|
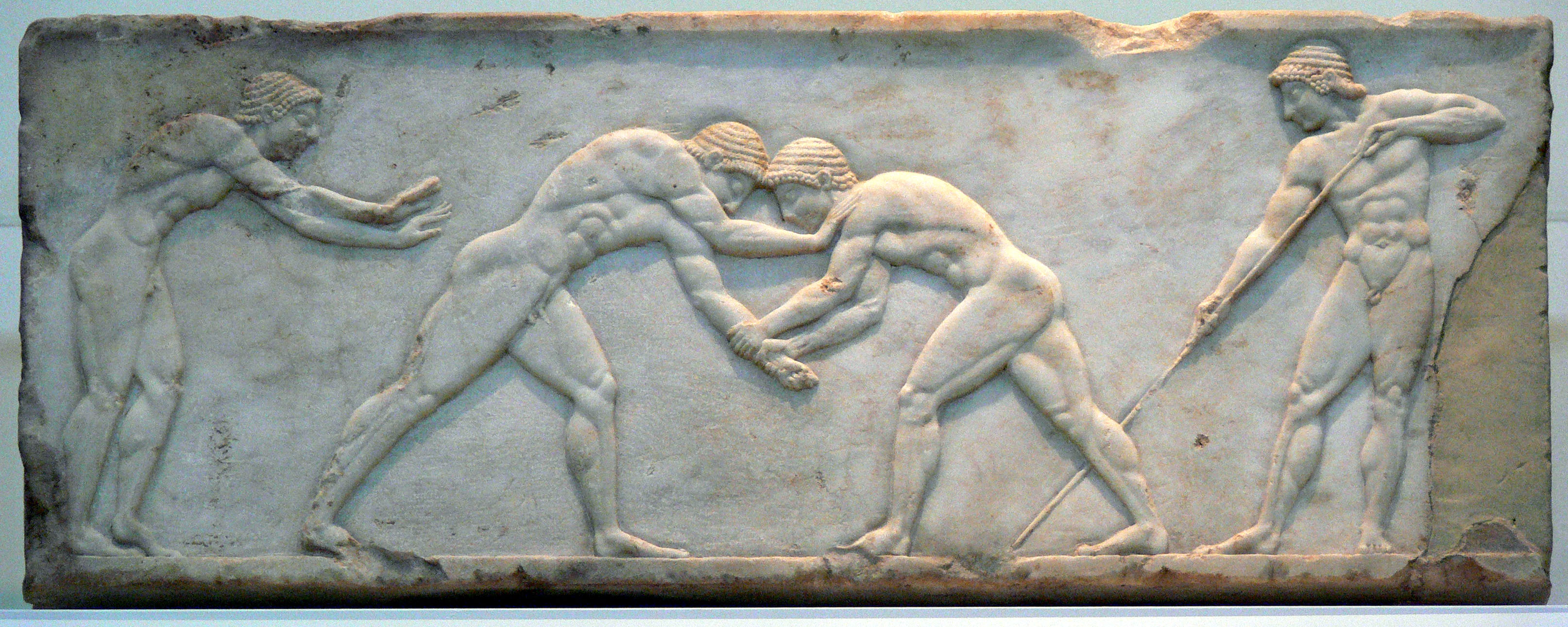
Ceroma
Ceroma ( el, κήρωμα) was a word which first appeared in the works of the two Roman poets Juvenal and Martial and has come to be defined as a mixture of oil, wax and earth; or, a cloth with which ancient wrestlers rubbed themselves, not only to make their limbs more sleek and less capable of gripping, but more pliable and fit for exercise. However, scholars point out that this definition is a misunderstanding of satire and its correct meaning is a "layer of mud or clay forming the floor of the wrestling ring in the times of the Empire". See also *Skin infections and wrestling *Pankration Pankration (; el, παγκράτιον) was a sporting event introduced into the Greek Olympic Games in 648 BC, which was an empty-hand submission sport with few rules. The athletes used boxing and wrestling techniques but also others, such as ... References Wrestling {{material-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Infections And Wrestling
Skin infections and wrestling is the role of skin infections in wrestling. This is an important topic in wrestling since breaks in the skin are easily invaded by bacteria or fungi and wrestling involves constant physical contact that can cause transmission of viral, bacterial, and fungal pathogens. These infections can also be spread through indirect contact, for example, from the skin flora of an infected individual to a wrestling mat, to another wrestler. According to the National Collegiate Athletic Association's (NCAA) Injury Surveillance System, ten percent of all time-loss injuries in wrestling are due to skin infections.Bubb, Bobert G. "Skin Infections." Wrestling Rules and Interpretations (2008): WA-15-A-18. Common forms of infection Bacterial infections, or pathogens, make up the largest category of include Furuncles, Carbuncles, Folliculitis, Impetigo, Cellulitis or Erysipelas, and Staphylococcal disease. These range in severity, but most are quickly identified by irr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juvenal
Decimus Junius Juvenalis (), known in English as Juvenal ( ), was a Roman poet active in the late first and early second century CE. He is the author of the collection of satirical poems known as the ''Satires''. The details of Juvenal's life are unclear, although references within his text to known persons of the late first and early second centuries CE fix his earliest date of composition. One recent scholar argues that his first book was published in 100 or 101. A reference to a political figure dates his fifth and final surviving book to sometime after 127. Juvenal wrote at least 16 poems in the verse form dactylic hexameter. These poems cover a range of Roman topics. This follows Lucilius—the originator of the Roman satire genre, and it fits within a poetic tradition that also includes Horace and Persius. The ''Satires'' are a vital source for the study of ancient Rome from a number of perspectives, although their comic mode of expression makes it problematic to acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman poet from Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of ''Epigrams'', published in Rome between AD 86 and 103, during the reigns of the emperors Domitian, Nerva and Trajan. In these short, witty poems he cheerfully satirises city life and the scandalous activities of his acquaintances, and romanticises his provincial upbringing. He wrote a total of 1,561 epigrams, of which 1,235 are in elegiac couplets. Martial has been called the greatest Latin epigrammatist, and is considered the creator of the modern epigram. Early life Knowledge of his origins and early life are derived almost entirely from his works, which can be more or less dated according to the well-known events to which they refer. In Book X of his ''Epigrams'', composed between 95 and 98, he mentions celebrating his fifty-seventh birthday; hence he was born during March 38, 39, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Wrestling
Greek wrestling ( grc-gre, πάλη, pálē), also known as Ancient Greek wrestling and Palé, was the most popular organized sport in Ancient Greece. A point was scored when one player touched the ground with his back, hip or shoulder, or conceding defeat due to a submission-hold or was forced out of the wrestling-area. Three points had to be scored to win the match. One particularly important position in this form of wrestling was one where one of the contestants was lying on his abdomen with the other on his back trying to strangle him (back mount). The athlete on the bottom would try to grasp an arm of the one on top and turn him over onto his back while the athlete on top would try to complete the choke without being rolled. Wrestling was the first competition to be added to the Olympic Games that was not a footrace. It was added in 708 B.C. (Miller, 46). The competitions were held in elimination-tournament style until one wrestler was crowned the victor. The wrestling area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenix (classics Journal)
''Phoenix'', originally ''The Phoenix'', is one of two peer-reviewed journals of the Classical Association of Canada (the other is ''Mouseion''), and the oldest classics journal published in Canada. ''Phoenix'' publishes two double issues a year containing scholarly papers embodying original research in all areas of Classical Studies: the literature, language, history, philosophy, religion, mythology, science, archaeology, art, architecture, and culture of the Greek and Roman worlds from earliest times to about AD 600. History ''The Phoenix'' was founded in 1946 as the first journal of classics in Canada, by the country's first organisation for the study of classics, the Ontario Classical Association The Ontario Classical Association (OCA) was founded in 1944 with Eric A. Havelock as its first president. The association promotes the study of classics through lobbying, scholarships, and colloquia for members. Its membership consists primarily .... When the nationwide Classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pankration
Pankration (; el, παγκράτιον) was a sporting event introduced into the Greek Olympic Games in 648 BC, which was an empty-hand submission sport with few rules. The athletes used boxing and wrestling techniques but also others, such as kicking, holds, joint-locks, and chokes on the ground, making it similar to modern mixed martial arts. The term comes from the Greek , meaning 'all of power', from (''pan'') 'all' and (''kratos'') 'strength, might, power'. History In Greek mythology, it was said that the heroes Heracles and Theseus invented pankration as a result of using both wrestling and boxing in their confrontations with opponents. Theseus was said to have used pankration to defeat the Minotaur in the Labyrinth. Heracles too was often depicted in ancient artworks subduing the Nemean lion using pankration. In this context, pankration was also referred to as ''pammachon'' or ''pammachion'' (πάμμαχον or παμμάχιον), meaning "total combat," from π ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |