|
Centre (department)
Centre ( French) or Sant ( Haitian Creole; both meaning "Center") is one of the ten departments (french: départements, links=no; ht, depatman, links=no) of Haiti, located in the center of the country along the border with the Dominican Republic. As of 2015, its estimated population was 746,236. Its capital is Hinche. History Taino Period The department was part of the Marien kasika and Maguana along side San Juan de la Maguana in the DR under the leadership of Caonabo. Spanish Period Much of the Centre Departement was Spanish territorial even after the Treaty of Ryswick. Many towns were built and settled by the Spanish like Hincha, Las Caobas, San Rafael and many more. French Period The southern part of the department was French territory with towns like Mirebalais. Haitian Period Haitian Revolution The department played a big part in the Revolution serving as maroon territory extending to the Baoruco. Toussaint Louverture capture the town of Hinche from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of Haiti
In the administrative divisions of Haiti, the department (french: département d'Haïti, ; ht, depatman Ayiti) is the first of four levels of government. Haiti is divided administratively into ten departments, which are further subdivided into 42 arrondissements, 145 communes, and 571 communal sections. In 2014, there was a proposal by the Chamber of Deputies to increase the number of departments from 10 to 14 —perhaps as high as 16. Administration Each departement has a departmental council (''conseil départemental'') compound of three members elected by the departmental assembly for a 4-year term. The departmental council is led by a president (''président''). The council is the executive organ of the department. Each department has a departmental assembly who assists the council in its work. The departmental assembly is the deliberative organ of the department. The members of the departmental assembly are also elected for 4 years. The departmental assembly is led by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirebalais
Mirebalais ( ht, Mibalè) is a commune in the Centre department of Haiti, approximately 60 km northeast of Port-au-Prince on National Road 3. The city was established in 1702. American Rotarians have made a number of mission-type trips to the city and surrounding areas since the 1980s. Located along the hydroelectric power transmission grid, the city normally has electricity throughout the day and night. During the United Nations occupation of 2005, Nepalese troops were stationed in the city, using the city jail as their headquarters. A U.S. military C-17 cargo plane carried out a large airdrop of food and supplies here in the wake of the 2010 Haiti earthquake. Health Mirebalais is served by the teaching hospital Hôpital Universitaire de Mirebalais, the largest solar-operated hospital in the world. Sport Mirebalais is home to the AS Mirebalais sports team. Notable Mirebalaisians * (1877-9 March 1920) successor to Charlemagne Péralte leading the Cacos resistance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Péligre Dam
The Péligre Dam is a gravity dam located off the Centre department on the Artibonite River of Haiti. At it is the tallest dam in Haiti. The dam was created as a flood-control and an energy-providing measure in the Artibonite River Valley during the 1950s, as part of the Artibonite Valley Agricultural Project. This dam impounds Lake Péligre. Despite its purpose of providing energy throughout Haiti, many contend that the energy provided by the dam is not distributed equitably. Furthermore, the dam has had significant environmental, social, and health consequences on the local people, who were forced to relocate as a result of the dam's completion. These are points of concern to academics, journalists, and human rights activists who, noting heavy North American involvement in the planning and construction of the dam, believe that neoliberal influences may be at play. Background Geography The Péligre dam is in the Artibonite watershed, the largest hydrographic basin in Haiti. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Péligre
Lake Péligre (french: Lac de Péligre) is the second largest lake in Haiti, and is located in the Centre department. It was created as a result of the construction of the Peligre Hydroelectric Dam on the Artibonite River in 1956–1957. The project was designed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and financed by the Export-Import Bank of the United States. According to Tracy Kidder's book ''Mountains Beyond Mountains'', Brown & Root was a contractor in the Péligre Dam project. There is a lot of controversy surrounding the dam. Much of the benefit of the dam's construction has gone to a small group of wealthy individuals, at the expense of the poor farmers who utilized much of the land that is now submerged. The extreme poverty those displaced families have faced has largely been untold, but is often mentioned in the talks of Dr. Paul Farmer Paul Edward Farmer (October 26, 1959 – February 21, 2022) was an American medical anthropology, medical anthropologist and physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artibonite (department)
Artibonite ( French) or Latibonit (Haitian Creole) is one of the ten departments of Haiti located in central Haiti. With an area of 4,887 km2 it is Haiti's largest department. As of 2015, its estimated population was 1,727,524. The region is the country's main rice-growing area. The main cities are Gonaïves (the capital) and Saint-Marc. In February 2004 an insurgency tried unsuccessfully to declare Artibonite's independence. Etymology The name L'Artibonite is derived from the Artibonite River the longest river on the Quisqueya island. L'Artibonite is derived from the Taino worJa'tibonicu'meaning The Great High Place of the Sacred Waters. Under Toussaint's administration of the island, the department was known as Toussaint's Department. History Taino Period During that period the actual department seats between the three casicas of Marien, Maguana, and Xaragua. The border between those chiefdoms is assumed to be the Artibonite River. Although the department's capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Jeanne
Hurricane Jeanne was a Saffir–Simpson scale, Category 3 hurricane that struck the Caribbean and the Eastern United States in September 2004. It was the deadliest hurricane in the Atlantic basin since Hurricane Mitch, Mitch in 1998 Atlantic hurricane season, 1998. It was the tenth named tropical cyclone, storm, the seventh tropical cyclone, hurricane, and the fifth major hurricane of the season, as well as the third hurricane and fourth named storm of 2004 Atlantic hurricane season, the season to make landfall in Florida. After wreaking havoc on Hispaniola, Jeanne struggled to reorganize, eventually strengthening and performing a complete loop over the open Atlantic. It headed westwards, strengthening into a Category 3 hurricane and passing over the islands of Great Abaco and Grand Bahama in the Bahamas on September 25. Jeanne made landfall later in the day in Florida just two miles (three kilometers) from where Hurricane Frances had struck a mere three weeks earlier. Building o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deforestation In Haiti
Deforestation in Haiti is a severe environmental problem. Haitians burn wood charcoal for 60% of their domestic energy production. In 1923 over 60% of Haiti's land was forested. In 2006, less than 2% of the land was forested. Targeting of Dominican Republic forests Dominican military officials have created a lucrative charcoal trade, and have hired Haitian labor to produce charcoal just over the border. Much of this charcoal is destined for Puerto Rico and the United States mainland, although a small amount crosses over the border into Haiti. Some estimates calculate the illegal movement of 115 tons of charcoal per week from the Dominican Republic to Haiti in 2014, but these estimates are based on incomplete surveys and the numbers are highly contested. Dominican officials estimate that at least 10 trucks per week are crossing the border loaded with charcoal. The uncertainty around how much charcoal is originating from the Dominican Republic will be settled by a nationwide cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haiti Saut-d'Eau
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island which it shares with the Dominican Republic. To its south-west lies the small Navassa Island, which is claimed by Haiti but is disputed as a United States territory under federal administration."Haiti" ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Haiti is in size, the third largest country in the by area, and has an estimated population of 11.4 million, making it the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
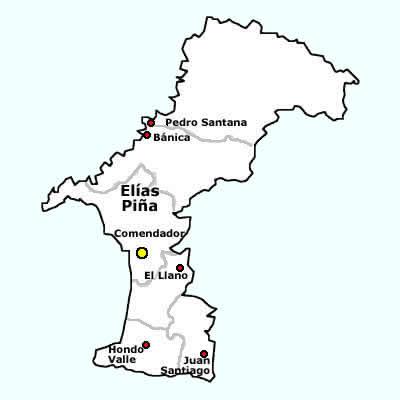
Elías Piña Province
Elías Piña () is a westernmost province which composing one of the 32 Provinces of the Dominican Republic, provinces of the Dominican Republic. It is divided into 6 municipalities and its capital city is Comendador, Elías Piña, Comendador. It is bordered by the provinces of Dajabón Province, Dajabón to the north-west, Santiago Rodríguez Province, Santiago Rodríguez to the north-east, San Juan Province (Dominican Republic), San Juan to the east, Independencia Province, Independencia to the south and the Nord-Est (department), Nord-Est department of Haiti to the west. It was created on 1942 with the name ''San Rafael''. In 1965, its name was changed to ''Estrelleta'' and, finally, in 1972 it got its current name. It was a ''municipio'' of the San Juan province before being elevated to the category of province. Location The Elías Piña province has the Dajabón Province, Dajabón and Santiago Rodríguez Province, Santiago Rodríguez provinces to the north, the San Juan Prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlemagne Péralte
Charlemagne Masséna Péralte (1886 – 1 November 1919) was a Haitian nationalist leader who opposed the United States occupation of Haiti in 1915. Leading guerrilla fighters called the Cacos, he posed such a challenge to the US forces in Haiti that the occupying forces had to upgrade their presence in the country; he was eventually killed by American troops. Péralte remains a highly praised hero in Haiti. Early life Péralte was born October 10th 1885 (or 1886) in the city of Hinche. His father was General Remi Massena Peralte. Guerrilla resistance An officer by career, Charlemagne Péralte was the military chief of the city of Léogâne when the US Marines invaded Haiti in July 1915. Refusing to surrender to foreign troops without fighting, Péralte resigned from his position and returned to his native town of Hinche to take care of his family's land. In 1917, he was arrested for a botched raid on the Hinche gendarmerie payroll, and was sentenced to five years of forced la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacos (military Group)
In Haitian history, Cacos were bodies of armed men, originally drawn from the country's enslaved population, who came to wield power in the mountainous regions of Haiti following the victory of the Haitian Revolution in 1804. The nickname "cacos" was derived from local terms for the red-plumed Hispaniolan trogon because the insurgents "used to hide, like the bird of the same name, under the leaves so as to come unexpectedly upon and attack their enemy." Resistance to the U.S. occupation, 1915–1934 The United States invaded Haiti–– ostensibly to restore order in the wake of the assassination of Haiti's president Vilbrun Guillaume Sam–– on 28 July 1915, and maintained a force of Marines to occupy the island until 1934. While U.S. forces were able to pacify the cities quite quickly, the Cacos maintained a rebellion in the mountainous areas to the north. Despite lack of local support, near Cap-Haïtien, the Cacos threatened to defeat the U.S. Marines at the Battle of Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combined arms, implementing its own infantry, artillery, aerial, and special operations forces. The U.S. Marine Corps is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. The Marine Corps has been part of the U.S. Department of the Navy since 30 June 1834 with its sister service, the United States Navy. The USMC operates installations on land and aboard sea-going amphibious warfare ships around the world. Additionally, several of the Marines' tactical aviation squadrons, primarily Marine Fighter Attack squadrons, are also embedded in Navy carrier air wings and operate from the aircraft carriers. The history of the Marine Corps began when two battalions of Continental Marines were formed on 10 November 1775 in Philadelphia as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |