|
Ceratopsians
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. The earliest known ceratopsian, ''Yinlong downsi'', lived between 161.2 and 155.7 million years ago.Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2011) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages,'Winter 2010 Appendix./ref> The last ceratopsian species, ''Triceratops prorsus'', became extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, . ''Triceratops'' is by far the best-known ceratopsian to the general public. It is traditional for ceratopsian genus names to end in "''-ceratops''", although this is not always the case. One of the first named genera was ''Ceratops'' itself, which lent its name to the group, although it is considered a ''nomen dubium'' today as its fossil remains have no distinguishing characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psittacosaurus
''Psittacosaurus'' ( ; "parrot lizard") is a genus of extinct ceratopsian dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of what is now Asia, existing between 126 and 101 million years ago. It is notable for being the most species-rich non-avian dinosaur genus. Up to 12 species are known, from across China, Mongolia, Russia, and Thailand. The species of ''Psittacosaurus'' were obligate bipeds at adulthood, with a high skull and a robust beak. One individual was found preserved with long filaments on the tail, similar to those of ''Tianyulong''. ''Psittacosaurus'' probably had complex behaviours, based on the proportions and relative size of the brain. It may have been active for short periods of time during the day and night, and had well-developed senses of smell and vision. ''Psittacosaurus'' was one of the earliest ceratopsians, but closer to ''Triceratops'' than ''Yinlong''. Once in its own family, Psittacosauridae, with other genera like ''Hongshanosaurus'', it is now considered to be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
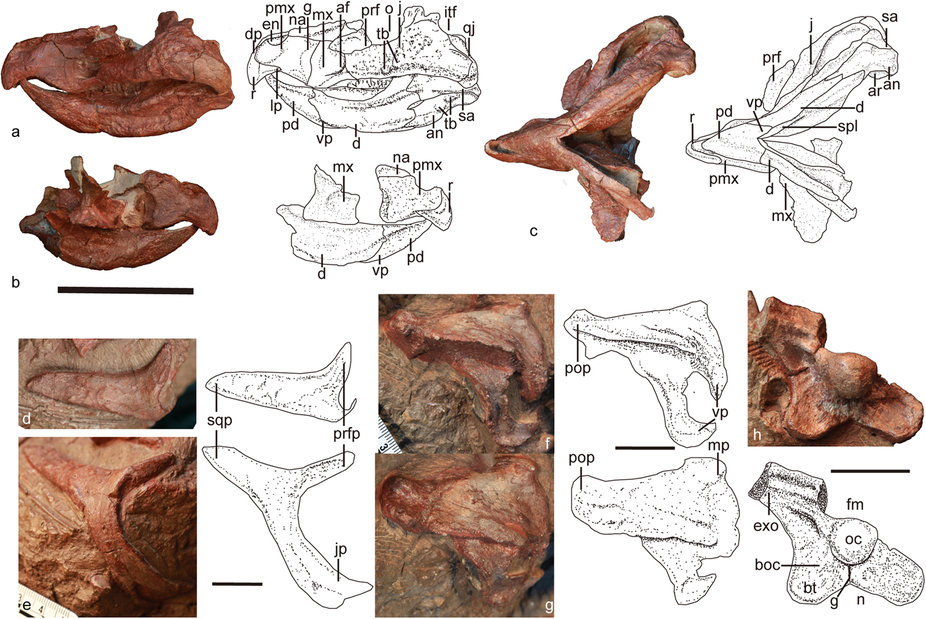
Protoceratopsidae
Protoceratopsidae is a family of basal (primitive) ceratopsians from the Late Cretaceous period. Although ceratopsians have been found all over the world, protoceratopsids are only definitively known from Cretaceous strata in Asia, with most specimens found in China and Mongolia. As ceratopsians, protoceratopsids were herbivorous, with constantly replacing tooth batteries made for slicing through plants and a hooked beak for grabbing them. Protoceratopsids were small ceratopsians around 1-2.5 m in length. Their bony frill and horns were much smaller than more derived members of Ceratopsia, such as ceratopsids. Description Protoceratopsids were relatively small ceratopsians, averaging around 1-2.5 m in length from head to tail. Protoceratopsids have a frill and rostral bone characteristic of all ceratopsians. Their snout is particularly wedge-shaped with tall and narrow nostrils situated high on it. The antorbital fenestra is unusually small, and the antorbital fossa sits high on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivore, herbivorous Chasmosaurinae, chasmosaurine Ceratopsidae, ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 68 million years ago in what is now North America. It is one of the last-known non-avian dinosaur genera, and became extinct in the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago. The name ''Triceratops'', which literally means 'three-horned face', is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words () meaning 'three', () meaning 'horn', and () meaning 'face'. Bearing a large bony neck frill, frill, three horn (anatomy), horns on the skull, and a large four-legged body, exhibiting convergent evolution with rhinoceroses and bovines, ''Triceratops'' is one of the most recognizable of all dinosaurs and the most well-known ceratopsid. It was also one of the largest, up to long and in body m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liaoceratops
''Liaoceratops'', meaning "Liaoning horned face", is a ceratopsian dinosaur believed to be an early relative of the horned ceratopsids. It lived in the Early Cretaceous, 126 million years ago. It was discovered in China by a team of American and Chinese scientists. ''Liaoceratops'' was much smaller than its later relatives, but offers a glimpse into the early evolution of this group of dinosaurs. Discoveries and naming ''Liaoceratops'' was discovered in the famous Liaoning Province of China, where several fossils of feathered dinosaurs have also been collected. The type species ''Liaoceratops yanzigouensis'' was in 2002 named and described by Xu Xing, Peter Makovicky, Wang Xiaolin, Mark Norell and You Hailu. The generic name is derived from Liaoning and the Greek ''keras'', "horn" and ''ops'', "face". The specific name refers to the town Yanzigou. The holotype IVPP V12738 has been found in the Yixian Formation dating from the Barremian. These beds have also yielded fossil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koreaceratops
''Koreaceratops'' () is a genus of basal ceratopsian dinosaur discovered in Albian-age Lower Cretaceous rocks of South Korea. Discovery It is based on KIGAM VP 200801, an articulated series of 36 caudal vertebrae associated with partial hind limbs and ischia. This specimen was found in a sandstone block that had been incorporated into the Tando dam at Hwaseong City; the way the specimen is cut off suggests that more of it was present before quarrying. The dam was built in 1994, and the bones were first brought to the attention of paleontologists in 2008, after a public official noticed them. The specimen came from the Sihwa Formation. ''Koreaceratops'' was described by Yuong-Nam Lee and colleagues in 2011. The genus name is a combination of "Korea" and the Greek ''κέρας'' (''keras'') meaning 'horn' and ''ὄψις'' (''opsis'') meaning 'face'. The type species is ''K. hwaseongensis'', named after Hwaseong City. Classification ''Koreaceratops'' is notable f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microceratus
''Microceratus'' (meaning "small-horned") is a genus of small ceratopsian dinosaur that lived in the Cretaceous period in Asia. It walked on two legs, had short front arms, a characteristic ceratopsian frill and beak-like mouth, and was around long. It was one of the first ceratopsians, or horned dinosaurs, along with ''Psittacosaurus'' in Mongolia. Discovery The type species, ''Microceratops gobiensis'', was first described by Bohlin in 1953, and so was the second species, ''M. sulcidens'', which may belong to ''Asiaceratops'' instead. However, the generic name was already preoccupied by an ichneumon wasp (subfamily Cryptinae) with the same name. Though much of the material has since been reassigned to the genus ''Graciliceratops'', a replacement name ''Microceratus'' was created by Mateus in 2008 for the type specimen. Classification ''Microceratus'' belonged to the Ceratopsia (Ancient Greek for "horned face"), a group of herbivorous dinosaurs with parrot-like beaks which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zuniceratops
''Zuniceratops'' ('Zuni-horned face') was a ceratopsian dinosaur from the mid Turonian of the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now New Mexico, United States. It lived about 10 million years earlier than the more familiar horned Ceratopsidae and provides an important window on their ancestry''.'' Description ''Zuniceratops'' measured about long. It probably weighed about , making it substantially smaller than most ceratopsids. The skull bears a well-developed pair of brow horns, similar to those of chasmosaurs and primitive centrosaurs, but the nose horn is absent. The brow horns are thought to have grown much larger with age. The snout is long and low, like that of chasmosaurines. The frill was a thin, broad, shield-like structure. It bore a pair of large holes but lacked epoccipital bones, as in ''Protoceratops''. Overall, the anatomy is much more primitive than that of the ceratopsids, but more advanced than in protoceratopsids. Discovery and species ''Zuniceratops'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turanoceratops
''Turanoceratops'' ("Turan horned face") is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur from the late Cretaceous Bissekty Formation of Uzbekistan. The fossils dated from the mid-late Turonian stage, roughly 90 million years ago. The skull bore a pair of long brow horns like those seen in the Ceratopsidae, although ''Turanoceratops'' appears to have been transitional between earlier ceratopsians and ceratopsids, and not a ceratopsid itself. Discovery and naming From the 1920s onwards, Soviet scientists discovered fragmentary fossils near Dzharakuduk in the district Navoi Viloyat, leading them to the conclusion that some ceratopsid must have been present. In 1988, paleontologist Lev Aleksandrovich Nesov based on these published the name ''Turanoceratops tardabilis'', but did not provide a description so that for the time being it remained a ''nomen nudum''. In 1989, Nesov, L.F. Kaznysjkina and Gennady Olegovich Cherepanov validly named the type species ''Turanoceratops tardabilis''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaiceratops
''Mosaiceratops'' is a genus of ceratopsian, described by Zheng, Jin & Xu in 2015 and found in the Xiaguan Formation of Neixiang County. ''Mosaiceratops'' lived in the upper Cretaceous in what is now the Henan Province of China. Although phylogenetic analyses have found ''Mosaiceratops'' to be the most basal neoceratopsian, the authors noted that several features in the premaxilla and nasal bones are shared with ''Psittacosaurus'', indicating that neoceratopsians evolved premaxillary teeth twice and that ''Psittacosaurus'' is not as primitive as previously thought.Zheng, W., Jin, X., & Xu, X. (2015)A psittacosaurid-like basal neoceratopsian from the Upper Cretaceous of central China and its implications for basal ceratopsian evolution ''Scientific reports'', 5. article number 14190: 1-9; doi:10.1038/srep14190 Discovery On the westbank of the river Tuanhe in Neixiang in Henan the skeleton was discovered of a small ceratopian. The fossil was prepared by Sheng Yiming and Yu Chaoh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beg Tse
''Beg'' (after the Himalayan war deity Beg-tse) is a genus of neoceratopsian dinosaur from the early Cretaceous period of Mongolia. The genus contains a single species, ''Beg tse'', known from a partial skull and very fragmentary postcrania. ''Beg'' represents the most basal neoceratopsian currently known. Discovery and naming The holotype, IGM 100/3652, was discovered in 2015 near the town of Tsogt-Ovoo in the Ömnögovi Province of Mongolia. Described from the Ulaanoosh Formation, the specimen is dated to 113 to 94 million years ago, at the boundary of the Lower and Upper Cretaceous. ''Beg'' is named after Beg-tse, a Himalayan deity who is the god of war in Mongolian culture. The deity is often depicted with a rugose face and/or body, similar to the appearance of the preserved skull of the dinosaur. Description Based on the size of the skull, about long, ''Beg'' was most likely a medium-sized basal ceratopsian, similar in size to ''Yinlong'' and ''Liaoceratops.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratopsidae
Ceratopsidae (sometimes spelled Ceratopidae) is a family of ceratopsian dinosaurs including ''Triceratops'', ''Centrosaurus'', and ''Styracosaurus''. All known species were quadrupedal herbivores from the Upper Cretaceous. All but one species are known from western North America, which formed the island continent of Laramidia during most of the Late Cretaceous. Ceratopsids are characterized by beaks, rows of shearing teeth in the back of the jaw, elaborate nasal horns, and a thin parietal-squamosal shelf that extends back and up into a frill. The group is divided into two subfamilies—Chasmosaurinae and Centrosaurinae. The chasmosaurines are generally characterized by long, triangular frills and well-developed brow horns. The centrosaurines had well-developed nasal horns or nasal bosses, shorter and more rectangular frills, and elaborate spines on the back of the frill. These horns and frills show remarkable variation and are the principal means by which the various species have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helioceratops
''Helioceratops'' is a genus of herbivorous neoceratopsian dinosaur from the Middle Cretaceous of China. Discovery and naming In 2000 and 2002, at the Liufangzi site of China's eastern Jilin province, excavations took place during which the jaws were found of a ceratopsian new to science. The type species ''Helioceratops brachygnathus'' was named and described in 2009 by Jin Liyong, Chen Jun, Zan Shuqin and Pascal Godefroit. The generic name means "sun horned face" from the Greek ''helios'', "sun", ''keras'', "horn" and ''ops'', "face". The reference is that the Sun rises in the East and ceratopsians also "rose" in the East; i.e. they originated in the Orient. The name also refers to a close relationship with ''Auroraceratops'', the "dawn ceratopian". The specific name means "short jaw" from the Greek βραχύς, ''brachys'' and γνάθος, ''gnathos'', in reference to the distinguishing short lower jaw. ''Helioceratops'' was discovered in a layer of the Quantou F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)