|
Ceyuan Haijing
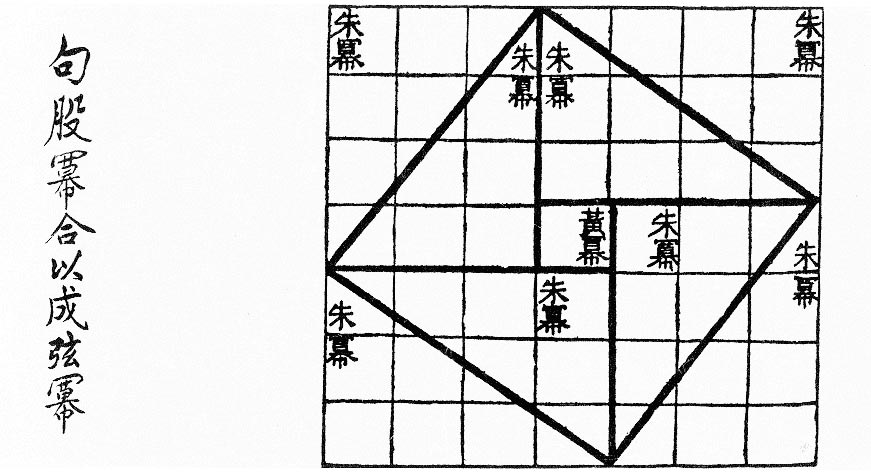
''Ceyuan haijing'' () is a treatise on solving geometry problems with the algebra of Tian yuan shu written by the mathematician Li Zhi in 1248 in the time of the Mongol Empire. It is a collection of 692 formula and 170 problems, all derived from the same master diagram of a round town inscribed in a right triangle and a square. They often involve two people who walk on straight lines until they can see each other, meet or reach a tree or pagoda in a certain spot. It is an algebraic geometry book, the purpose of book is to study intricated geometrical relations by algebra. Majority of the geometry problems are solved by polynomial equations, which are represented using a method called tian yuan shu, "coefficient array method" or literally "method of the celestial unknown". Li Zhi is the earliest extant source of this method, though it was known before him in some form. It is a positional system of rod numerals to represent polynomial equations. ''Ceyuan haijing'' was first introd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Mathematics
Mathematics in China emerged independently by the 11th century BCE. The Chinese independently developed a real number system that includes significantly large and negative numbers, more than one numeral system ( base 2 and base 10), algebra, geometry, number theory and trigonometry. Since the Han Dynasty, as diophantine approximation being a prominent numerical method, the Chinese made substantial progress on polynomial evaluation. Algorithms like regula falsi and expressions like continued fractions are widely used and have been well-documented ever-since. They deliberately find the principal ''n''th root of positive numbers and the roots of equations. The major texts from the period, ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'' and the ''Book on Numbers and Computation'' gave detailed processes for solving various mathematical problems in daily life. All procedures were computed using a counting board in both texts, and they included inverse elements as well as Euclidean divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Wenjun
Wu Wenjun ( zh, s=吴文俊; 12 May 1919 – 7 May 2017), also commonly known as Wu Wen-tsün, was a Chinese mathematician, historian, and writer. He was an academician at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), best known for the Wu's method of characteristic set. Biography Wu's Ancestral home (China), ancestral hometown was Jiashan, Zhejiang. He was born in Shanghai and graduated from Shanghai Jiao Tong University in 1940. In 1945, Wu taught several months at Zhijiang Campus, Zhejiang University, Hangchow University (later merged into Zhejiang University) in Hangzhou. In 1947, he went to France for further study at the University of Strasbourg. In 1949, he received his PhD, for his thesis ''Sur les classes caractéristiques des structures fibrées sphériques'', written under the direction of Charles Ehresmann. Afterwards, he did some work in Paris with René Thom and discovered the Wu class and Wu formula in algebraic topology. In 1951 he was appointed to a post at Peking U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length Of Line Segments
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the International System of Units (SI) system the base unit for length is the metre. Length is commonly understood to mean the most extended dimension of a fixed object. However, this is not always the case and may depend on the position the object is in. Various terms for the length of a fixed object are used, and these include height, which is vertical length or vertical extent, and width, breadth or depth. Height is used when there is a base from which vertical measurements can be taken. Width or breadth usually refer to a shorter dimension when length is the longest one. Depth is used for the third dimension of a three dimensional object. Length is the measure of one spatial dimension, whereas area is a measure of two dimensions (length square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miscellaneous Formula
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segment Numbers
Segment or segmentation may refer to: Biology *Segmentation (biology), the division of body plans into a series of repetitive segments **Segmentation in the human nervous system *Internodal segment, the portion of a nerve fiber between two Nodes of Ranvier *Segment, in fruit anatomy, a section of a citrus fruit *Parts of a genome, especially in virology Computing and communications *Memory segmentation, the division of computer memory into segments **Segment descriptor **Data segment **Code segment *Image segmentation, the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple segments * Time-series segmentation, the process of partitioning a time-series into a sequence of discrete segments in order to reveal the underlying properties of its source *Network segmentation, splitting a computer network into subnetworks **Network segment *Packet segmentation, the process of dividing a data packet into smaller units **Segmentation and reassembly *TCP segmentation, the process of dividin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definitions And Formula
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Definitions can be classified into two large categories: intensional definitions (which try to give the sense of a term), and extensional definitions (which try to list the objects that a term describes).Lyons, John. "Semantics, vol. I." Cambridge: Cambridge (1977). p.158 and on. Another important category of definitions is the class of ostensive definitions, which convey the meaning of a term by pointing out examples. A term may have many different senses and multiple meanings, and thus require multiple definitions. In mathematics, a definition is used to give a precise meaning to a new term, by describing a condition which unambiguously qualifies what a mathematical term is and is not. Definitions and axioms form the basis on which all of modern mathematics is to be constructed. Basic terminology In modern usage, a definition is something, typically expressed in words, that attac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counting Rods
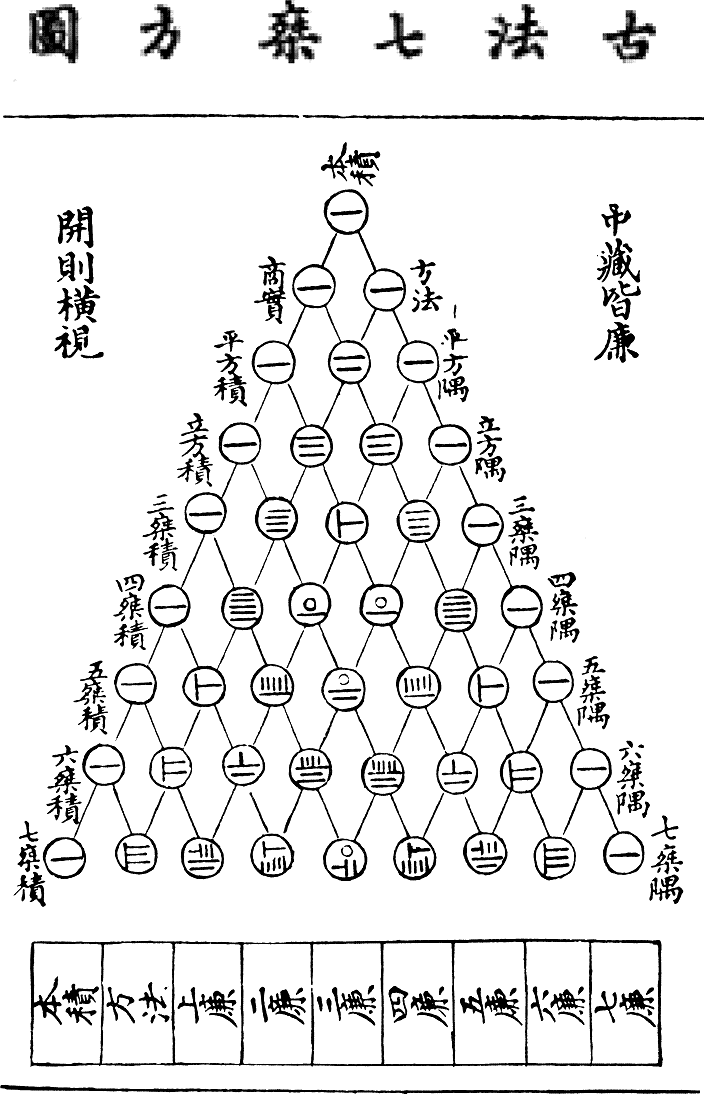
Counting rods () are small bars, typically 3–14 cm long, that were used by mathematicians for calculation in ancient East Asia. They are placed either horizontally or vertically to represent any integer or rational number. The written forms based on them are called rod numerals. They are a true positional numeral system with digits for 1–9 and a blank for 0, from the Warring states period (circa 475 BCE) to the 16th century. History Chinese arithmeticians used counting rods well over two thousand years ago. In 1954 forty-odd counting rods of the Warring States period (5th century BCE to 221 BCE) were found in Zuǒjiāgōngshān (左家公山) Chu Grave No.15 in Changsha, Hunan. In 1973 archeologists unearthed a number of wood scripts from a tomb in Hubei dating from the period of the Han dynasty (206 BCE to 220 CE). On one of the wooden scripts was written: "当利二月定算𝍥". This is one of the earliest examples of using counting-rod numerals in writing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tian Yuan Shu
''Tian yuan shu'' () is a Chinese system of algebra for polynomial equations. Some of the earliest existing writings were created in the 13th century during the Yuan dynasty. However, the tianyuanshu method was known much earlier, in the Song dynasty and possibly before. History The Tianyuanshu was explained in the writings of Zhu Shijie (''Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns'') and Li Zhi (''Ceyuan haijing''), two Chinese mathematicians during the Mongol Yuan dynasty. However, after the Ming overthrew the Mongol Yuan, Zhu and Li's mathematical works went into disuse as the Ming literati became suspicious of knowledge imported from Mongol Yuan times. Only recently, with the advent of modern mathematics in China has the tianyuanshu been re-deciphered. Meanwhile, ''tian yuan shu'' arrived in Japan, where it is called ''tengen-jutsu''. Zhu's text '' Suanxue qimeng'' was deciphered and was important in the development of Japanese mathematics (''wasan'') in the 17th and 18th centuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |