|
Cetiocaridae
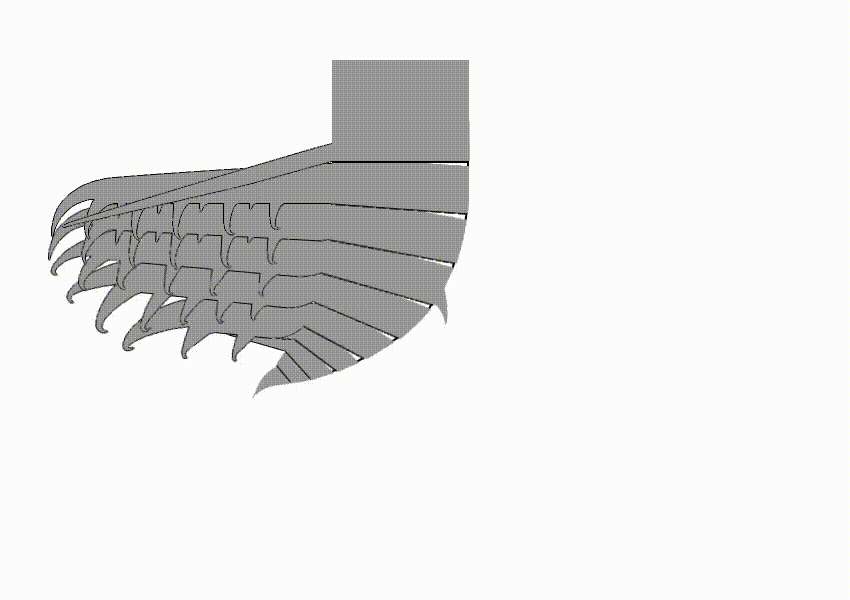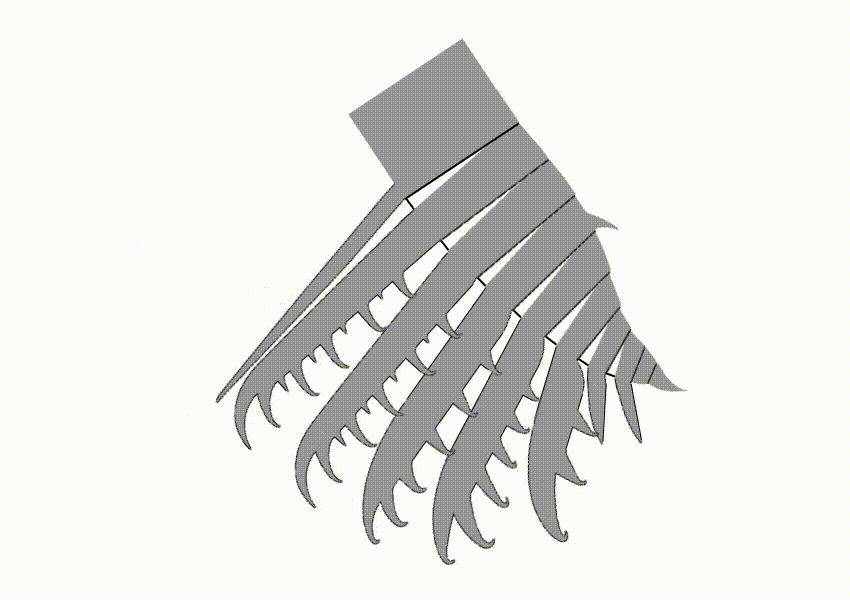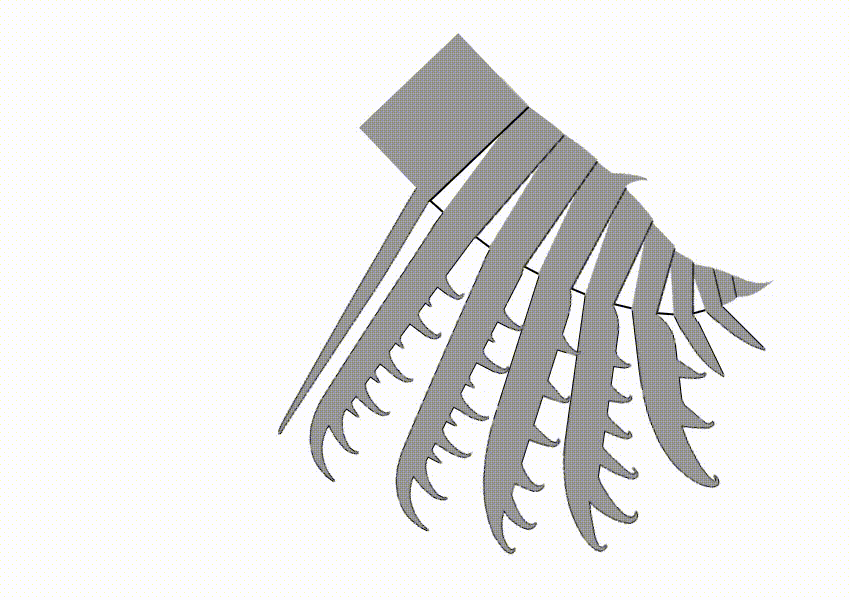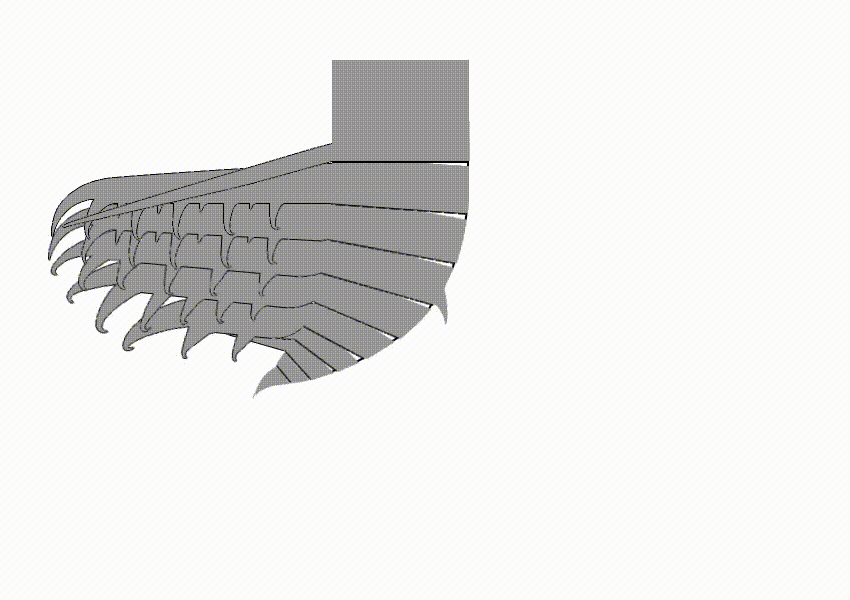
Tamisiocarididae is a family of radiodonts, extinct marine animals related to arthropods, that bore finely-spined appendages that were presumably used in filter-feeding. When first discovered, the clade was named Cetiocaridae after a speculative evolution artwork, ''Bearded Ceticaris'' by John Meszaros, that depicted a hypothetical filter-feeding radiodont at a time before any were known to exist. However, the family name was not valid according to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, as no real genus named "Cetiocaris" exists, and in 2019 it was formally replaced by the name Tamisiocarididae, after the only valid genus of the clade at the time. The family is only known from Series 2 of the Cambrian, unlike other radiodont families, which persisted longer into the Cambrian. All known species would have lived in tropical or subtropical waters, suggesting a preference for warmer waters. Description Like most radiodonts, cetiocarids have spiny frontal appendages. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalocarida
Radiodonta is an extinct Order (biology), order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. They may be referred to as radiodonts, radiodontans, radiodontids, anomalocarids, or anomalocaridids, although the last two originally refer to the family Anomalocarididae, which previously included all species of this order but is now restricted to only a few species. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts included the earliest large predators known, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa ''Anomalocaris, Anomalocaris canadensis'', ''Hurdia, Hurdia victoria'', ''Peytoia nathorsti'', ''Titanokorys gainesii, Titanokorys gainessii, Cambroraster, Cambroraster falcatus'' and ''Amplectobelua, Amplectobelua symbrachiata'', the Ordovician ''Aegirocassis, Aegiroca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiodonta
Radiodonta is an extinct Order (biology), order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. They may be referred to as radiodonts, radiodontans, radiodontids, anomalocarids, or anomalocaridids, although the last two originally refer to the family Anomalocarididae, which previously included all species of this order but is now restricted to only a few species. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts included the earliest large predators known, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa ''Anomalocaris, Anomalocaris canadensis'', ''Hurdia, Hurdia victoria'', ''Peytoia nathorsti'', ''Titanokorys gainesii, Titanokorys gainessii, Cambroraster, Cambroraster falcatus'' and ''Amplectobelua, Amplectobelua symbrachiata'', the Ordovician ''Aegirocassis, Aegiroca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculative Evolution
Speculative evolution is a genre of speculative fiction and an artistic movement focused on hypothetical scenarios in the evolution of life, and a significant form of fictional biology. It is also known as speculative biology and it is referred to as speculative zoology in regards to hypothetical animals. Works incorporating speculative evolution may have entirely conceptual species that evolve on a planet other than Earth, or they may be an alternate history focused on an alternate evolution of terrestrial life. Speculative evolution is often considered hard science fiction because of its strong connection to and basis in science, particularly biology. Speculative evolution is a long-standing trope within science fiction, often recognized as beginning as such with H. G. Wells's 1895 novel ''The Time Machine'', which featured several imaginary future creatures. Although small-scale speculative faunas were a hallmark of science fiction throughout the 20th century, ideas were onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houcaris
''Houcaris'' is a genus of tamisiocarididid radiodonts known from Cambrian Series 2 of China and the United States. It contains two species, ''Houcaris saron'' and ''Houcaris magnabasis'', both of which were originally named as species of the related genus ''Anomalocaris''. The genus ''Houcaris'' was established for the two species in 2021 and honors Hou Xianguang, who had discovered and named the type species ''H. saron'' in 1995 along with his colleagues Jan Bergström and Per E. Ahlberg. Species ''Houcaris saron'' ''H. saron'', known from Maotianshan Shale in Yunnan, is first described in 1995 as ''Anomalocaris saron''. This species is only known from frontal appendages. There is a specimen (ELRC 20001) that is previously considered as whole body fossil of this species, but later study shows that this specimen is not belonging to this species, and later given own genus ''Innovatiocaris''. Length of frontal appendage is up to at least 12 cm. Sometimes considered to belong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houcaris Magnabasis
''Houcaris'' is a genus of tamisiocarididid radiodonts known from Cambrian Series 2 of China and the United States. It contains two species, ''Houcaris saron'' and ''Houcaris magnabasis'', both of which were originally named as species of the related genus ''Anomalocaris''. The genus ''Houcaris'' was established for the two species in 2021 and honors Hou Xianguang, who had discovered and named the type species ''H. saron'' in 1995 along with his colleagues Jan Bergström and Per E. Ahlberg. Species ''Houcaris saron'' ''H. saron'', known from Maotianshan Shale in Yunnan, is first described in 1995 as ''Anomalocaris saron''. This species is only known from frontal appendages. There is a specimen (ELRC 20001) that is previously considered as whole body fossil of this species, but later study shows that this specimen is not belonging to this species, and later given own genus ''Innovatiocaris''. Length of frontal appendage is up to at least 12 cm. Sometimes considered to belong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculative Evolution
Speculative evolution is a genre of speculative fiction and an artistic movement focused on hypothetical scenarios in the evolution of life, and a significant form of fictional biology. It is also known as speculative biology and it is referred to as speculative zoology in regards to hypothetical animals. Works incorporating speculative evolution may have entirely conceptual species that evolve on a planet other than Earth, or they may be an alternate history focused on an alternate evolution of terrestrial life. Speculative evolution is often considered hard science fiction because of its strong connection to and basis in science, particularly biology. Speculative evolution is a long-standing trope within science fiction, often recognized as beginning as such with H. G. Wells's 1895 novel ''The Time Machine'', which featured several imaginary future creatures. Although small-scale speculative faunas were a hallmark of science fiction throughout the 20th century, ideas were onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurdiidae
Hurdiidae is an extinct cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan Family (biology), family of radiodonts, a group of Crown group#Stem groups, stem-group arthropods, which lived during the Paleozoic Era. It is the most long-lived radiodont clade, lasting from the Cambrian period to the Devonian period. Description Hurdiidae is characterized by Radiodonta#Frontal appendage, frontal appendages with distal region composed of 5 subequal blade-like endites, alongside the enlarged head carapaces and tetraradial mouthpart (Radiodonta#Oral cone, oral cone). The Radiodonta#Frontal appendage, frontal appendages of hurdiids have a distinctive morphology, with the appendage of most species bearing five equally-sized elongate blade-like ventral spines known as endites. Subsequent podomeres were reduced in size and with only small endites or none. Each podomere bore only a single endite, unlike other radiodonts, in which the endites were paired. In most species, the endites were curved med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houcaris Saron
''Houcaris'' is a genus of tamisiocarididid radiodonts known from Cambrian Series 2 of China and the United States. It contains two species, ''Houcaris saron'' and ''Houcaris magnabasis'', both of which were originally named as species of the related genus ''Anomalocaris''. The genus ''Houcaris'' was established for the two species in 2021 and honors Hou Xianguang, who had discovered and named the type species ''H. saron'' in 1995 along with his colleagues Jan Bergström and Per E. Ahlberg. Species ''Houcaris saron'' ''H. saron'', known from Maotianshan Shale in Yunnan, is first described in 1995 as ''Anomalocaris saron''. This species is only known from frontal appendages. There is a specimen (ELRC 20001) that is previously considered as whole body fossil of this species, but later study shows that this specimen is not belonging to this species, and later given own genus ''Innovatiocaris''. Length of frontal appendage is up to at least 12 cm. Sometimes considered to belong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurdia
''Hurdia'' is an extinct genus of hurdiid radiodont that lived 505 million years ago during the Cambrian Period. As a radiodont like ''Peytoia'' and ''Anomalocaris'', it is part of the ancestral lineage that led to euarthropods. Description ''Hurdia'' was one of the largest organisms in the Cambrian oceans, ''H. victoria'' reached approximately in length, while ''H. triangulata'' reached up to just . Its head bore a pair of rake-like frontal appendages which shovelled food into its pineapple-ring-like mouth (oral cone). Like other hurdiids, ''Hurdia'' bore a large frontal carapace protruding from its head composed of three sclerites: a central component known as the H-element and two lateral components known as P-elements. The function of this organ remains mysterious; it cannot have been protective as there was no underlying soft tissue. Originally, it is estimated that body flaps ran along the sides of the organisms, from which large gills were suspended. However, anatomy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoart
Paleoart (also spelled palaeoart, paleo-art, or paleo art) is any original artistic work that attempts to depict prehistoric life according to scientific evidence. Works of paleoart may be representations of fossil remains or imagined depictions of the living creatures and their ecosystems. While paleoart is typically defined as being scientifically informed, it is often the basis of depictions of prehistoric animals in popular culture, which in turn influences public perception of and fuels interest in these animals. The word paleoart is also used in other informal sense, as a name for prehistoric art, most often cave paintings. Alternative concept of this term is the domain of archeological society. The term "paleoart"–which is a portmanteau of ''paleo'', the Ancient Greek word for "old", and "art"–was introduced in the late 1980s by Mark Hallett for art that depicts subjects related to paleontology, but is considered to have originated as a visual tradition in early 180 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplectobelua
''Amplectobelua'' (meaning "embracing beast") is an extinct genus of late Early Cambrian amplectobeluid radiodont, a group of stem arthropods that mostly lived as free-swimming predators during the first half of the Paleozoic Era. Anatomy The body structures other than frontal appendages are only known from the type species ''Amplectobelua symbrachiata''. Like other radiodonts, ''Amplectobelua'' had a pair of jointed frontal appendages, a head covered by dorsal and lateral sclerites (the latter had been misinterpreted as huge eyes), a limbless body with dorsal gills (setal blades), and a series of flaps on both sides that extended along the length of its body. ''Amplectobelua'' had a specialized frontal appendage, in which it has a distinct 3-segmented shaft region and 12-segmented distal articulated region, and the spine on the fourth segment (first segment of distal articulated region) hooked forward to oppose the tip of the appendage, allowing it to grasp prey like a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalocaris Briggsi
''Anomalocaris'' ("unlike other shrimp", or "abnormal shrimp") is an extinct genus of radiodont, an order of early-diverging stem-group arthropods. The first fossils of ''Anomalocaris'' were discovered in the ''Ogygopsis'' Shale of the Stephen Formation in British Columbia, Canada by Joseph Frederick Whiteaves, with more examples found by Charles Doolittle Walcott in the Burgess Shale unit of the Stephen Formation. Other closely related fossils have been found in the older Emu Bay Shale of Australia, as well as possibly elsewhere. Originally several fossilized parts discovered separately (the mouth, frontal appendages and trunk) were thought to be three separate creatures, a misapprehension corrected by Harry B. Whittington and Derek Briggs in a 1985 journal article. With a body length close to 40 centimetres, ''A. canadensis'' is thought to be one of the earliest examples of an apex predator, though others have been found in older Cambrian lagerstätten deposits. Discovery '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |