|
Central Duct Excision
Central duct excision is the surgical removal (excision) of all lactiferous duct under the nipple. The excision of a single duct is called microdochectomy, a mere incision of a mammary duct (without excision) is ''microdochotomy''. Indication Central duct excision is a standard treatment of in case there is nipple discharge which stems from multiple ducts or cannot be traced back to a single duct. It is also indicated if there is bloody nipple discharge in patients beyond childbearing age. Duct excision may be indicated for the treatment of recurrent breast abscess and mastitis,, p. 1694 and the total removal of all ducts from behind the nipple has been recommended to avoid further recurrence. In particular if the patient wishes to preserve breastfeeding ability, the condition of the mammary duct system is investigated by means of galactography (ductography) or ductoscopy in order to determine whether the excision of a single duct (microdochectomy) would be sufficient. Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactiferous Duct
Lactiferous ducts are ducts that converge and form a branched system connecting the nipple to the lobules of the mammary gland. When lactogenesis occurs, under the influence of hormones, the milk is moved to the nipple by the action of smooth muscle contractions along the ductal system to the tip of the nipple. They are also referred to as ''galactophores'', ''galactophorous ducts'', ''mammary ducts'', ''mamillary ducts'' or ''milk ducts''. Structure Lactiferous ducts are lined by a columnar epithelium supported by myoepithelial cells. Prior to 2005, it was thought within the areola the lactiferous duct would dilate to form the lactiferous sinus in which milk accumulates between breastfeeding sessions. However past studies have shown that the lactiferous sinus does not exist. Function The columnar epithelium plays a key role in balancing milk production, milk stasis and reabsorption. The cells of the columnar epithelium form tight junctions which are regulated by hormones and lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipple
The nipple is a raised region of tissue on the surface of the breast from which, in females, milk leaves the breast through the lactiferous ducts to feed an infant. The milk can flow through the nipple passively or it can be ejected by smooth muscle contractions that occur along with the ductal system. The nipple is surrounded by the areola, which is often a darker colour than the surrounding skin. A nipple is often called a teat when referring to non-humans. Nipple or teat can also be used to describe the flexible mouthpiece of a baby bottle. In humans, the nipples of both males and females can be stimulated as part of sexual arousal. In many cultures, human female nipples are sexualized, or "regarded as sex objects and evaluated in terms of their physical characteristics and sexiness." Anatomy In mammals, a nipple (also called mammary papilla or teat) is a small projection of skin containing the outlets for 15–20 lactiferous ducts arranged cylindrically around the tip. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microdochectomy
Microdochectomy is the surgical removal (excision) of a lactiferous duct. A mere incision of a mammary duct (without excision) is called ''microdochotomy''. Indication Microdochectomy is a standard treatment of in case there is nipple discharge which stems from a single duct. There are preliminary indications that if ductoscopy and close follow-up are performed, in some cases microdochectomy may not be necessary despite bloody nipple discharge. Duct excision may also be indicated for the treatment of recurrent breast abscess and mastitis;, p. 1694 in this case however the total removal of all ducts from behind the nipple has been recommended to avoid further recurrence. Galactography may be used to investigate the condition of the mammary duct system before the intervention. Pre-operatively, also breast ultrasound and mammogram are performed to rule out other abnormalities of the breast. If the condition involves only a single duct, then microdochectomy may be indicated, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipple Discharge
Nipple discharge is fluid from the nipple, with or without squeezing the breast. The discharge can be milky, clear, green, purulent, bloody, or faintly yellow. The consistency can be thick, thin, sticky, or watery. Nipple discharge may be normal, such as milk in late pregnancy or after childbirth, and in newborns during the first weeks of life. It may also be normal following squeezing, in women during the reproductive years. It is likely abnormal if it occurs in men, contains blood, is from only one breast, or is associated with a breast lump, swelling, redness or overlying skin changes. Reasons for abnormal discharge include an intraductal papilloma, duct ectasia, blocked milk duct, infected breast (mastitis or breast abscess), breast cancer, certain medications, and conditions that raise prolactin. Milky discharge in a non-pregnant, non-breast feeding women is evaluated differently to other abnormal nipple discharge. Often, the cause can be determined based on symptoms and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastitis
Mastitis is inflammation of the breast or udder, usually associated with breastfeeding. Symptoms typically include local pain and redness. There is often an associated fever and general soreness. Onset is typically fairly rapid and usually occurs within the first few months of delivery. Complications can include abscess formation. Risk factors include poor latch, cracked nipples, use of a breast pump, and weaning. The bacteria most commonly involved are '' Staphylococcus'' and '' Streptococci''. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms. Ultrasound may be useful for detecting a potential abscess. Prevention is by proper breastfeeding techniques. When infection is present, antibiotics such as cephalexin may be recommended. Breastfeeding should typically be continued, as emptying the breast is important for healing. Tentative evidence supports benefits from probiotics. About 10% of breastfeeding women are affected. Types When it occurs in breastfeeding mothers, it is known as puer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's life and continue as often and as much as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfeeding has a numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactography
Galactography or ductography (or ''galactogram'', ''ductogram'') is a medical diagnostic procedure for viewing the milk ducts. The procedure involves the radiography of the ducts after injection of a radiopaque substance into the duct system through the nipple. The procedure is used for investigating the pathology of nipple discharge. Galactography is capable of detecting smaller abnormalities than mammograms, MRI or ultrasound tests. With galactography, a larger part of the ductal system can be visualized than with the endoscopic investigation of a duct (called galactoscopy or ductoscopy). Causes for nipple discharge include duct ectasia, intraductal papilloma, and occasionally ductal carcinoma in situ or invasive ductal carcinoma. The standard treatment of galactographically suspicious breast lesions is to perform a surgical intervention on the concerned duct or ducts: if the discharge clearly stems from a single duct, then the excision of the duct ( microdochectomy) is indicate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ductoscopy
Ductoscopy or mammary ductoscopy (also: ''breast duct endoscopy'', ''galactoscopy'') is a medical diagnostic procedure for viewing and collecting epithelial cells and other internal features of the milk ducts. It is capable of detecting smaller abnormalities than mammograms, MRI or ultrasound tests. Ductoscopy can be performed in a physician's office or as an outpatient in a clinic. A fiber optic scope less than a millimeter thick is inserted into the milk duct at the nipple and threaded deep into the breast through the duct. No incision is involved. An imaging system displays the output of the scope on a computer monitor. Samples of epithelial cells can be collected onto microscope slides for further analysis. Local anesthetic may be employed to reduce discomfort. Latest Mammary Ductoscope, also called Micro Endoscope, is available with the diameter of 0.35 mm. The endoscopes is used along with a 3-way cannula. The other two ports are used for saline irrigation and Biopsy For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Ultrasound
Breast ultrasound is the use of medical ultrasonography to perform imaging of the breast. It can be considered either a diagnostic or a screening procedure. It may be used either with or without a mammogram. It may be useful in younger women, where the denser fibrous tissue of the breast may make mammograms more difficult to interpret. Automated whole-breast ultrasound (AWBU) is an ultrasound investigation of the breast that is largely independent of the operator skill and that allows the reconstruction of volumetric images of the breast. Using high-frequency ultrasound, a diagnostic evaluation of the lactiferous ducts by means of ultrasound (duct sonography) can be performed. In this manner, dilated ducts and intraductal masses can be made visible. Another technique for visualizing the system of lactiferous ducts is galactography, which allows a wider area of the lactiferous duct system to be visualized. A type of ultrasound examination to measure tissue stiffness, which is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
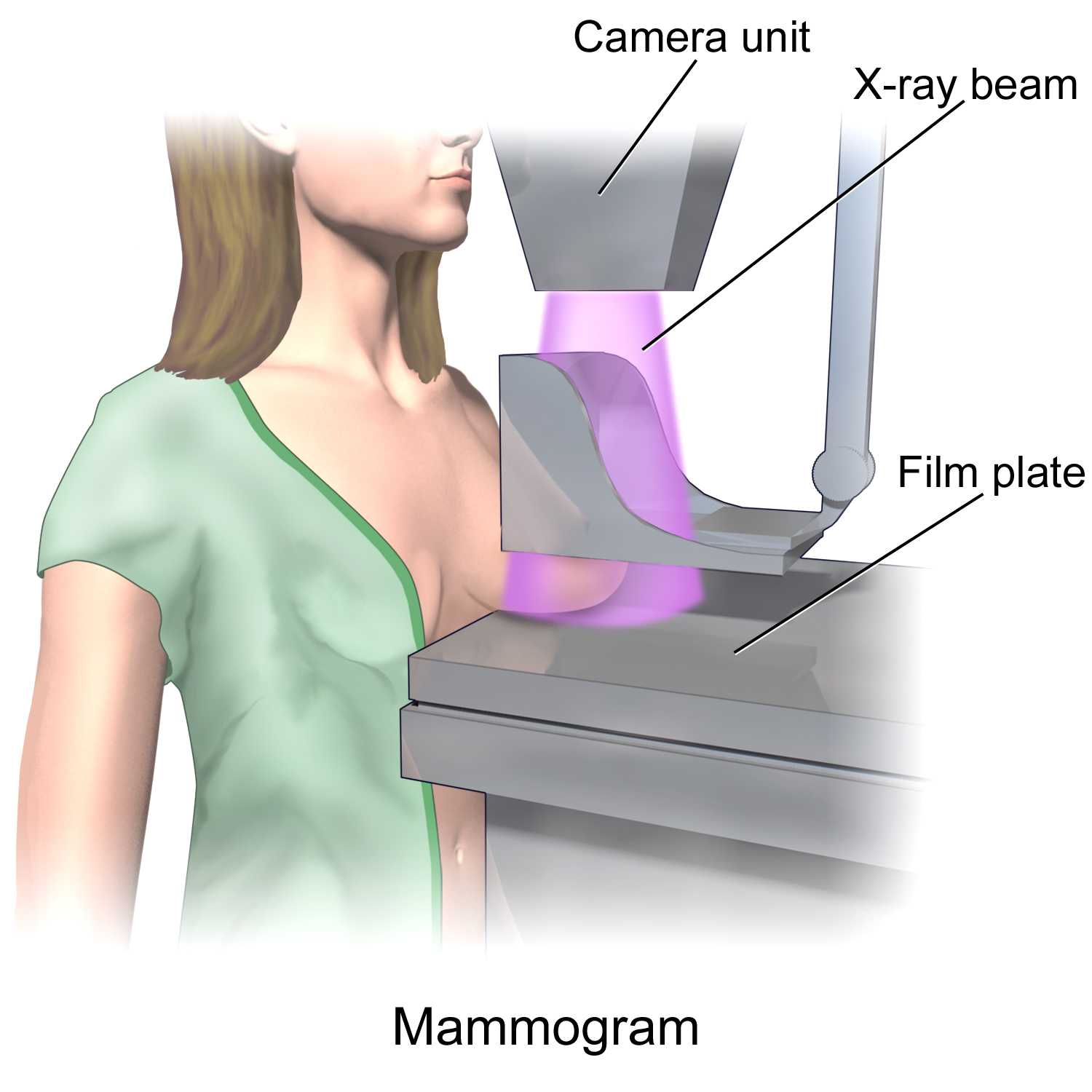
Mammogram
Mammography (also called mastography) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D (tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment and/or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palpable masses that may or may not be seen on mammo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Areola
The human areola (''areola mammae'', or ) is the pigmented area on the breast around the nipple. Areola, more generally, is a small circular area on the body with a different histology from the surrounding tissue, or other small circular areas such as an inflamed region of skin. The mature human female nipple has several small openings arranged radially around the tip of the lactiferous ducts from which milk is released during lactation. Other small openings in the areola are sebaceous glands, also known as areolar glands. Shade The areolae can range from pink to red to brown to dark brown or nearly black, but generally tend to be paler among people with lighter skin tones and darker among people with darker skin tones. A reason for the differing color may be to make the nipple area more visible to the infant. Size and shape The size and shape of areolae and nipples are also highly variable, with those of women usually being larger than those of men and prepubescent girl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, apoptosis is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates in the surrounding tissue an inflammatory response, which attracts leukocytes and nearby phagocytes which eliminate the dead cells by phagocytosis. However, microbial damaging substances released by leukocytes would crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |