|
Cenél
CenĂ©l is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * CenĂ©l Conaill, the name of the "kindred" or descendants of Conall Gulban, son of Niall NoĂgiallach defined by oral and recorded history * CenĂ©l nEĂ³gain (in English, Cenel Eogan) is the name of the "kindred" or descendants of EĂ³gan mac NĂ©ill, son of Niall NoĂgiallach who founded the kingdom of TĂr EĂ³gain in the 5th century *Kin groups forming part of Dal Riata, most of which, after a varied evolution eventually became the Scottish region of Argyll **CenĂ©l nĂ“engusa, a kin group who ruled the island of Islay, and perhaps nearby Colonsay. After spending 4 centuries as part of Norway, and another 4 as part of the quasi-independent Lordship of the Isles, this region became Scottish in the late 15th century. ** CenĂ©l nGabrĂ¡in, the "kindred" of GabrĂ¡n, who ruled Kintyre, Knapdale (at that time including the lands between Loch Awe and Loch Fyne - Craignish, Ardscotnish Ardscotnish, also known as Ardskeodni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenél NÓengusa
The CenĂ©l nĂ“engusa were a kin group who ruled the island of Islay, and perhaps nearby Colonsay, off the western coast of Scotland in the early Middle Ages. The Senchus fer n-Alban, a census and genealogy of the kingdom of DĂ¡l Riata, lists the CenĂ©l nĂ“engusa as one of the three kin groups making up the kingdom in Argyll. The others were the CenĂ©l nGabrĂ¡in of Kintyre and the CenĂ©l Loairn of Lorne, Scotland, Lorn. A fourth group, the CenĂ©l Comgaill, of Cowal and the Isle of Bute, later split from the CenĂ©l nGabrĂ¡in. The Senchus portrays DĂ¡l Riata as it existed in the mid-seventh century. The Senchus traces the descent of the CenĂ©l nĂ“engusa from Ă“engus MĂ³r mac Eirc, brother of Fergus MĂ³r, a relationship which is almost certainly an invention. The CenĂ©l nĂ“engusa are the only kindred from which no historical kings of DĂ¡l Riata are recorded by the Irish annals. Ă“engus MĂ³r is said to have had two sons, Nadsluaig and Fergna, and their descendants are listed in the Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenél Comgaill
Comgall mac Domangairt was king of DĂ¡l Riata in the early 6th century. He was the son of Domangart RĂ©ti and grandson of Fergus MĂ³r. The ''Annals of Ulster'' report his death in 538, 542 and 545, the ''Annals of Tigernach'' in 537. Comgall Nothing certain is known of Comgall beyond the fact of his death, but he is significant as the eponymous founder of the CenĂ©l Comgaill, one of the kindreds of DĂ¡l Riata named by the ''Senchus fer n-Alban''. The ''Senchus'', in fact, speaks of the Crich Comgaill, but the ''Annals of Ulster'' use the term cenĂ©l in a report of '' c''. 710. The ''Senchus'' says that Comgall had one son, Conall, and that Conall had seven sons, although six are named, Loingsech, Nechtan, Artan, Tuatan, Tutio, Coirpre. It may be that Coirpe was a later addition as the Senchus speaks of the people of Coirpre as being distinct from the sons of Erc. As with all claimed early genealogies, this need not be taken as reliable information. Unlike CenĂ©l nGabrĂ¡in and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CenĂ©l NGabrĂ¡in
The CenĂ©l nGabrĂ¡in was a kingroup, presumed to descend from GabrĂ¡n mac Domangairt, which dominated the kingship of DĂ¡l Riata until the late 7th century and continued to provide kings thereafter. Kings of Alba and of Scotland traced their descent through GabrĂ¡n to his grandfather Fergus MĂ³r, who was seen as the ultimate founder of the royal house as late as the 16th and 17th centuries, long after the Gaelic origins of the kingdom. Unlike the CenĂ©l Loairn, the Senchus Fer n-Alban does not list any kindreds within the CenĂ©l nGabrĂ¡in. However, probable descendants of GabrĂ¡n, such as DĂºnchad mac Conaing and his many kinsmen, would appear to have disputed the succession with the descendants of Eochaid Buide grandson of GabrĂ¡n, so that this absence of explicit segments in the kindred may be misleading.Sharpe, "The thriving of Dalriada", argues for the unimportance of such segments. A genealogy of David I of Scotland in the Book of Ballymote notes the following divisions: * Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenél Conaill
CenĂ©l is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *CenĂ©l Conaill, the name of the "kindred" or descendants of Conall Gulban, son of Niall NoĂgiallach defined by oral and recorded history *CenĂ©l nEĂ³gain (in English, Cenel Eogan) is the name of the "kindred" or descendants of EĂ³gan mac NĂ©ill, son of Niall NoĂgiallach who founded the kingdom of TĂr EĂ³gain in the 5th century *Kin groups forming part of Dal Riata, most of which, after a varied evolution eventually became the Scottish region of Argyll **CenĂ©l nĂ“engusa, a kin group who ruled the island of Islay, and perhaps nearby Colonsay. After spending 4 centuries as part of Norway, and another 4 as part of the quasi-independent Lordship of the Isles, this region became Scottish in the late 15th century. ** CenĂ©l nGabrĂ¡in, the "kindred" of GabrĂ¡n, who ruled Kintyre, Knapdale (at that time including the lands between Loch Awe and Loch Fyne - Craignish, Ardscotnish, Glassary, and Glenary), the island of Arran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CenĂ©l NEĂ³gain
CenĂ©l is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *CenĂ©l Conaill, the name of the "kindred" or descendants of Conall Gulban, son of Niall NoĂgiallach defined by oral and recorded history *CenĂ©l nEĂ³gain (in English, Cenel Eogan) is the name of the "kindred" or descendants of EĂ³gan mac NĂ©ill, son of Niall NoĂgiallach who founded the kingdom of TĂr EĂ³gain in the 5th century *Kin groups forming part of Dal Riata, most of which, after a varied evolution eventually became the Scottish region of Argyll **CenĂ©l nĂ“engusa, a kin group who ruled the island of Islay, and perhaps nearby Colonsay. After spending 4 centuries as part of Norway, and another 4 as part of the quasi-independent Lordship of the Isles, this region became Scottish in the late 15th century. ** CenĂ©l nGabrĂ¡in, the "kindred" of GabrĂ¡n, who ruled Kintyre, Knapdale (at that time including the lands between Loch Awe and Loch Fyne - Craignish, Ardscotnish, Glassary, and Glenary), the island of Arran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorne, Scotland
Lorne (or Lorn; gd, Latharna) is an ancient province (medieval Latin: ''provincia'') in the west of Scotland, which is now a district in the Argyll and Bute council area. The district gives its name to the ''Lynn of Lorn National Scenic Area'', one of forty such areas in Scotland, which have been defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection from inappropriate development. The national scenic areas cover 15,726 ha, of which 10,088 ha are marine seascape, and includes the whole of the island of Lismore, along with neighbouring areas on the mainland such as Benderloch and Port Appin, and the Shuna Island. The region may have given its name to the traditional Scottish breakfast dish Lorne sausage. Geography Lorn is bordered on the west by the Firth of Lorne, which separates it from Mull. The northern border is Glen Coe, and Rannoch Moor, which detach it from Lochaber, while on the east, the Bridge of Orchy hills, and Glen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
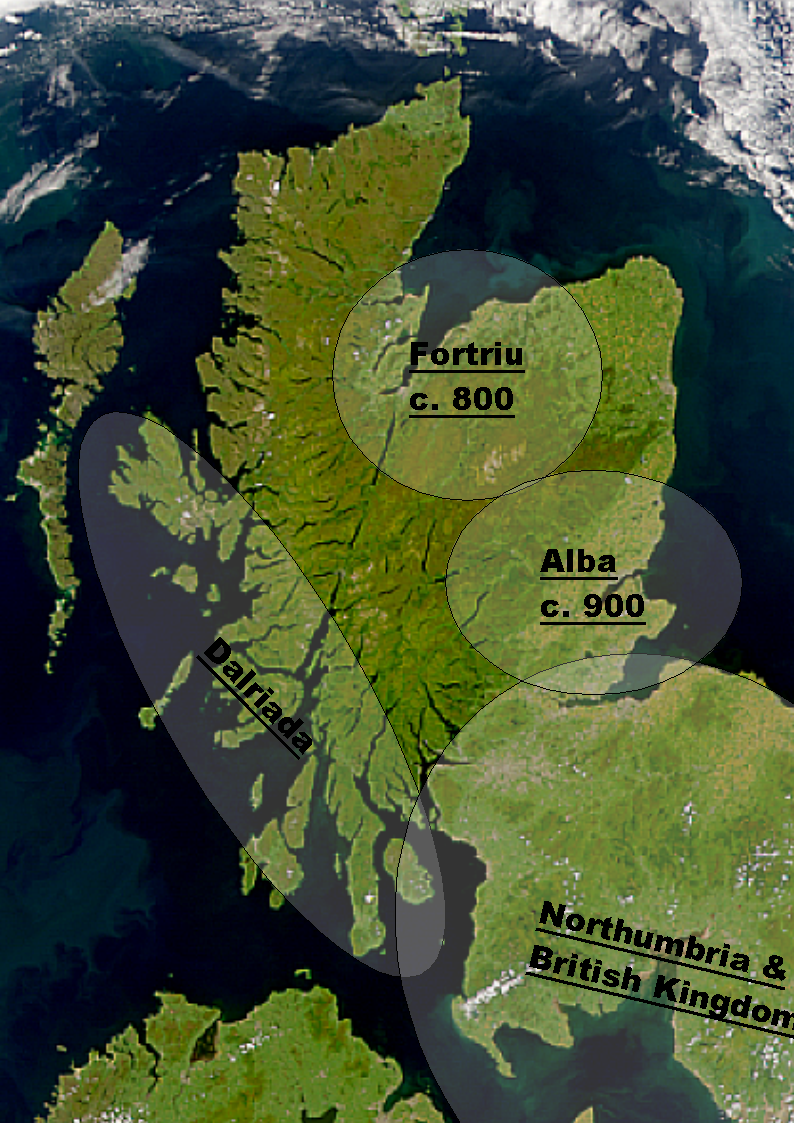
Kingdom Of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba ( la, Scotia; sga, Alba) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the First War of Scottish Independence. Alba included Dalriada, but not large parts of the present day Scottish Lowlands, which were then divided between Strathclyde and Northumbria as far north as the Firth of Forth. Fortriu, a Pictish kingdom in the north, was added to Alba in the tenth century. Until the early 13th century, Moray was not considered part of Alba, which was seen as extending only between the Firth of Forth and the River Spey. The name of Alba is one of convenience, as throughout this period both the ruling and lower classes of the Kingdom were predominantly Pictish-Gaels, later Pictish-Gaels and Scoto-Normans. This differs markedly from the period of the House of Stuart, beginning in 1371, in which the ruling classe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Mull
The Isle of Mull ( gd, An t-Eilean Muileach ) or just Mull (; gd, Muile, links=no ) is the second-largest island of the Inner Hebrides (after Skye) and lies off the west coast of Scotland in the Council areas of Scotland, council area of Argyll and Bute. Covering , Mull is the fourth-largest island in Scotland and Great Britain. From 2001 to 2020, the population has gradually increased: during 2020 the populace was estimated to be 3,000, in the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 census it was approximately 2,800, and in 2001, it was measured at 2,667 people. It has the eighth largest Island population in Scotland. In the summer, these numbers are augmented by an influx of many tourists. Much of the year-round population lives in the colourful main settlement of Tobermory, Mull, Tobermory. There are two distilleries on the island: the Tobermory distillery, formerly named Ledaig, produces single malt Scotch whisky and another, opened in 2019 and located in the vicinity of Tir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenél Loairn
The CenĂ©l Loairn, the descendants of Loarn mac Eirc, controlled parts of northern Argyll around the Firth of Lorne, most probably centred in Lorne but perhaps including the islands of Mull and Colonsay, Morvern and Ardnamurchan. The boundary to the east was the Druim Alban mountain ridge that separated DĂ¡l Riata from Pictland. The chief places of the kingdom appear to have been at Dun Ollaigh, near Oban and Dunadd near Crinan. The chief religious site may have been on Lismore, later the seat of the High Medieval bishop of Argyll. Descendants of Loarn Several kings of DĂ¡l Riata were members of the CenĂ©l Loairn, and thus claimed descent from Loarn : *Ferchar Fota *Ainbcellach mac Ferchair *Selbach mac Ferchair *DĂºngal mac Selbaig *Muiredach mac Ainbcellaig In High Medieval times the Mormaers of Moray claimed descent from Loarn: * FindlĂ¡ech mac RuaidrĂ * MĂ¡el Coluim mac MĂ¡il Brigti * Gille CoemgĂ¡in mac MĂ¡il Brigti *Mac Bethad mac FindlĂ¡ich (also king of Alba) * Lulach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowal
Cowal ( gd, CĂ²mhghall) is a peninsula in Argyll and Bute, in the west of Scotland, that extends into the Firth of Clyde. The northern part of the peninsula is covered by the Argyll Forest Park managed by Forestry and Land Scotland. The Arrochar Alps and Ardgoil peninsula in the north fringe the edges of the sea lochs whilst the forest park spreads out across the hillsides and mountain passes, making Cowal one of the remotest areas in the west of mainland Scotland. The Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park extends into Cowal. The peninsula is separated from Knapdale by Loch Fyne, and from Inverclyde and North Ayrshire to the east by the Firth of Clyde. Loch Long and its arm, Loch Goil are to the north-east. The south of the peninsula is split into three forks by Loch Striven and Loch Riddon (Loch Ruel). The Isle of Bute lies to the south separated by the narrow Kyles of Bute which connect the Firth of Clyde to Loch Riddon. Cowal's only burgh is Dunoon in the south-east, fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kintyre
Kintyre ( gd, Cinn Tìre, ) is a peninsula in western Scotland, in the southwest of Argyll and Bute. The peninsula stretches about , from the Mull of Kintyre in the south to East and West Loch Tarbert in the north. The region immediately north of Kintyre is known as Knapdale. Kintyre is long and narrow, at no point more than from west coast to east coast, and is less than wide where it connects to Knapdale. The east side of the Kintyre Peninsula is bounded by Kilbrannan Sound, with a number of coastal peaks such as Torr Mor. The central spine of the peninsula is mostly hilly moorland, the highest point being Beinn an Tuirc at .Ordnance Survey. Landranger 1:50,000 Map Sheet 68 (South Kintyre & Cambeltown) The coastal areas and hinterland, however, are rich and fertile. Kintyre has long been a prized area for settlers, including the early Scots who migrated from Ulster to western Scotland and the Vikings or Norsemen who conquered and settled the area just before the start of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knapdale
Knapdale ( gd, Cnapadal, IPA: ˆkraÊ°pÉ™t̀ªÉ™É«̀ª forms a rural district of Argyll and Bute in the Scottish Highlands, adjoining Kintyre to the south, and divided from the rest of Argyll to the north by the Crinan Canal. It includes two parishes, North Knapdale and South Knapdale. The area is bounded by sea to the east and west (Loch Fyne and the Sound of Jura respectively), whilst the sea loch of West Loch Tarbert almost completely cuts off the area from Kintyre to the south.Ordnance Survey. Landranger 1:50000 Map Sheet 55 (Lochgilphead & Loch Awe)Ordnance Survey. Landranger 1:50000 Map Sheet 62 (North Kintyre & Tarbert) The name is derived from two Gaelic elements: ''Cnap'' meaning hill and ''Dall'' meaning field. Knapdale gives its name to the Knapdale National Scenic Area, one of the forty national scenic areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure their protection from inappropriate development. The designated area covers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |