|
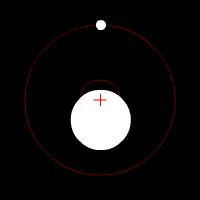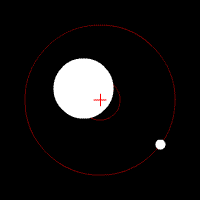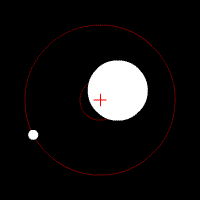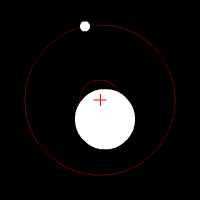
Centre Of Buoyancy
The metacentric height (GM) is a measurement of the initial static stability of a floating body. It is calculated as the distance between the centre of gravity of a ship and its #Metacentre, metacentre. A larger metacentric height implies greater initial stability against overturning. The metacentric height also influences the natural Frequency, period of rolling of a hull, with very large metacentric heights being associated with shorter periods of roll which are uncomfortable for passengers. Hence, a sufficiently, but not excessively, high metacentric height is considered ideal for passenger ships. Metacentre When a ship heels (rolls sideways), the centre of buoyancy of the ship moves laterally. It might also move up or down with respect to the water line. The point at which a vertical line through the heeled centre of buoyancy crosses the line through the original, vertical centre of buoyancy is the metacentre. The metacentre remains directly above the centre of buoyancy by defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Captain (1869)
HMS ''Captain'' was a major warship built for the Royal Navy as a semi-private venture, following a dispute between the designer and the Admiralty. With wrought-iron armour, steam propulsion, and the main battery mounted in rotating armoured turrets, the ship was, at first appearance, quite innovative and formidable. However, poor design and design changes resulted in a vessel that was overweight and ultimately unstable. In terms of seaworthiness she was reported as closely comparable to the higher freeboard turret-ship HMS ''Monarch'', but her reduced freeboard added a sense of "sluggishness". The ''Captain'' capsized in heavy seas, only five months after being commissioned, with the loss of nearly 500 lives. Background The history of the ''Captain'' can be traced back to the Crimean War and the experiences of British captain Cowper Phipps Coles in 1855. Coles and a group of British sailors constructed a raft with guns protected by a "cupola" and used the raft, named the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limit Of Positive Stability
In sailing, the limit of positive stability (LPS) or angle of vanishing stability (AVS) is the angle from the vertical at which a boat will no longer stay upright but will capsize, becoming :wikt:inverted, inverted, or Turtling (sailing), turtled. For example, if a boat with an LPS of 120 Degree (angle), degrees rolls past this point, i.e. its Mast (sailing), mast is already at an angle of 30 degrees below the water, it will continue to roll and be completely upside down in the water. Except for Dinghy sailing, dinghy sailboats and multihulls, most larger sailboats (monohull keelboats) have lead or other heavy materials in their keel at the bottom of their hulls to keep them from capsizing or turtling. The LPS was a part of the Offshore Racing Rules and is used to measure how Ship stability, stable or seaworthy a sailboat is. The modern offshore racing rules published by the International Sailing Federation may also use the measurement. See also *Angle of loll *Capsizing * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Loll
Angle of loll is the state of a ship that is unstable when upright (i.e. has a negative metacentric height) and therefore takes on an angle of heel to either port or starboard. When a vessel has negative metacentric height (GM) ''i.e.'', is in unstable equilibrium, any external force applied to the vessel will cause it to start heeling. As it heels, the moment of inertia of the vessel's waterplane (a plane intersecting the hull at the water's surface) increases, which increases the vessel's BM (distance from the centre of ''B''uoyancy to the ''M''etacenter). Since there is relatively little change in KB (distance from the ''K''eel to the centre of ''B''uoyancy) of the vessel, the KM (distance from ''K''eel to the ''M''etacentre) of the vessel increases. At some angle of heel (say 10°), KM will increase sufficiently equal to KG (distance from the keel to the centre of gravity), thus making GM of vessel equal to zero. When this occurs, the vessel goes to neutral equilibrium, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtling (sailing)
In dinghy sailing, a boat is said to be turtling or to turn turtle when the boat is fully inverted with the mast pointing down to the lake bottom, riverbed, or seabed. The name stems from the appearance of the upside-down boat, similar to the carapace (top shell) of a sea turtle. at Internet ArchiveHowever, "to turn turtle" means putting a turtle on its back by grabbing it by the flipper, and conversely is used to refer to a vessel that has turned upside down, or which has cast off its crew. A related nautical turtle metaphor is the term Turtleback Deck or "''deck, turtle'' nautical: A term applied to a weather deck that is rounded over from the shell of the ship so that it has a shape similar to the back of a turtle. Used on ships of the whaleback type and on the forward weather deck of torpedo boats." The term can be applied to any vessel; turning turtle is less frequent but more dangerous on ships than on smaller boats.In larger vessels a capsize almost inevitably leads to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclining Test
An inclining test is a test performed on a ship to determine its stability, lightship weight and the coordinates of its center of gravity. The test is applied to newly constructed ships greater than 24m in length, and to ships altered in ways that could affect stability. Inclining test procedures are specified by the International Maritime Organization and other international associations. The weight of a vessel can be readily determined by reading draughts and comparing with the known hydrostatic properties. The metacentric height (GM), which dominates stability, can be estimated from the design, but an accurate value must be determined by an inclining test. The inclining test is usually done inshore in calm weather, in still water, and free of mooring restraints to achieve accuracy. The GM position is determined by moving weights transversely to produce a known overturning moment in the range of 1-4 degrees if possible. Knowing the restoring properties (buoyancy) of the vessel fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, ''A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A''.Keesing, R.M. (1981). Cultural anthropology: A contemporary perspective (2nd ed.) p.149. Sydney: Holt, Rinehard & Winston, Inc. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics. Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect. That is, positive feedback is Phase (waves), in phase with the input, in the sense that it adds to make the input larger. Positive feedback tends to cause Control theory#Stability, system i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius Of Gyration
''Radius of gyration'' or gyradius of a body about the axis of rotation is defined as the radial distance to a point which would have a moment of inertia the same as the body's actual distribution of mass, if the total mass of the body were concentrated there. Mathematically the radius of gyration is the root mean square distance of the object's parts from either its center of mass or a given axis, depending on the relevant application. It is actually the perpendicular distance from point mass to the axis of rotation. One can represent a trajectory of a moving point as a body. Then radius of gyration can be used to characterize the typical distance travelled by this point. Suppose a body consists of n particles each of mass m. Let r_1, r_2, r_3, \dots , r_n be their perpendicular distances from the axis of rotation. Then, the moment of inertia I of the body about the axis of rotation is :I = m_1 r_1^2 + m_2 r_2^2 + \cdots + m_n r_n^2 : If all the masses are the same (m), then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Added Mass
In fluid mechanics, added mass or virtual mass is the inertia added to a system because an accelerating or decelerating body must move (or deflect) some volume of surrounding fluid as it moves through it. Added mass is a common issue because the object and surrounding fluid cannot occupy the same physical space simultaneously. For simplicity this can be modeled as some volume of fluid moving with the object, though in reality "all" the fluid will be accelerated, to various degrees. The dimensionless added mass coefficient is the added mass divided by the displaced fluid mass – i.e. divided by the fluid density times the volume of the body. In general, the added mass is a second-order tensor, relating the fluid acceleration vector to the resulting force vector on the body. Background Friedrich Bessel proposed the concept of added mass in 1828 to describe the motion of a pendulum in a fluid. The period of such a pendulum increased relative to its period in a vacuum (even after ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Acceleration
In physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of an object in free fall within a vacuum (and thus without experiencing drag). This is the steady gain in speed caused exclusively by the force of gravitational attraction. All bodies accelerate in vacuum at the same rate, regardless of the masses or compositions of the bodies; the measurement and analysis of these rates is known as gravimetry. At a fixed point on the surface, the magnitude of Earth's gravity results from combined effect of gravitation and the centrifugal force from Earth's rotation. At different points on Earth's surface, the free fall acceleration ranges from , depending on altitude, latitude, and longitude. A conventional standard value is defined exactly as . Locations of significant variation from this value are known as gravity anomalies. This does not take into account other effects, such as buoyancy or drag. Relation to the Universal Law Newton's law of universal gravitation states that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
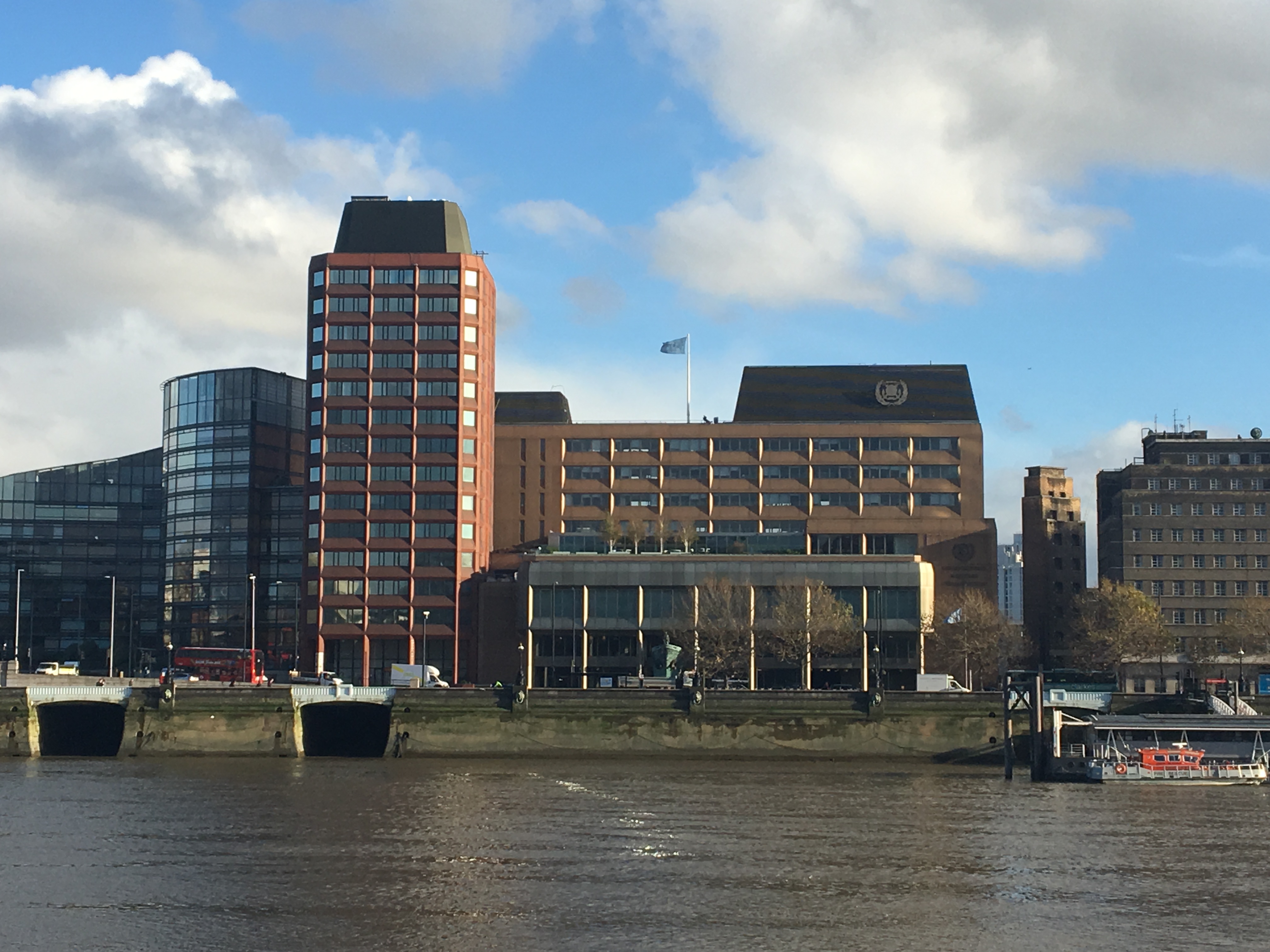
International Maritime Organization
The International Maritime Organization (IMO, French: ''Organisation maritime internationale'') is a specialised agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating shipping. The IMO was established following agreement at a UN conference held in Geneva in 1948 and the IMO came into existence ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959. Headquartered in London, United Kingdom, IMO currently has 175 Member States and three Associate Members. The IMO's primary purpose is to develop and maintain a comprehensive regulatory framework for shipping and its remit today includes maritime safety, environmental concerns, legal matters, technical co-operation, maritime security and the efficiency of shipping. IMO is governed by an assembly of members which meets every two years. Its finance and organization is administered by a council of 40 members elected from the assembly. The work of IMO is conducted through five committees and these are supported by technical subcommitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |