|
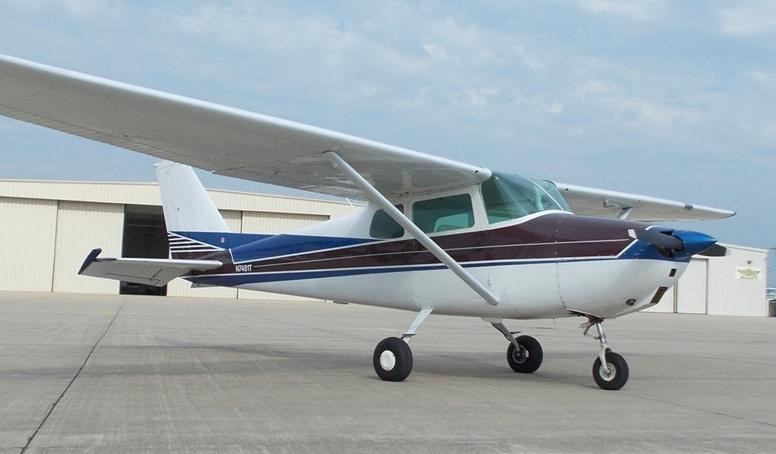
Cessna 172
The Cessna 172 Skyhawk is an American four-seat, single-engine, Monoplane#High, high wing, fixed-wing aircraft made by the Cessna Aircraft Company."Cessna Skyhawk" (2013), Cessna Aircraft Company. Retrieved 2013-04-12. First flown in 1955, more 172s have been built than List of most-produced aircraft, any other aircraft. It was developed from the 1948 Cessna 170 but with tricycle landing gear rather than conventional landing gear. The Skyhawk name was originally used for a trim package, but was later applied to all standard-production 172 aircraft, while some upgraded versions were marketed as the Cutlass. Measured by its longevity and popularity, the Cessna 172 is the most successful aircraft in history. Cessna delivered the first production model in 1956, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cessna Aircraft Company
Cessna () is an American brand of general aviation aircraft owned by Textron Aviation since 2014, headquartered in Wichita, Kansas. Originally, it was a brand of the Cessna Aircraft Company, an American general aviation aircraft manufacturing corporation also headquartered in Wichita. The company produced small, Reciprocating engine, piston-powered aircraft, as well as business jets. For much of the mid-to-late 20th century, Cessna was one of the highest-volume and most diverse producers of general aviation aircraft in the world. It was founded in 1927 by Clyde Cessna and Victor Roos and was purchased by General Dynamics in 1985, then by Textron, Textron, Inc. in 1992. In March 2014, when Textron purchased the Beechcraft and Hawker Aircraft corporations, Cessna ceased operations as a subsidiary company and joined the others as one of the three distinct brands produced by Textron Aviation. Throughout its history, and especially in the years following World War II, Cessna became b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cessna
Cessna () is an American brand of general aviation aircraft owned by Textron Aviation since 2014, headquartered in Wichita, Kansas. Originally, it was a brand of the Cessna Aircraft Company, an American general aviation aircraft manufacturing corporation also headquartered in Wichita. The company produced small, piston-powered aircraft, as well as business jets. For much of the mid-to-late 20th century, Cessna was one of the highest-volume and most diverse producers of general aviation aircraft in the world. It was founded in 1927 by Clyde Cessna and Victor Roos and was purchased by General Dynamics in 1985, then by Textron, Inc. in 1992. In March 2014, when Textron purchased the Beechcraft and Hawker Aircraft corporations, Cessna ceased operations as a subsidiary company and joined the others as one of the three distinct brands produced by Textron Aviation. Throughout its history, and especially in the years following World War II, Cessna became best-known for produci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility Aircraft
A utility aircraft is a general-purpose light airplane or helicopter, usually used for transporting people, freight or other supplies, but is also used for other duties when more specialized aircraft are not required or available. The term can also refer to an aircraft type certificated under American, Canadian, European or Australian regulations as a ''Utility Category Aircraft'', which indicates that it is permitted to conduct limited aerobatics. The approved maneuvers include chandelles, lazy eights, spins and steep turns over 60° of bank.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 535. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. In the United States, military utility aircraft are given the prefix U in their designations. See also * FAR Part 23 (refers to "utility category" in United States aviation regulations) * Utility helicopter * Angel Flight Angel Flight is the name used by a number of groups whose members provide free air transportation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
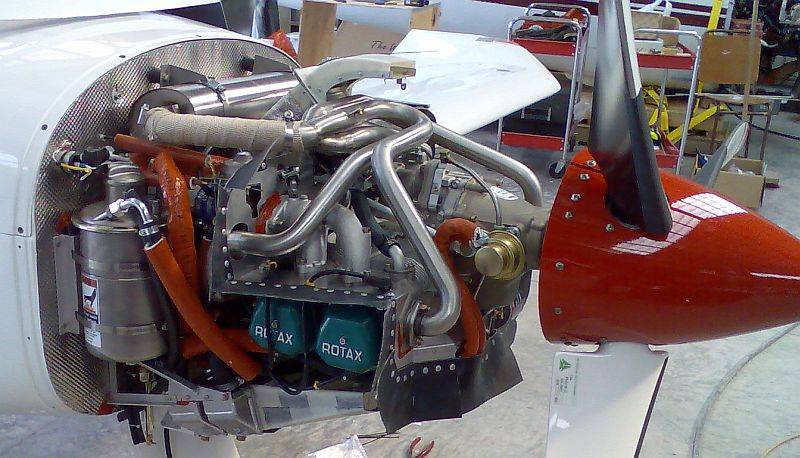
Fuel Injected
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines. All compression-ignition engines (e.g. diesel engines), and many spark-ignition engines (i.e. petrol engines, such as Otto or Wankel), use fuel injection of one kind or another. Mass-produced diesel engines for passenger cars (such as the Mercedes-Benz OM 138) became available in the late 1930s and early 1940s, being the first fuel-injected engines for passenger car use. In passenger car petrol engines, fuel injection was introduced in the early 1950s and gradually gained prevalence until it had largely replaced carburettors by the early 1990s. The primary difference between carburetion and fuel injection is that fuel injection atomizes the fuel through a small nozzle under high pressure, while a carburettor relies on suction created by intake ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
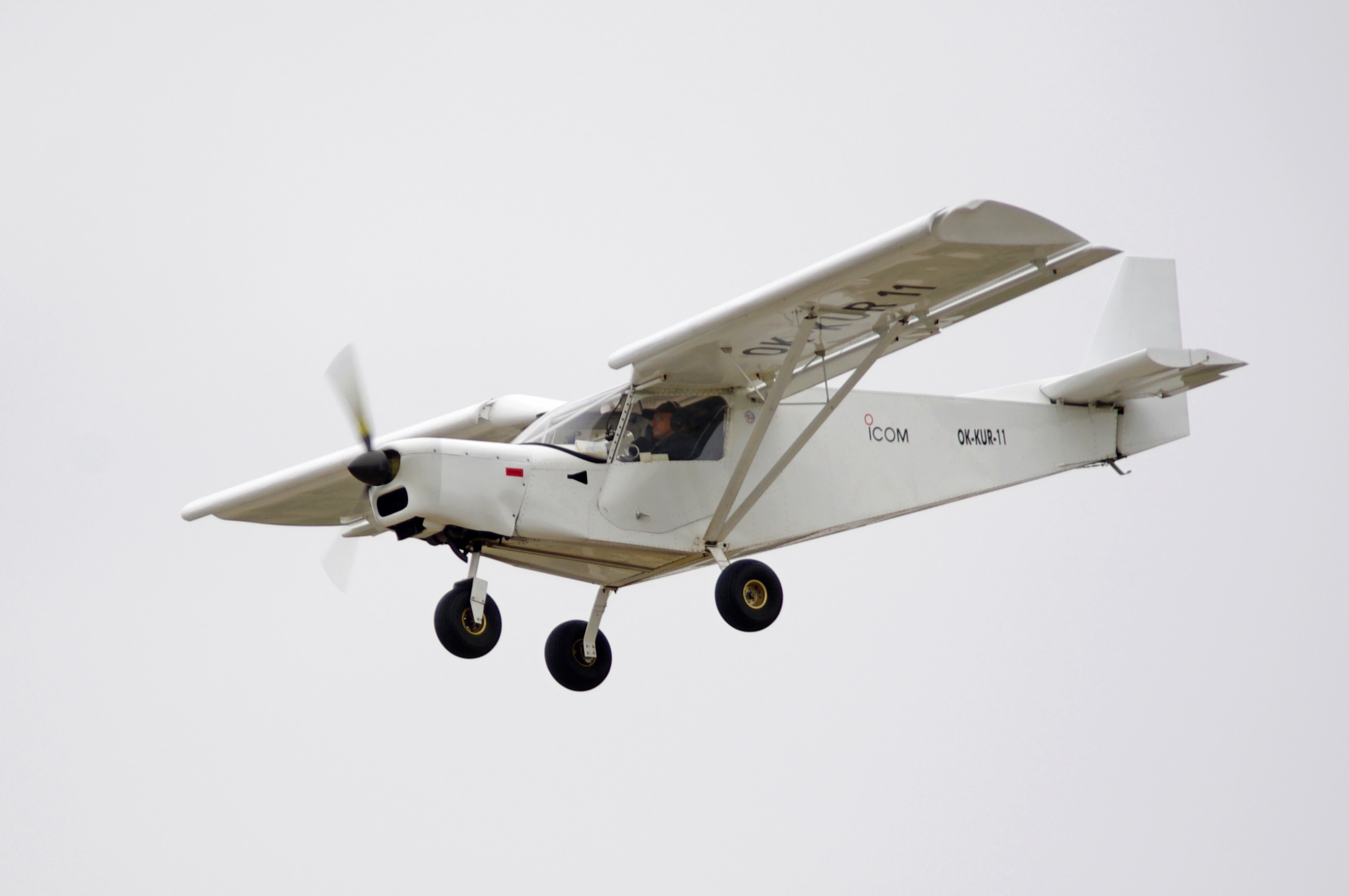
STOL
A short takeoff and landing (STOL) aircraft is a conventional fixed-wing aircraft that has short runway requirements for takeoff and landing. Many STOL-designed aircraft also feature various arrangements for use on airstrips with harsh conditions (such as high altitude or ice). STOL aircraft, including those used in scheduled passenger airline operations, have also been operated from STOLport airfields which feature short runways. Design considerations Many fixed-wing STOL aircraft are bush planes, though some, like the de Havilland Canada Dash-7, are designed for use on prepared airstrips; likewise, many STOL aircraft are taildraggers, though there are exceptions like the PAC P-750 XSTOL, the Quest Kodiak, the de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter and the Peterson 260SE. Autogyros also have STOL capability, needing a short ground roll to get airborne, but capable of a near-zero ground roll when landing. Runway length requirement is a function of the square of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Pants
An aircraft fairing is a structure whose primary function is to produce a smooth outline and reduce drag.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, Third Edition'', page 206. Aviation Supplies & Academics Inc, Newcastle Washington, 1997. These structures are covers for gaps and spaces between parts of an aircraft to reduce form drag and interference drag, and to improve appearance.Bingelis, Tony: ''The Sportplane Builder'', pages 261-265. Experimental Aircraft Association Aviation Foundation, 1979. Types On aircraft, fairings are commonly found on: ; Belly fairing : Also called a "ventral fairing", it is located on the underside of the fuselage between the main wings. It can also cover additional cargo storage or fuel tanks. ; Cockpit fairing : Also called a "cockpit pod", it protects the crew on ultralight trikes. Commonly made from fiberglass, it may also incorporate a windshield.Cliche, Andre: ''Ultralight Aircraft Shopper's Guide'' 8th Edition, page C-17. Cyb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing Tip
A wing tip (or wingtip) is the part of the wing that is most distant from the fuselage of a fixed-wing aircraft. Because the wing tip shape influences the size and drag of the wingtip vortices, tip design has produced a diversity of shapes, including: * Squared-off * Aluminium tube bow * Rounded * Hoerner style * Winglets * Drooped tips * Raked wingtips * Tip tanks * Sails * Fences * End plates Winglets have become popular additions to high speed aircraft to increase fuel efficiency by reducing drag from wingtip vortices. In lower speed aircraft, the effect of the wingtip shape is less apparent, with only a marginal performance difference between round, square, and Hoerner style tips The slowest speed aircraft, STOL aircraft, may use wingtips to shape airflow for controllability at low airspeeds. Wing tips are also an expression of aircraft design style, so their shape may be influenced by marketing considerations as well as by aerodynamic requirements. Wing tips a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
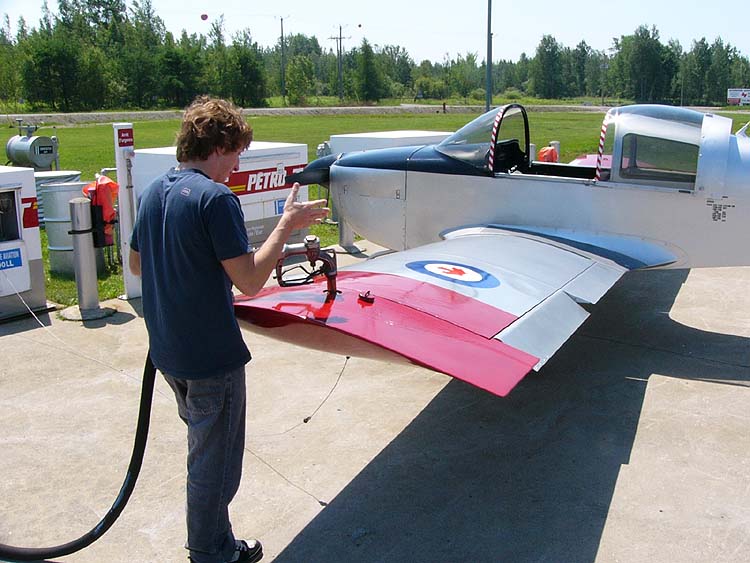
Avgas
Avgas (aviation gasoline, also known as aviation spirit in the UK) is an aviation fuel used in aircraft with spark-ignited internal combustion engines. ''Avgas'' is distinguished from conventional gasoline (petrol) used in motor vehicles, which is termed ''mogas'' (motor gasoline) in an aviation context. Unlike motor gasoline, which has been formulated since the 1970s to allow the use of platinum-content catalytic converters for pollution reduction, the most commonly used grades of avgas still contain tetraethyllead (TEL), a toxic substance used to prevent engine knocking (premature detonation). There are ongoing experiments aimed at eventually reducing or eliminating the use of TEL in aviation gasoline. Kerosene-based jet fuel is formulated to suit the requirements of turbine engines which have no octane requirement and operate over a much wider flight envelope than piston engines. Kerosene is also used by most diesel piston engines developed for aviation use, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant-speed Propeller
In aeronautics, a variable-pitch propeller is a type of propeller (airscrew) with blades that can be rotated around their long axis to change the blade pitch. A controllable-pitch propeller is one where the pitch is controlled manually by the pilot. Alternatively, a constant-speed propeller is one where the pilot sets the desired engine speed ( RPM), and the blade pitch is controlled automatically without the pilot's intervention so that the rotational speed remains constant. The device which controls the propeller pitch and thus speed is called a propeller governor or constant speed unit. Reversible propellers are those where the pitch can be set to negative values. This creates reverse thrust for braking or going backwards without the need to change the direction of shaft revolution. Some aircraft have ground-adjustable propellers, however these are not considered variable-pitch. These are typically found only on light aircraft and microlights. Purpose When an aircraft is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic management, certification of personnel and aircraft, setting standards for airports, and protection of U.S. assets during the launch or re-entry of commercial space vehicles. Powers over neighboring international waters were delegated to the FAA by authority of the International Civil Aviation Organization. Created in , the FAA replaced the former Civil Aeronautics Board, Civil Aeronautics Administration (CAA) and later became an agency within the United States Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Transportation. Major functions The FAA's roles include: *Regulating U.S. commercial space transportation *Regulating air navigation facilities' geometric and flight inspection standards *Encouraging and developing civil aeronautics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-Britain
Air-Britain, traditionally sub-titled "The International Association of Aviation Enthusiasts", is a non-profit aviation society founded in July 1948. As from 2015, it is constituted as a British charitable trust and book publisher. History Air-Britain was formed in 1948 as an amateur association of aviation enthusiasts. In April 1968, it was incorporated into a company limited by guarantee, Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd. On 16 April 2015, the status of Air-Britain changed from a Private company limited by guarantee, in the form of Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd, to a British charity, in the form of Air-Britain Trust Ltd. Air-Britain organised an annual international aircraft recognition contest that started with an event in September 1961, for all comers, and attracted applications from individuals and teams from various sources such as Royal Observer Corps (ROC), Air Training Corps (ATC), and Air-Britain regional branches. The annual aircraft recognition contest was discontinued af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)