|
Ceratomyxa Shasta
''Ceratonova shasta'' (syn. ''Ceratomyxa shasta'') is a myxosporean parasite that infects salmonid fish on the Pacific coast of North America. It was first observed at the Crystal Lake Hatchery, Shasta County, California, and has now been reported from Idaho, Oregon, Washington, British Columbia and Alaska. Life history In addition to the fish host, ''C. shasta'' infects a freshwater polychaete worm. Actinospores are released from the worm, and infect fish, on contact, in the water column. Neither horizontal (fish to fish), nor vertical (fish to egg) transmissions have been documented under laboratory conditions, suggesting that the worm host is necessary for completion of the life cycle. Spores are released back into freshwater system after its fish host dies, however the complete life cycle, host and vector interaction is not fully understood (especially the ecology of the polychaete host). Research indicates that the potential for infection is enhanced when water temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elmer Noble
Elmer Ray Noble, (16 January 1909 – 8 March 2001) was professor of zoology at the University of California, Santa Barbara, and an internationally recognized protozoologist and parasitologist. Noble was born in Pyongyang, Korea, to American Methodist missionary parents, William Arthur Noble and Mattie Wilcox Noble. He lived with his family in Korea until 1927, when he and his identical twin brother, Glenn Arthur Noble, moved to the United States to attend the University of California, Berkeley, where he earned a B.A. in zoology, an M.A. in zoology, and a Ph.D. in protozoology and parasitology. Noble joined the UC Santa Barbara faculty in 1936, where he worked for 38 years before retiring in 1974. At UC Santa Barbara, he was, in turn; Chairman of the Department of Biological Sciences, Dean of Liberal Arts, Acting Provost, Acting Chancellor, Vice Chancellor, and Vice Chancellor for Graduate Affairs. He held administrative offices in the following professional societies: *P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascites
Ascites is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than one liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size, increased weight, abdominal discomfort, and shortness of breath. Complications can include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. In the developed world, the most common cause is liver cirrhosis. Other causes include cancer, heart failure, tuberculosis, pancreatitis, and blockage of the hepatic vein. In cirrhosis, the underlying mechanism involves high blood pressure in the portal system and dysfunction of blood vessels. Diagnosis is typically based on an examination together with ultrasound or a CT scan. Testing the fluid can help in determining the underlying cause. Treatment often involves a low-salt diet, medication such as diuretics, and draining the fluid. A transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) may be placed but is associated with co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Aquatic Animal Health
The American Fisheries Society (established 1870 in New York City), is the "world’s oldest and largest organization dedicated to strengthening the fisheries profession, advancing fisheries science, and conserving fisheries resources." It is a member-driven 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization governed by an executive director, a governing board, and officers who are guided by the AFS's organizational documents, a constitution, and a set of rules. Their stated mission is "to improve the conservation and sustainability of fishery resources and aquatic ecosystems by advancing fisheries and aquatic science and promoting the development of fisheries professionals." AFS publishes five peer-reviewed fish journals, books, and the magazine ''Fisheries'', organizes seminars and workshops that promote scientific research and fisheries management, and encourages fisheries education through 58 university-based student subunits. AFS has 48 chapters comprising four geographic regions in North America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinook Salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon in North America, as well as the largest in the genus ''Oncorhynchus''. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other vernacular names for the species include king salmon, Quinnat salmon, Tsumen, spring salmon, chrome hog, Blackmouth, and Tyee salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name ''chavycha'' (чавыча). Chinook are anadromous fish native to the North Pacific Ocean and the river systems of western North America, ranging from California to Alaska, as well as Asian rivers ranging from northern Japan to the Palyavaam River in the Arctic northeast Siberia. They have been introduced to other parts of the world, including New Zealand, thriving in Lake Michigan Great Lakes of North America and Michigan's western rivers, and Patagonia. A large Chinook is a prized and sought-after catch for a sporting angler. The flesh of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
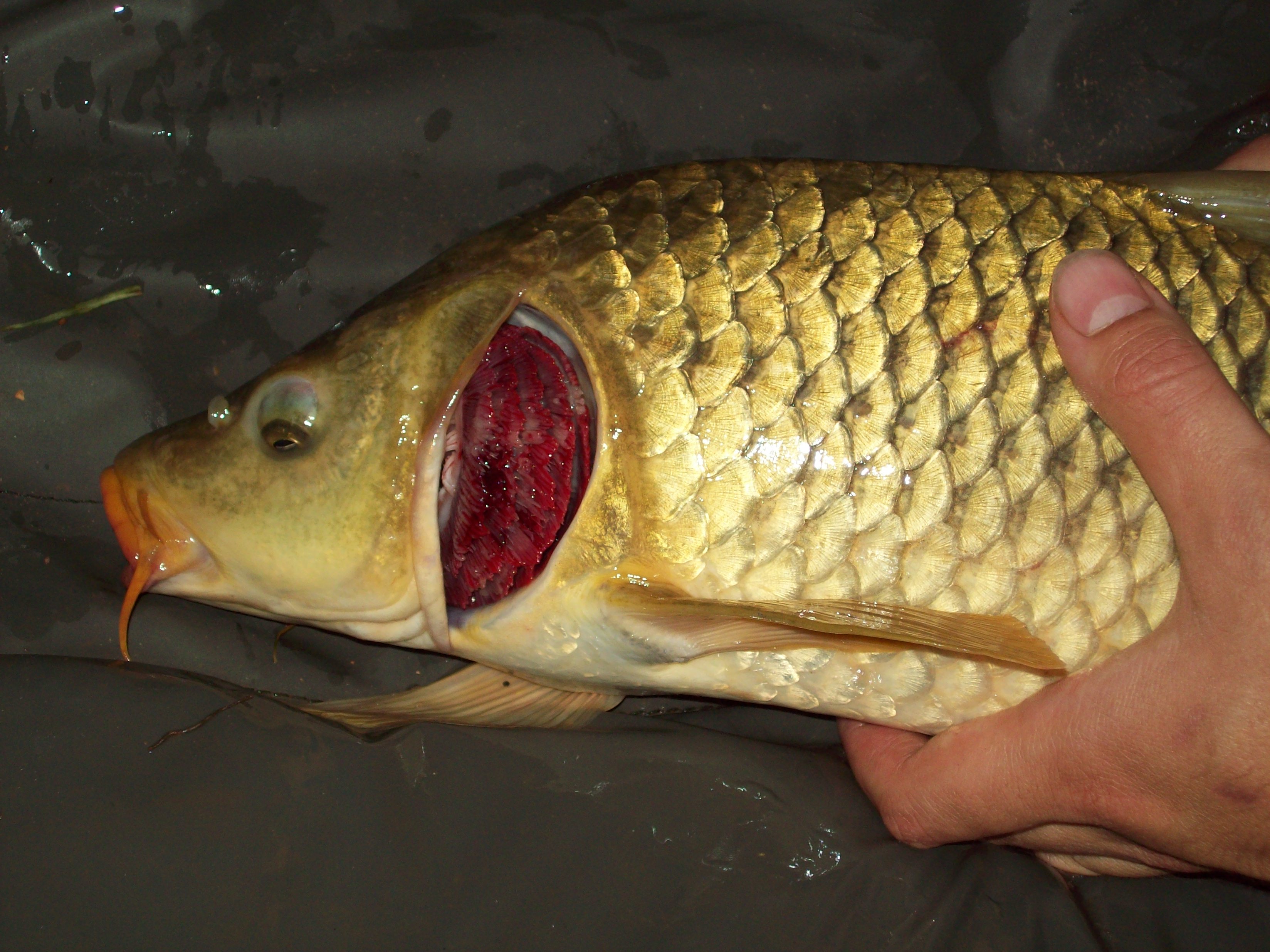
Gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist. The microscopic structure of a gill presents a large surface area to the external environment. Branchia (pl. branchiae) is the zoologists' name for gills (from Ancient Greek ). With the exception of some aquatic insects, the filaments and lamellae (folds) contain blood or coelomic fluid, from which gases are exchanged through the thin walls. The blood carries oxygen to other parts of the body. Carbon dioxide passes from the blood through the thin gill tissue into the water. Gills or gill-like organs, located in different parts of the body, are found in various groups of aquatic animals, including mollusks, crustaceans, insects, fish, and amphibians. Semiterrestrial marine animals such as crabs and mudskippers have gill cham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonads
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sperm in the form of spermatozoa. The female gonad, the ovary, produces egg cells. Both of these gametes are haploid cells. Some hermaphroditic animals have a type of gonad called an ovotestis. Evolution It is hard to find a common origin for gonads, but gonads most likely evolved independently several times. Regulation The gonads are controlled by luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone, produced and secreted by gonadotropes or gonadotrophins in the anterior pituitary gland. This secretion is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone produced in the hypothalamus. Development Gonads start developing as a common primordium (an organ in the earliest stage of development), in the form of genital ridges, which are only late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .σπλήν Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek-English Lexicon'', on Perseus Digital Library The spleen plays very important roles in regard to s (erythrocytes) and the . It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood, which can be valuable in case of |
Gall Bladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
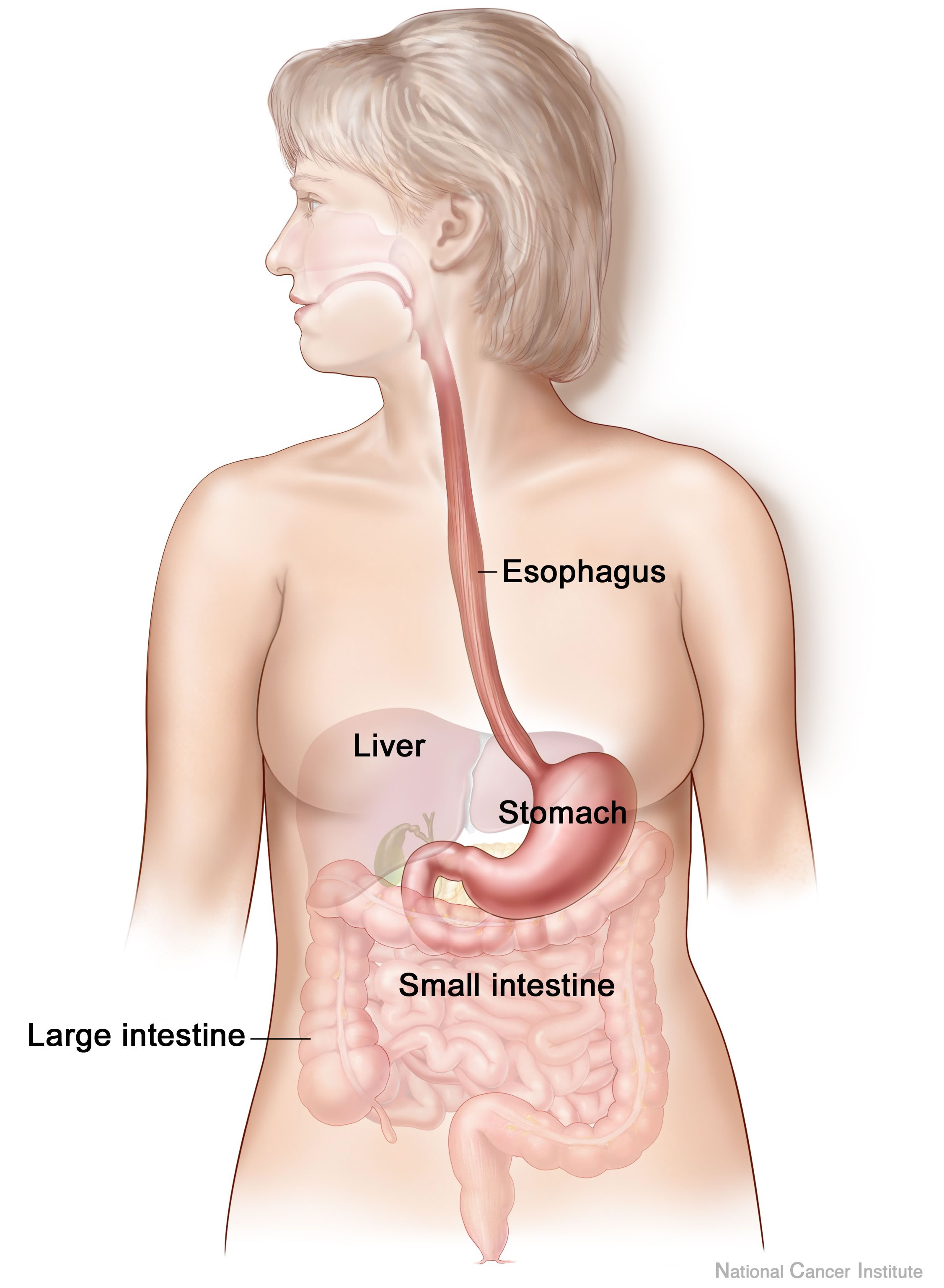
Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to enter the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |