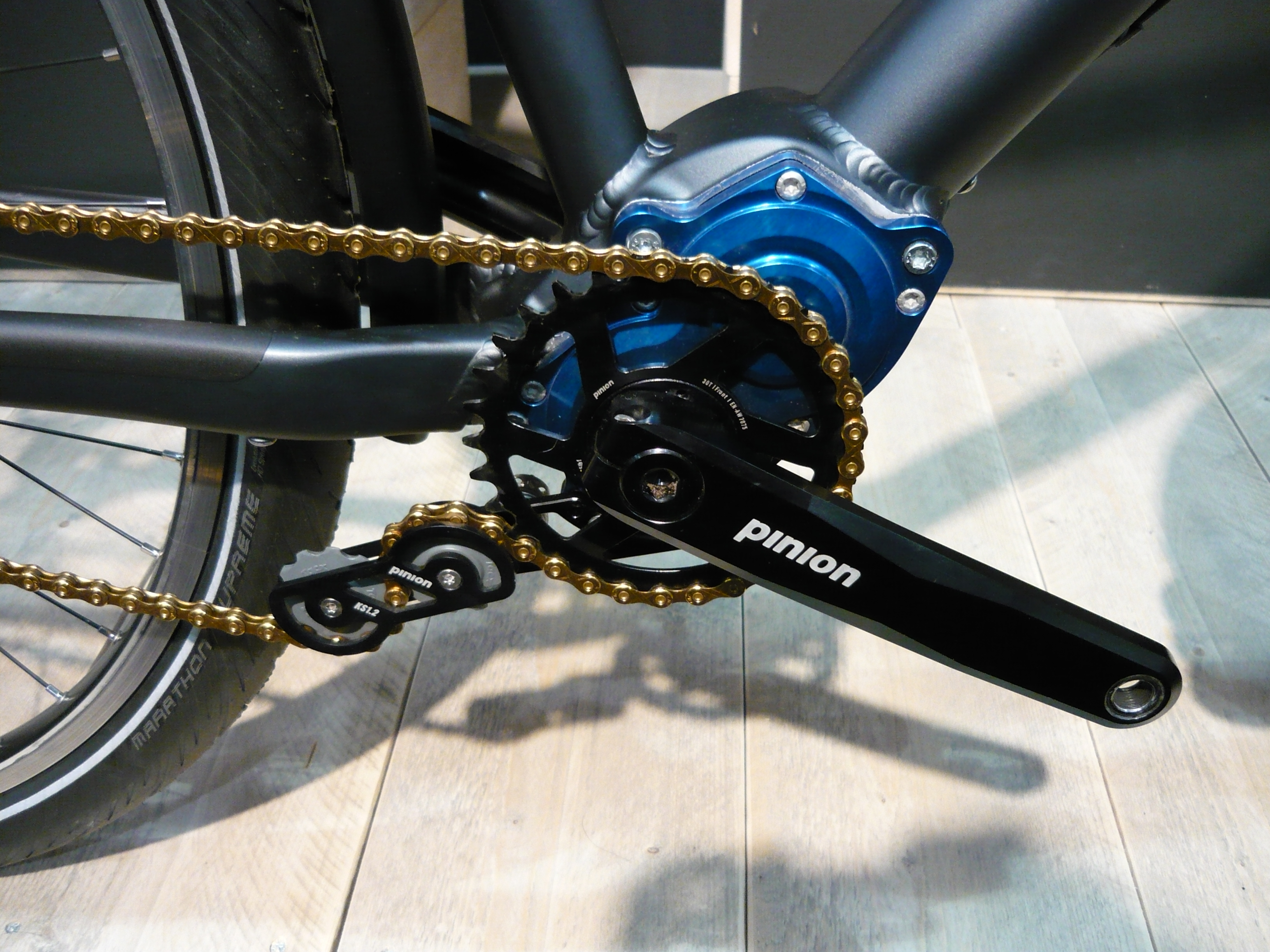
Bicycle Chain
A bicycle chain is a roller chain that transfers power from the pedals to the drive-wheel of a bicycle, thus propelling it. Most bicycle chains are made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but some are nickel-plated to prevent rust, or simply for aesthetics. History Obsolete chain designs previously used on bicycles included the block chain, the skip-link chain, and the Simpson lever chain. The first chains were of a simple, bushing-less design. These had inherent reliability problems and a bit more friction (and mechanical efficiency losses) than modern chains. With these limitations in mind, the Nevoigt brothers, of the German Diamant Bicycle Company, designed the roller chain in 1898, which uses bushings. More recently, the "bushingless roller chain" design has superseded the bushed chain. This design incorporates the bearing surface of the bushing into the inner side plate, with each plate creating half of the bushing. This reduces the number of parts needed to assem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle Frame
A bicycle frame is the main component of a bicycle, onto which wheels and other components are fitted. The modern and most common frame design for an upright bicycle is based on the safety bicycle, and consists of two triangles: a main triangle and a paired rear triangle. This is known as the ''diamond frame''. Frames are required to be strong, stiff and light, which they do by combining different materials and shapes. A frameset consists of the frame and fork of a bicycle and sometimes includes the headset and seat post. Frame builders will often produce the frame and fork together as a paired set. Variations Besides the ubiquitous diamond frame, many different frame types have been developed for the bicycle, several of which are still in common use today. Diamond In the diamond frame, the main "triangle" is not actually a triangle because it consists of four tubes: the head tube, top tube, down tube and seat tube. The rear triangle consists of the seat tube joined by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered transport, human-powered or motorized bicycle, motor-powered assisted, bicycle pedal, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two bicycle wheel, wheels attached to a bicycle frame, frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist. Bicycles were introduced in the 19th century in Europe. By the early 21st century, more than 1 billion were in existence. These numbers far exceed the number of cars, both in total and ranked by the number of individual models produced. They are the principal means of transportation in many regions. They also provide a popular form of recreation, and have been adapted for use as children's toys, Physical fitness, general fitness, military and police applications, courier services, bicycle racing, and bicycle stunts. The basic shape and configuration of a typical Safety bicycle, upright or "safety bicycle", has changed little since the first Chain drive, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
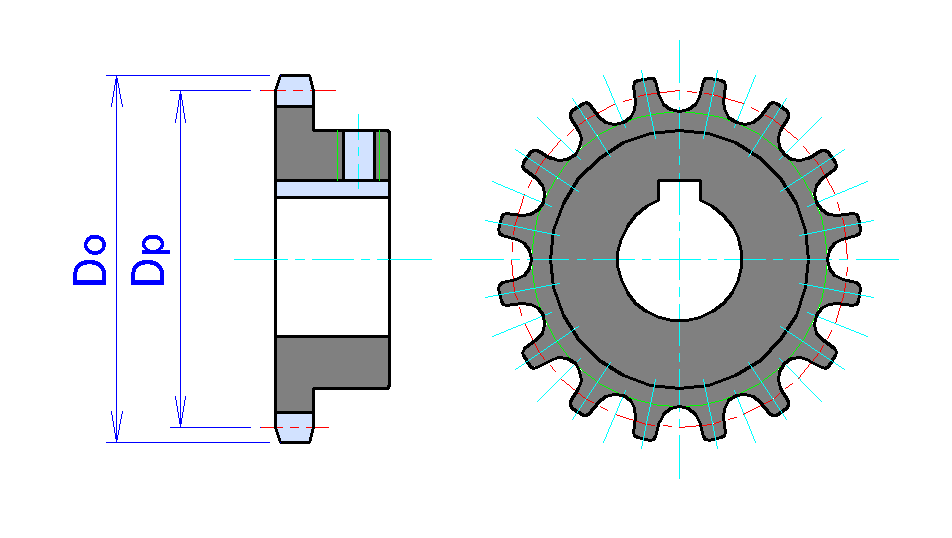
Sprocket
A sprocket, sprocket-wheel or chainwheel is a profiled wheel with teeth that mesh with a chain, track or other perforated or indented material. The name 'sprocket' applies generally to any wheel upon which radial projections engage a chain passing over it. It is distinguished from a gear in that sprockets are never meshed together directly, and differs from a pulley in that sprockets have teeth and pulleys are smooth except for timing pulleys used with toothed belts. Sprockets are used in bicycles, motorcycles, tracked vehicles, and other machinery either to transmit rotary motion between two shafts where gears are unsuitable or to impart linear motion to a track, tape etc. Perhaps the most common form of sprocket may be found in the bicycle, in which the pedal shaft carries a large sprocket-wheel, which drives a chain, which, in turn, drives a small sprocket on the axle of the rear wheel. Early automobiles were also largely driven by sprocket and chain mechanism, a practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankset
The crankset (in the US) or chainset (in the UK), is the component of a bicycle drivetrain that converts the reciprocating motion of the rider's legs into rotational motion used to drive the chain or belt, which in turn drives the rear wheel. It consists of one or more sprockets, also called ''chainrings'' or ''chainwheels'' attached to the '' cranks'', ''arms'', or ''crankarms'' to which the pedals attach. It is connected to the rider by the pedals, to the bicycle frame by the bottom bracket, and to the rear sprocket, cassette or freewheel via the chain. Parts Cranks The two ''cranks'', one on each side and usually mounted 180° apart, connect the bottom bracket axle to the pedals. Lengths Bicycle cranks can vary in length to accommodate different sized riders and different types of cycling. Crank length is measured from the center of the pedal spindle to the center of the bottom bracket spindle or axle. The larger bicycle component manufacturers typically offe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-speed Bicycle
A single-speed bicycle is a type of bicycle with a single gear ratio. These bicycles are without derailleur gears, hub gearing or other methods for varying the gear ratio of the bicycle. There are many types of modern single speed bicycles; BMX bicycles, most bicycles designed for children, cruiser type bicycles, classic commuter bicycles, unicycles, bicycles designed for track racing, fixed-gear road bicycles, and single-speed mountain and cyclocross bikes. Although most fixed-gear bicycles (fixies) are technically single speed, the term single-speed generally refers to a single gear ratio bicycle with a freewheel mechanism to allow it to coast. Vis-à-vis multi-speed bicycles Advantages A single-speed bicycle is generally cheaper, lighter, and mechanically simpler than its multi-geared equivalent. Without derailleurs or other gearing systems, there are fewer parts on the bicycle that require maintenance, making this type of cycle useful for city commuting in all wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derailleur
Shimano 600 front derailleur (1980) A derailleur is a variable-ratio bicycle gearing system consisting of a chain, multiple sprockets of different sizes, and a mechanism to move the chain from one sprocket to another. Modern front and rear derailleurs typically consist of a moveable chain-guide that is operated remotely by a Bowden cable attached to a shifter mounted on the down tube, handlebar stem, or handlebar. When a rider operates the lever while pedalling, the change in cable tension moves the chain-guide from side to side, "derailing" the chain onto different sprockets. Etymology ''Dérailleur'' is a French word, derived from the derailment of a train from its tracks. Its first recorded use was 1930. History A modern road bicycle drivetrain with front and rear derailleurs Various derailleur systems were designed and built in the late 19th century. One example is the Protean two-speed derailleur available on the Whippet safety bicycle. The French bicycle t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle Gearing
Bicycle gearing is the aspect of a bicycle drivetrain that determines the relation between the cadence, the rate at which the rider pedals, and the rate at which the drive wheel turns. On some bicycles there is only one gear and, therefore, the gear ratio is fixed, but most modern bicycles have multiple gears and thus multiple gear ratios. A shifting mechanism allows selection of the appropriate gear ratio for efficiency or comfort under the prevailing circumstances: for example, it may be comfortable to use a high gear when cycling downhill, a medium gear when cycling on a flat road, and a low gear when cycling uphill. Different gear ratios and gear ranges are appropriate for different people and styles of cycling. A cyclist's legs produce power optimally within a narrow pedalling speed range, or cadence. Gearing can be optimized to use this narrow range as efficiently as possible. As in other types of transmissions, the gear ratio is closely related to the mechanical a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)