|
CfA2 Great Wall
The Great Wall (also called Coma Wall), sometimes specifically referred to as the CfA2 Great Wall, is an immense galaxy filament. It is one of the largest known superstructures in the observable universe. This structure was discovered c. 1989 by a team of American astronomers led by Margaret J. Geller and John Huchra while analyzing data gathered by the second CfA Redshift Survey of the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA). Characteristics According to Chown, "The filament is about 300 million lightyears wide, 15 million lightyears thick and it snakes for at least 500 million lightyears across the Universe." Components It was discovered in 1989 by Margaret Geller and John Huchra based on redshift survey data from the CfA Redshift Survey. It is not known how much further the wall extends due to the light absorption in the plane of the Milky Way The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Galaxy Filament
In cosmology, galaxy filaments are the largest known structures in the universe, consisting of walls of galactic superclusters. These massive, thread-like formations can commonly reach 50 to 80 megaparsecs ()—with the largest found to date being the Hercules-Corona Borealis Great Wall at around in length—and form the boundaries between voids. Due to the accelerating expansion of the universe, the individual clusters of gravitationally bound galaxies that make up galaxy filaments are moving away from each other at an accelerated rate; in the far future they will dissolve. Galaxy filaments form the cosmic web and define the overall structure of the observable universe. Discovery Discovery of structures larger than superclusters began in the late 1980s. In 1987, astronomer R. Brent Tully of the University of Hawaii's Institute of Astronomy identified what he called the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex. The CfA2 Great Wall was discovered in 1989, followed by the Sloa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lambda-CDM Model
The Lambda-CDM, Lambda cold dark matter, or ΛCDM model is a mathematical model of the Big Bang theory with three major components: # a cosmological constant, denoted by lambda (Λ), associated with dark energy; # the postulated cold dark matter, denoted by CDM; # ordinary matter. It is the current ''standard model'' of Big Bang cosmology, as it is the simplest model that provides a reasonably good account of: * the existence and structure of the cosmic microwave background; * the large-scale structure in the distribution of galaxies; * the observed abundances of hydrogen (including deuterium), helium, and lithium; * the accelerating expansion of the universe observed in the light from distant galaxies and supernovae. The model assumes that general relativity is the correct theory of gravity on cosmological scales. It emerged in the late 1990s as a concordance cosmology, after a period when disparate observed properties of the universe appeared mutually inconsistent, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Great Wall Filament
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements * Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size * Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent People * List of people known as "the Great" * Artel Great (born 1981), American actor * Great Osobor (born 2002), Spanish-born British basketball player Other uses * ''Great'' (1975 film), a British animated short about Isambard Kingdom Brunel * ''Great'' (2013 film), a German short film * Great (supermarket), a supermarket in Hong Kong * GReAT, Graph Rewriting and Transformation, a Model Transformation Language * Gang Resistance Education and Training, or GREAT, a school-based and police officer-instructed program * Global Research and Analysis Team (GReAT), a cybersecurity team at Kaspersky Lab *'' Great!'', a 2018 EP by Momoland *Great! TV, British TV channel group * ''The Great'' (TV series), an American comedy-drama See also * * * * * The Great (other) The Great is the moniker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Astronomical Objects Discovered In 1989
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptians, Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sloan Great Wall
The Sloan Great Wall (SGW) is a cosmic structure formed by a giant wall of galaxies (a galaxy filament). Its discovery was announced from Princeton University on October 20, 2003, by J. Richard Gott III, Mario Jurić, and their colleagues, based on data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Size The wall measures in length, located approximately one billion light-years away. In the sky, it is located within the region of the constellations Corvus, Hydra and Centaurus. It is approximately 1/60 of the diameter of the observable universe, making it the sixth largest known object after the large quasar groups Clowes-Campusano LQG, U1.11, Huge-LQG, the Giant GRB Ring and the galaxy filament Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall (Her-CrB GW), respectively. The Sloan Great Wall is between 1.8–2.7 times longer than the CfA2 Great Wall of galaxies (discovered by Margaret Geller and John Huchra of Harvard University in 1989). It also contains several galactic superclusters, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Redshift Survey
In astronomy, a redshift survey is a astronomical surveys, survey of a section of the sky to measure the redshift of astronomical objects: usually galaxies, but sometimes other objects such as galaxy clusters or quasars. Using Hubble's law, the redshift can be used to estimate the distance of an object from Earth. By combining redshift with angular position data, a redshift survey maps the 3D distribution of matter within a field of the sky. These observations are used to measure detailed statistical properties of the Large-scale structure of the cosmos, large-scale structure of the universe. In conjunction with observations of early structure in the cosmic microwave background, these results can place strong constraints on cosmological parameters such as the average matter density and the Hubble constant. Generally the construction of a redshift survey involves two phases: first the selected area of the sky is imaged with a wide-field telescope, then galaxies brighter than a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Observable Universe
The observable universe is a Ball (mathematics), spherical region of the universe consisting of all matter that can be observation, observed from Earth; the electromagnetic radiation from these astronomical object, objects has had time to reach the Solar System and Earth since the beginning of the metric expansion of space, cosmological expansion. Assuming the universe is isotropy, isotropic, the distance to the edge of the observable universe is equidistant, the same in every direction. That is, the observable universe is a sphere, spherical region centered on the observer. Every location in the universe has its own observable universe, which may or may not overlap with the one centered on Earth. The word ''observable'' in this sense does not refer to the capability of modern technology to detect light or other information from an object, or whether there is anything to be detected. It refers to the physical limit created by the speed of light itself. No signal can travel faster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Big Ring
The Big Ring is a ring-shaped large-scale structure formed by galaxies and galaxy clusters near the constellation Boötes with a diameter of 1.3 billion light years, located 9.2 billion light years away. It was discovered in 2024 by Alexia Lopez, a PhD student at the University of Central Lancashire. In 2021, she discovered the Giant Arc, a similar structure located in the same region. It is a significant astronomical discovery, as it challenges the Cosmological Principle. Currently, there is no known cause for its formation within our current understanding of the universe. The Big Ring is the seventh large structure discovered that contradicts the understanding of smooth matter distribution across the largest scale of the universe. Characteristics The Big Ring is composed of numerous galaxies and galaxy clusters that form a continuous, almost perfect ring-like pattern in space. With its diameter of 1.3 billion light years and a circumference of 4 billion light years, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Giant Arc
The Giant Arc is a large-scale structure discovered in June 2021 that spans 3.3 billion light years. This structure of galaxies exceeds the 1.2 billion light year size threshold of the currently accepted model of cosmology, potentially challenging the cosmological principle that at large enough scales the universe is considered to be the same in every place (homogeneous) and in every direction (isotropic). The Giant Arc consists of galaxies and galactic clusters, as well as gas and dust. It is located 9.2 billion light-years away at redshift ~0.8, and it stretches across roughly 1/15th of the radius of the observable universe. It was discovered using data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey by the team of Alexia M. Lopez, a doctoral candidate in cosmology at the University of Central Lancashire. The Giant Arc was discovered using a new method for finding large-scale structure by looking for intervening Mg II absorption lines in background quasars. It consists of two parts, GA- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cosmic String
Cosmic strings are hypothetical 1-dimensional topological defects which may have formed during a symmetry-breaking phase transition in the early universe when the topology of the vacuum manifold associated to this symmetry breaking was not simply connected. In less formal terms, they are hypothetical long, thin defects in the fabric of space that might have formed according to string theory. They might have formed in the early universe during a process where certain symmetries were broken. Their existence was first contemplated by the theoretical physicist Tom Kibble in the 1970s. The formation of cosmic strings is somewhat analogous to the imperfections that form between crystal grains in solidifying liquids, or the cracks that form when water freezes into ice. The phase transitions leading to the production of cosmic strings are likely to have occurred during the earliest moments of the universe's evolution, just after cosmological inflation, and are a fairly generic predic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
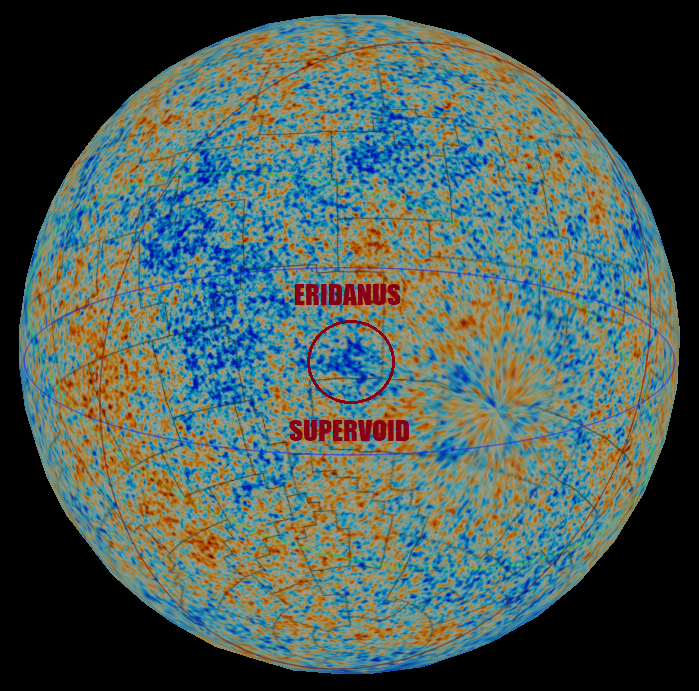
CMB Cold Spot
The CMB Cold Spot or WMAP Cold Spot is a region of the sky seen in microwaves that has been found to be unusually large and cold relative to the expected properties of the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR). The "Cold Spot" is approximately 70 μK (0.00007 K) colder than the average CMB temperature (approximately 2.7 K), whereas the root mean square of typical temperature variations is only 18 μK.After the dipole anisotropy, which is due to the Doppler shift of the microwave background radiation due to our peculiar velocity relative to the comoving cosmic rest frame, has been subtracted out. This feature is consistent with the Earth moving at some 627 km/s towards the constellation Virgo. At some points, the "cold spot" is 140 μK colder than the average CMB temperature. The radius of the "cold spot" subtends about 5°; it is centered at the galactic coordinate , ( equatorial: ''α'' = , ''δ'' = ). It is, therefore, in the South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall
The Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall (HCB) or simply the Great Wall is a galaxy filament that is the List of largest cosmic structures, largest known structure in the observable universe, measuring approximately 10 billion Light-year, light-years in length (the observable universe is about 93 billion light-years in diameter). This massive superstructure is a region of the sky seen in the data set mapping of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) that has been found to have a concentration of similarly distanced GRBs that is unusually higher than the expected average distribution. It was discovered in early November 2013 by a team of American and Hungarian astronomers led by István Horváth, Jon Hakkila and Zsolt Bagoly while analyzing data from the Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission, together with other data from ground-based telescopes. It is the largest known formation in the universe, exceeding the size of the Huge-LQG by about a factor of two. The overdensity lies at the Second, Third and F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |