|
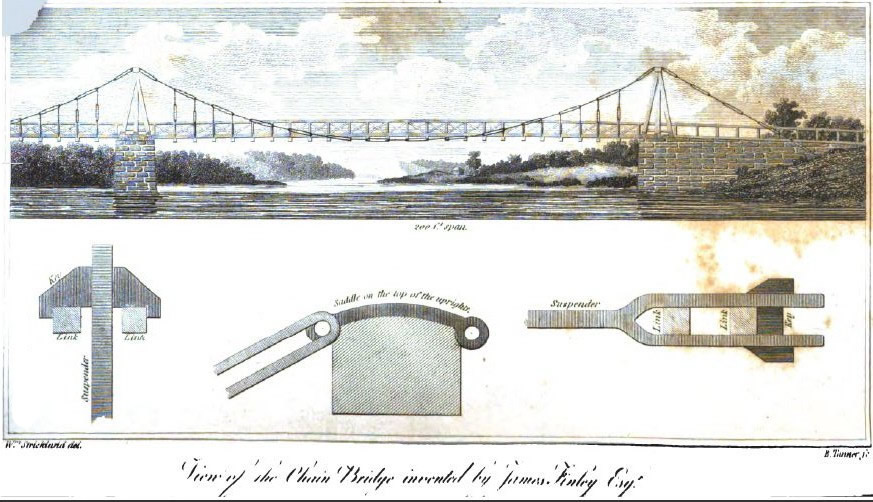
Chain Bridge At Falls Of Schuylkill
Chain Bridge at Falls of Schuylkill was an 1808 iron-chain suspension bridge built across the Schuylkill River, north of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Designed by inventor James Finley, it became the model for his later chain suspension bridges. It collapsed in 1816 under a heavy load of snow. History The Chain Bridge had two spans: an eastern one of 200 feet (60.96 m), and a western one of about 100 feet (30.48 m). The bridge's chain cables were carried over paired A-frame wooden towers on its east and west abutments, and a third pair of towers atop a stone pier built in the river. Its chains were made of 1.5-inch-square (3.8 cm) iron bar wrought into links of between 8 and 12 feet (2.44 and 3.66 m) in length. These were used for both the cables and the vertical suspenders. The suspenders were attached to 10-by-5-inch (25.4 cm x 12.7 cm) wooden joists spaced 10 feet (3 m) apart, and covered by a 2.5-inch-thick (6.4 cm) wooden deck that was 18 feet (5.5 m) wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Strickland (architect)
William Strickland (November 1788 – April 6, 1854), was a noted architect and civil engineer in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and Nashville, Tennessee. A student of Benjamin Latrobe and mentor to Thomas Ustick Walter, Strickland helped establish the Greek Revival movement in the United States. A pioneering engineer, he wrote a seminal book on railroad construction, helped build several early American railroads, and designed the first ocean breakwater in the Western Hemisphere. He was elected as a member of the American Philosophical Society in 1820. Life and career Strickland was born in the Navesink section of Middletown Township, New Jersey, and moved with his family to Philadelphia as a child. In his youth, he was a landscape painter, illustrator for periodicals, theatrical scene painter, engraver, and pioneer aquatintist. His Greek Revival designs drew much inspiration from the plates of ''The Antiquities of Athens''. Strickland and Latrobe competed to design the Second Bank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurel Hill Cemetery
Laurel Hill Cemetery is a historic rural cemetery in the East Falls neighborhood of Philadelphia. Founded in 1836, it was the second major rural cemetery in the United States after Mount Auburn Cemetery in Boston, Massachusetts. The cemetery is in size and overlooks the Schuylkill River. The cemetery grew to its current size through the purchase of four land parcels between 1836 and 1861. It contains over 11,000 family lots and more than 33,000 graves, including many adorned with grand marble and granite funerary monuments, elaborately sculpted hillside tombs and mausoleums., Aaron V. Wunsch, National Park Service, 1998. It is affiliated with West Laurel Hill Cemetery in nearby Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania and is an accredited arboretum with over 6,000 trees and shrubs representing 700 species. In 1977, Laurel Hill Cemetery was listed on the National Register of Historic Places and in 1998, became the first cemetery in the United States to be designated a National Historic Landm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Road Bridges In Pennsylvania
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation. There are many types of roads, including parkways, avenues, controlled-access highways (freeways, motorways, and expressways), tollways, interstates, highways, thoroughfares, and local roads. The primary features of roads include lanes, sidewalks (pavement), roadways (carriageways), medians, shoulders, verges, bike paths (cycle paths), and shared-use paths. Definitions Historically many roads were simply recognizable routes without any formal construction or some maintenance. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) defines a road as "a line of communication (travelled way) using a stabilized base other than rails or air strips open to public traffic, primarily for the use of road motor vehicles running on their own wheels", which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demolished Bridges In The United States
Demolition (also known as razing, cartage, and wrecking) is the science and engineering in safely and efficiently tearing down of buildings and other artificial structures. Demolition contrasts with deconstruction, which involves taking a building apart while carefully preserving valuable elements for reuse purposes. For small buildings, such as houses, that are only two or three stories high, demolition is a rather simple process. The building is pulled down either manually or mechanically using large hydraulic equipment: elevated work platforms, cranes, excavators or bulldozers. Larger buildings may require the use of a wrecking ball, a heavy weight on a cable that is swung by a crane into the side of the buildings. Wrecking balls are especially effective against masonry, but are less easily controlled and often less efficient than other methods. Newer methods may use rotational hydraulic shears and silenced rock-breakers attached to excavators to cut or break through wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Bridges
A chain is a wikt:series#Noun, serial assembly of connected pieces, called links, typically made of metal, with an overall character similar to that of a rope in that it is flexible and curved in compression (physics), compression but line (geometry), linear, rigid, and load-bearing in tension (physics), tension. A chain may consist of two or more links. Chains can be classified by their design, which can be dictated by their use: * Those designed for lifting, such as when used with a Hoist (device), hoist; for pulling; or for securing, such as with a bicycle lock, have links that are torus shaped, which make the chain flexible in two dimensions (the fixed third dimension being a chain's length). Small chains serving as jewellery are a mostly decorative analogue of such types. * Those designed for transferring power in machines have links designed to mesh with the teeth of the sprockets of the machine, and are flexible in only one dimension. They are known as roller chains, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridges In Philadelphia
Transportation in Philadelphia involves the various modes of transport within the city and its required infrastructure. In addition to facilitating intracity travel, Philadelphia's transportation system connects Philadelphia to towns of its metropolitan area and surrounding areas within the Northeast megalopolis. The city is crossed by the Delaware Expressway (Interstate 95 or I-95) and the Schuylkill Expressway (I-76), which are the principal thoroughfares for intercity traffic. The Vine Street Expressway ( I-676) travels between I-76 and I-95 in Center City Philadelphia, and the Roosevelt Boulevard (U.S. Route 1) carries crosstown traffic in northern Philadelphia. Philadelphia's public transit system is mainly operated by the Southeast Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA), which maintains an extensive system utilizing buses, rapid transit, commuter rail, trolleys, and the Philadelphia trackless trolley (trolleybus) system. The main rail station of Philadelphia is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suspension Bridges In Pennsylvania
Suspension or suspended may refer to: Science and engineering * Suspension (topology), in mathematics * Suspension (dynamical systems), in mathematics * Suspension of a ring, in mathematics * Suspension (chemistry), small solid particles suspended in a liquid **Colloidal suspension * Cell suspension or suspension culture, in biology * Suspension (mechanics), system allowing a machine to move smoothly with reduced shock * The superstructure of a suspension bridge * Suspensory behavior, arboreal locomotion of primates * Magnetic suspension, a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields * Car suspension Temporary revocation of privileges * Suspension (punishment), temporary exclusion as a punishment ** Suspension from the UK parliament ** Suspension (Catholic canonical penalty) * Suspension of driving privileges ("suspended driver's license") * Administrative License Suspension (ALS), US, driving license suspension without a court hearing Enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridges Completed In 1808
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridges Over The Schuylkill River
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Crossings Of The Schuylkill River
This is a list of bridges and other crossings of the Schuylkill River, from the Delaware River upstream to the source. All locations are in Pennsylvania. Crossings See also * * * References {{Reflist Schuylkill River The Schuylkill River ( , ) is a river running northwest to southeast in eastern Pennsylvania. The river was improved by navigations into the Schuylkill Canal, and several of its tributaries drain major parts of Pennsylvania's Coal Region. It fl ... Schuylkill * Schuylkill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spider Bridge At Falls Of Schuylkill
Spider Bridge at Falls of Schuylkill was an iron-wire footbridge erected in 1816 over the Schuylkill River, north of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Though a modest and temporary structure, it is thought to have been the first wire-cable suspension bridge in the world. Chain bridge The Chain Bridge at Falls of Schuylkill, an iron-chain suspension bridge designed by James Finley (engineer), James Finley, was built at East Falls, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, Falls of Schuylkill in 1808. It was among the earliest suspension bridges erected in the United States. To supply materials for its construction, ironmakers Josiah White and Erskine Hazard built a rolling mill along the river near its eastern abutment. Although Finley patented his Falls of Schuylkill bridge and publicized it widely, it was not a success: "Part of the superstructure broke down in September, 1810, while a drove of cattle was crossing it, and in January, 1816, the bridge fell down, occasioned by the great weight of sno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Museum Of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 Fifth Avenue, along the Museum Mile on the eastern edge of Central Park on Manhattan's Upper East Side, is by area one of the world's largest art museums. The first portion of the approximately building was built in 1880. A much smaller second location, The Cloisters at Fort Tryon Park in Upper Manhattan, contains an extensive collection of art, architecture, and artifacts from medieval Europe. The Metropolitan Museum of Art was founded in 1870 with its mission to bring art and art education to the American people. The museum's permanent collection consists of works of art from classical antiquity and ancient Egypt, paintings, and sculptures from nearly all the European masters, and an extensive collection of American and modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |