|
Central America Bioregion
The Central America bioregion is a biogeographic region comprising southern Mexico and Central America. The bioregion covers the southern portion of Mexico, all of Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua, and all but easternmost Panama. WWF defines bioregions as "geographic clusters of ecoregions that may span several habitat types, but have strong biogeographic affinities, particularly at taxonomic levels higher than the species level (genus, family)."Dinerstein, Eric; David Olson; Douglas J. Graham; et al. (1995). ''A Conservation Assessment of the Terrestrial Ecoregions of Latin America and the Caribbean.'' World Bank, Washington DC. The bioregion lies in the tropics, and is home to tropical moist broadleaf forests, tropical dry broadleaf forests, and tropical coniferous forests. The higher mountains are home to cool-climate montane forests, grasslands and shrublands. Origins and prehistory Central America connects North America to South Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeographic
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area.Brown University, "Biogeography." Accessed February 24, 2014. . Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms. Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, taxonomy, geology, physical geography, palaeontology, and climatology.Dansereau, Pierre. 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency of Norway), Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-tailed Deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced to New Zealand, all the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean (Cuba, Jamaica Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ..., Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico), and some countries in Europe, such as the Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Romania and Serbia. In the Americas, it is the most widely distributed wild ungulate. In North America, the species is widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains as well as in southwestern Arizona and most of Mexico, except Baja California peninsula, Lower California. It is mostly displaced by the black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baird's Tapir
The Baird's tapir (''Tapirus bairdii''), also known as the Central American tapir, is a species of tapir native to Mexico, Central America, and northwestern South America. It is the largest of the three species of tapir native to the Americas, as well as the largest native land mammal in both Central and South America. Names The Baird's tapir is named after the American naturalist Spencer Fullerton Baird, who traveled to Mexico in 1843 and observed the animals. However, the species was first documented by another American naturalist, W. T. White. Like the other American tapirs (the mountain tapir and the South American tapir), the Baird's tapir is commonly called ''danta'' by people in all areas. In the regions around Oaxaca and Veracruz, it is referred to as the ''anteburro''. Panamanians, and Colombians call it ''macho de monte'', and in Belize, where the Baird's tapir is the national animal, it is known as the mountain cow. In Mexico, it is called ''tzemen'' in Tzeltal; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
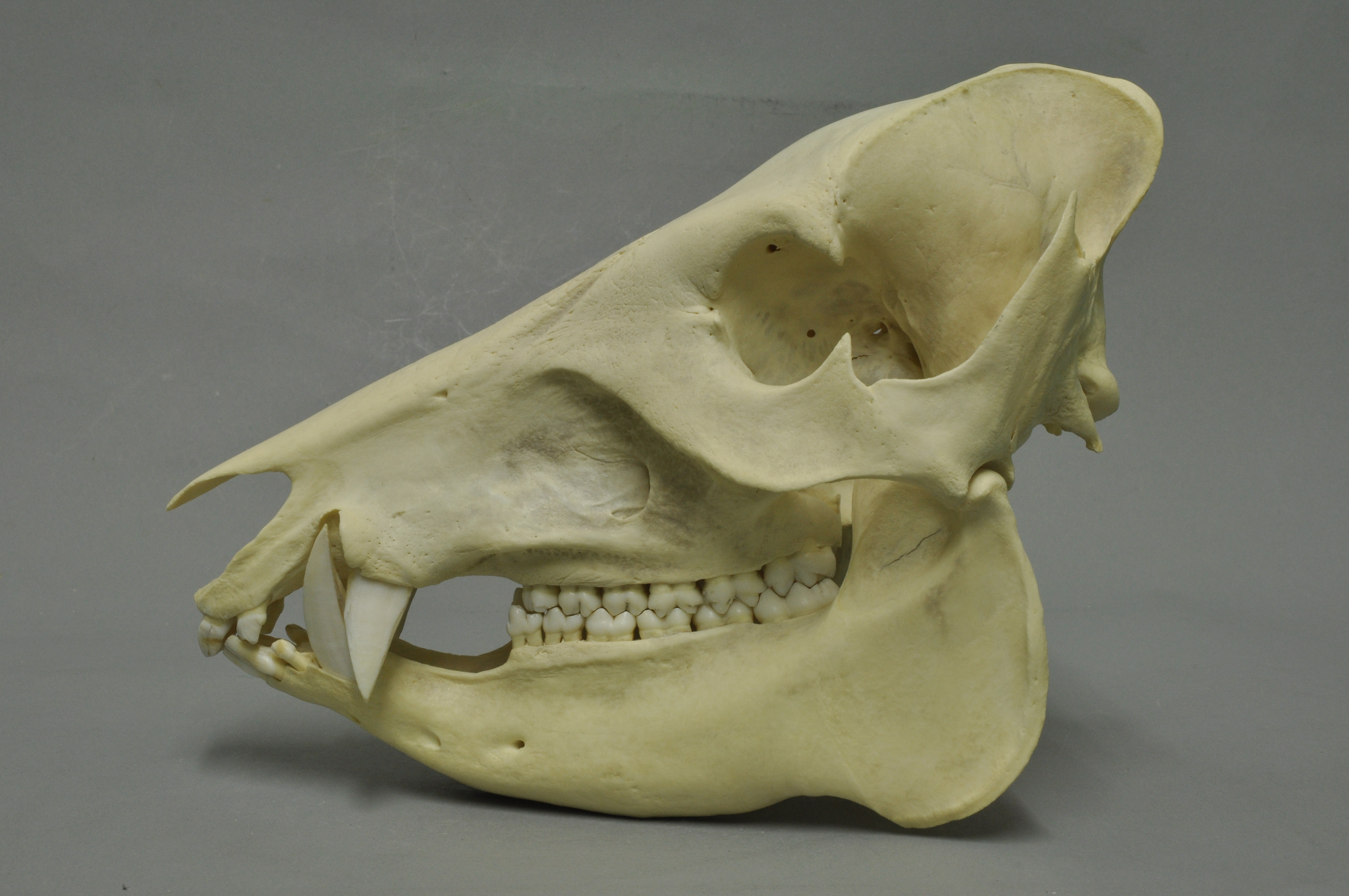
White-lipped Peccary
The white-lipped peccary (''Tayassu pecari'') is a species of peccary found in Central America, Central and South America and the only member of the genus ''Tayassu''. Multiple subspecies have been identified. White-lipped peccaries are similar in appearance to pigs, but covered in dark hair (except on certain regions, such as the throat, where it is cream (color), cream). The range of ''T. pecari'', which extends from Mexico to Argentina, has become fragmented, and the species's population is declining overall (especially in Mexico and Central America). They can be found in a variety of habitats. Social animals, white-lipped peccaries typically forage in large groups, which can have as many as 300 peccaries. They are an important part of their ecosystem and multiple efforts are being made to preserve them in the wild. Not all disappearances are explained, but human activities play a role, with two major threats being deforestation and hunting; the latter is very common in rural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drimys
''Drimys'' is a genus of about eight species of woody evergreen flowering plants, in the family Winteraceae. The species are native to the Neotropics, ranging from southern Mexico to the southern tip of South America. They are primitive dicots, associated with the humid temperate Antarctic flora of the Southern Hemisphere, which evolved millions of years ago on the ancient supercontinent of Gondwana. Members of the family generally have aromatic bark and leaves, and some are used to extract essential oils. ;Accepted species Seven species are currently accepted.''Drimys'' J.R.Forst. & G.Forst. ''Plants of the World Online'', Kew Science. Accessed 24 April 2022. *'' |
Weinmannia
''Weinmannia'' is a genus of trees and shrubs in the family Cunoniaceae. It is the largest genus of the family with about 150 species. It is also the most widespread genus, occurring in Central and South America including the Caribbean, Madagascar and surrounding islands, Malesia and the islands of the South Pacific. It is absent from mainland Africa and Australia, but some fossils have been attributed to ''Weinmannia'' in Australia. Leaves are simple or pinnate, with a margin usually toothed, and interpetiolar stipules. Flowers are bisexual, white, arranged in racemes. The fruit is a capsule opening vertically from the top to the base. Seeds hairy without wings. Taxonomy The genus has been divided into five sections: * ''Fasciculata'' (mostly Malesia, from Sumatra to Fiji) * ''Inspersa'' (Madagascar) * ''Leiospermum'' (mostly Pacific, from Bismarck archipelago to the Marquesas) * ''Spicata'' (Madagascar and Comores) * ''Weinmannia'' (Central and South America, Mascarenes) A phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyssa Talamancala
Nyssa may refer to: People * Gregory of Nyssa (335–395), 4th-century Christian bishop, theologian, and saint * Nyssa (''Doctor Who''), a fictional character in ''Doctor Who'' * Nyssa Raatko, a Batman super villainess Places * Nyssa (Alexander), a town spared by Alexander the Great in his invasion of Central Asia * Nyssa (Cappadocia), a Roman city and bishopric * Nyssa (Caria), a Hellenistic city, Asian Turkey * Nyssa (Lycia), an ancient city, Asian Turkey * Nyssa, Oregon, a city in the United States Other * ''Nyssa'' (plant), the genus name for tupelo trees * New York State Snowmobile Association * New York State Sociological Association See also * Neisse (other) * Nisa (other) * Nissa (other) * Nisse (other) * Nysa (other) Nysa may refer to: Greek Mythology * Nysa (mythology) or Nyseion, the mountainous region or mount (various traditional locations), where nymphs raised the young god Dionysus * Nysiads, nymphs of Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonobalanus Excelsa
''Trigonobalanus excelsa'' is a species of plant in the family Fagaceae. It is a tree endemic to Colombia. It is commonly known as black oak. The genus '' Trigonobalanus'' is related to the true oaks (''Quercus'') and includes three known species, ''T. excelsa'' and two species native to Southeast Asia. Description ''Trigonobalanus excelsa'' is a tree which can grow to 20-40 meters tall. Range and habitat ''Trigonobalanus excelsa'' is known from five locations in the Colombian Andes. These locations are on different mountain ranges and distant from one another. The species' estimated area of occupancy (AOO) is less than 500 km2. * The largest population is in Huila Department at the southern end of the Cordillera Oriental. It includes a black oak forest in Cueva de los Guácharos National Natural Park totaling 40,000 ha, and mountaintop black oak groves 50 km north in the towns of Pitalito, Suaza, Timaná, and Acevedo. Black oak is found only on the western slope of the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matudaea
''Matudaea'' is a genus of plant in family Hamamelidaceae. Species of ''Matudaea'' range from southern Mexico through Central America to Colombia. 'Matudaea'' Lundell ''Plants of the World Online'', Kew Science. Accessed 27 January 2023. The genus name of ''Matudaea'' is in honour of Eizi Matuda (1894–1978), who was a Mexican botanist of Japanese origin. The genus was circumscribed by Cyrus Longworth Lundell Cyrus Longworth Lundell (November 5, 1907 – March 28, 1994) was an American botanist. Education Lundell did his undergraduate studies at Columbia University and Southern Methodist University. He completed his BA at the later in 1932. He then ent ... in Lloydia vol.3 on page 209 in 1940. Accepted species * '' Matudaea colombiana'' Lozano Colombia * '' Matudaea menzelii'' Walther * '' Matudaea trinervia'' Lundell southern Mexico to Costa Rica References Hamamelidaceae Saxifragales genera Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Neotropical realm flora {{Saxifr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ticodendron
''Ticodendron incognitum'' is the only species of ''Ticodendron'', and the only member of the family Ticodendraceae. It is most closely related to the family Betulaceae. It was discovered only in 1989 in Costa Rica, having been overlooked previously due to its habitat in poorly researched cloud forests and its very 'ordinary' appearance; further research showed its range extends from southern Mexico (Veracruz, Oaxaca, Chiapas), south through Central America to Panama. It is a tree, 20–30 m tall, superficially resembling an alder in appearance, with alternate, simple leaves 5–12 cm long with a serrated margin. It is generally dioecious, with separate male and female plants. Fossil record †''Ferrignocarpus bivalvis'' fossil fruits, from the Middle Eocene of Oregon and the Early Eocene London Clay flora of southern England England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Iris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species extending into Central America, as well as the northern and southern Andes. Description With a few exceptions, alders are deciduous, and the leaves are alternate, simple, and serrated. The flowers are catkins with elongate male catkins on the same plant as shorter female catkins, often before leaves appear; they are mainly wind-pollinated, but also visited by bees to a small extent. These trees differ from the birches (''Betula'', another genus in the family) in that the female catkins are woody and do not disintegrate at maturity, opening to release the seeds in a similar manner to many conifer cones. The largest species are red alder (''A. rubra'') on the west coast of North America, and black alder (''A. glutinosa''), native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |