|
Cerro Aspero Batholith
Cerro Aspero Batholith ( es, batolito de Cerro Aspero) is a group of plutons in southern Sierras Pampeanas in central Argentina. The batholith covers an approximate area of 440 km2 and lies about 50 km south of the larger Achala Batholith. The batholith contains various circular plutons emplaced by stoping at pressures of 2 kbar or less. Alpa Corral, El Talita and Los Cerros are the three largest individual plutons and together they make up the bulk of the batholith. The most common rock type is monzogranite with biotite and an igneous texture that is equigranular but varies from coarse grained to porphyritic. The emplacement of plutons occurred in the Middle to Late Devonian period. Contact aureoles for the batholith are, contrary to other batholiths, largely undeformed. The relation of the magmatic episode represented by the Cerro Aspero Batholith to the Famatinian orogeny is not fully understood. Alternatively it is grouped as a "Achaliano" igneous cycle. Vertical to near-ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluton (geology)
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and compositions, illustrated by examples like the Palisades Sill of New York and New Jersey; the Henry Mountains of Utah; the Bushveld Igneous Complex of South Africa; Shiprock in New Mexico; the Ardnamurchan intrusion in Scotland; and the Sierra Nevada Batholith of California. Because the solid country rock into which magma intrudes is an excellent insulator, cooling of the magma is extremely slow, and intrusive igneous rock is coarse-grained (phaneritic). Intrusive igneous rocks are classified separately from extrusive igneous rocks, generally on the basis of their mineral content. The relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase, and feldspathoid is particularly important in classifying intrusive igneous rocks. Intrusions m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including regional, contact, hydrothermal, shock, and dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasing temperature and pressure characterize ''retrograde metamorphism''. Metamorphic petrology is the study of metamorphism. Metamorphic petrologists re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian Magmatism
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Argentina
The geology of Argentina includes ancient Precambrian basement rock affected by the Grenville orogeny, sediment filled basins from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic as well as newly uplifted areas in the Andes. Geologic history, stratigraphy and tectonics The oldest rocks in Argentina date to the Precambrian. Strontium, oxygen and carbon isotope data from carbonate rocks in the Sierra de Pie de Palo are part of an ophiolite unit related to the Grenville orogeny, formed as cover rock in the Appalachian margin of the continent Laurentia around 720 million years ago. These Neoproterozoic age rocks are believed to have formed above much older Archean craton rock. Throughout the late Proterozoic, sections of Argentina were part of a metamorphic mobile belt adjacent to the Brazilian Shield. Regional metamorphism produced scheelite belts and wolframite in parts of San Luis and Cordoba Provinces. To the north, along the Bolivian border in the Altiplano, drilling has revealed Precambrian Hornblend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian Argentina
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Córdoba Province, Argentina
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batholiths Of South America
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, such as granite, quartz monzonite, or diorite (see also ''granite dome''). Formation Although they may appear uniform, batholiths are in fact structures with complex histories and compositions. They are composed of multiple masses, or ''plutons'', bodies of igneous rock of irregular dimensions (typically at least several kilometers) that can be distinguished from adjacent igneous rock by some combination of criteria including age, composition, texture, or mappable structures. Individual plutons are solidified from magma that traveled toward the surface from a zone of partial melting near the base of the Earth's crust. Traditionally, these plutons have been considered to form by ascent of relatively buoyant magma in large masses called ''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revista De La Asociación Geológica Argentina
The ''Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina'' is an open access peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Asociación Geológica Argentina. The journal is released under a CC-BY-NC 2.5 license. - official website See also * ''Andean Geology
''Andean Geology'' (formerly ''Revista Geológica de Chile'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published three times per year by the National Geology and Mining Service, Chile's geology and mining agency. The journal covers the field of geol ... ''
* '' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
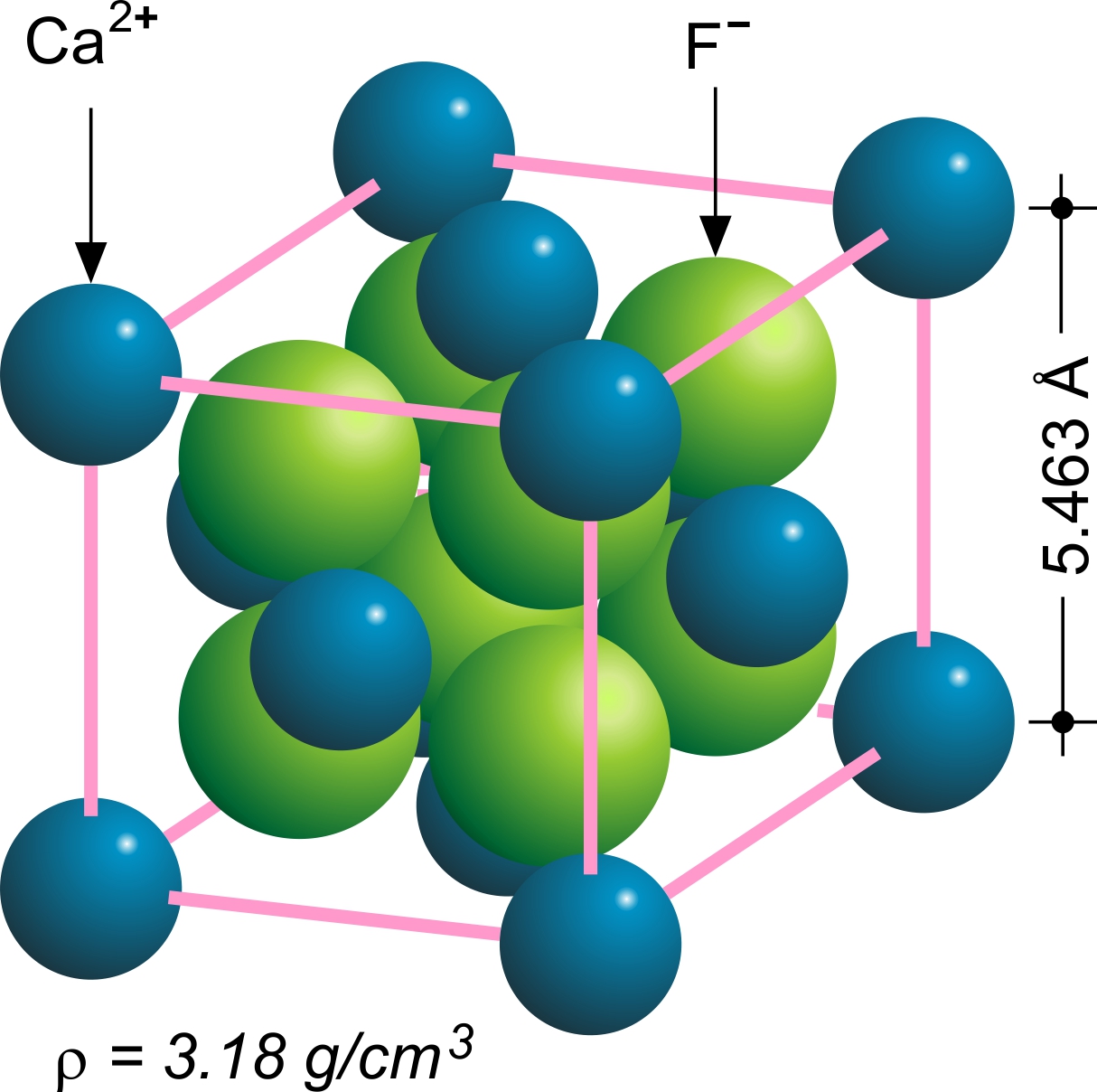
Fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 4 as fluorite. Pure fluorite is colourless and transparent, both in visible and ultraviolet light, but impurities usually make it a colorful mineral and the stone has ornamental and lapidary uses. Industrially, fluorite is used as a flux for smelting, and in the production of certain glasses and enamels. The purest grades of fluorite are a source of fluoride for hydrofluoric acid manufacture, which is the intermediate source of most fluorine-containing fine chemicals. Optically clear transparent fluorite lenses have low dispersion, so lenses made from it exhibit less chromatic aberration, making them valuable in microscopes and telescopes. Fluorite optics are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Famatinian Orogeny
The Famatinian orogeny ( es, Orogenia de Famatina) is an orogeny that predates the rise of the Andes and that took place in what is now western South America during the Paleozoic, leading to the formation of the Famatinian orogen also known as the Famatinian belt. The Famatinian orogeny lasted from the Late Cambrian to at least the Late Devonian and possibly the Early Carboniferous, with orogenic activity peaking about 490 to 460 million years ago. The orogeny involved metamorphism and deformation in the crust and the eruption and intrusion of magma along a Famatinian magmatic arc that formed a chain of volcanoes. The igneous rocks of the Famatinian magmatic arc are of calc-alkaline character and include gabbros, tonalites and granodiorites. The youngest igneous rocks of the arc are granites. The relationship of the orogeny with the Achala and Cerro Aspero batholiths of central Argentina is not fully understood. These Devonian batholiths are possibly of post-orogenic chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of South American Earth Sciences
The ''Journal of South American Earth Sciences'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier. It covers the earth sciences, primarily on issues that are relevant to South America, Central America, the Caribbean, Mexico, and Antarctica. The journal was established in 1988 and the editor-in-chief is James Kellogg ( University of South Carolina). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2012 impact factor of 1.533. See also *''Ameghiniana'' *''Andean Geology'' *''Brazilian Journal of Geology'' *''Latin American Journal of Sedimentology and Basin Analysis'' *''Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina The ''Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina'' is an open access peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Asociación Geológica Argentina. The journal is released under a CC-BY-NC 2.5 license. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |