|
Centers (Fourth Way)
In G.I. Gurdjieff's Fourth Way teaching, also known as The Work, centers or brains refer to separate apparatuses within a being that dictate its specific functions. According to this teaching, there are three main centers: intellectual, emotional, and moving. These centers in the human body are analogous to a three-storey factory, the intellectual center being the top storey, the emotional center being the middle one, and the moving center being the bottom storey. The moving center, or the bottom storey is further divided into three separate functions: sex, instinctive, and motor. Gurdjieff classified plants as having one brain, animals two and humans three brains. In ''Beelzebub's Tales to His Grandson'', Gurdjieff greatly expanded his idea of humans as "three brained beings". In the book ''The Fourth Way'', Ouspensky refers to the "center of gravity" as being a center which different people primarily operate from (intellectuals, artists, and sports enthusiasts, for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Way
The Fourth Way is an approach to self-development developed by George Gurdjieff over years of travel in the East (c. 1890 – 1912). It combines and harmonizes what he saw as three established traditional "ways" or "schools": those of the body, the emotions, and the mind, or of fakirs, monks and yogis, respectively. Students often refer to the Fourth Way as "The Work", "Work on oneself", or "The System". The exact origins of some of Gurdjieff's teachings are unknown, but various sources have been suggested. The term "Fourth Way" was further used by his student P. D. Ouspensky in his lectures and writings. After Ouspensky's death, his students published a book entitled ''The Fourth Way'' based on his lectures. According to this system, the three traditional schools, or ways, "are permanent forms which have survived throughout history mostly unchanged, and are based on religion. Where schools of yogis, monks or fakirs exist, they are barely distinguishable from religious schools. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beelzebub's Tales To His Grandson
''Beelzebub's Tales to His Grandson'' or ''An Objectively Impartial Criticism of the Life of Man'' is the first volume of the ''All and Everything'' trilogy written by the Greek-Armenia mystic G. I. Gurdjieff. The All and Everything trilogy also includes ''Meetings with Remarkable Men'' (first published in 1963) and ''Life Is Real Only Then, When 'I Am''' (first privately printed in 1974). Purpose and significance The book was intended to be the main study tool for Gurdjieff's Fourth Way teachings. As Gurdjieff's idea of "work" is central to those teachings, Gurdjieff went to great lengths in order to increase the effort needed to read and understand it. Gurdjieff himself once said, “I bury the bone so deep that the dogs have to scratch for it." The book covers many topics. It is an allegory and myth in a literary form all its own. In his prospectus for ''All and Everything'', printed at the beginning of each part of the trilogy, Gurdjieff states his aim in the first volume o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Way (book)
''The Fourth Way'' (1957) is a book about the Fourth Way, a system of self-development as introduced by Greek-Armenian philosopher G.I. Gurdjieff. It is a compilation of the lectures of P. D. Ouspensky at London and New York City between the years 1921 through 1946, published posthumously by his students in 1957. The term "The Fourth Way" has also come to be used as a general descriptive term for the body of ideas and teachings which Gurdjieff brought to the west from his study of eastern schools.The Fourth Way, P.D, Ouspensky, Alfred A. Knopf 1957, chapter 1 Ouspensky was given the task of bringing these ideas to a wider audience in an unadulterated form by Gurdjieff. ''The Fourth Way'' is considered to be the most comprehensive statement of Gurdjieff's ideas as taught by Ouspensky. The book consists of adaptations of Ouspensky's lectures, and the accompanying question and answer sessions. The Fourth Way The 'Fourth Way' to which the title refers is a method of inner developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emotion
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or displeasure. There is currently no scientific consensus on a definition. Emotions are often intertwined with mood, temperament, personality, disposition, or creativity. Research on emotion has increased over the past two decades with many fields contributing including psychology, medicine, history, sociology of emotions, and computer science. The numerous theories that attempt to explain the origin, function and other aspects of emotions have fostered more intense research on this topic. Current areas of research in the concept of emotion include the development of materials that stimulate and elicit emotion. In addition, PET scans and fMRI scans help study the affective picture processes in the brain. From a mechanistic perspective, emotions can be defined as "a positive or negative experience that is as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
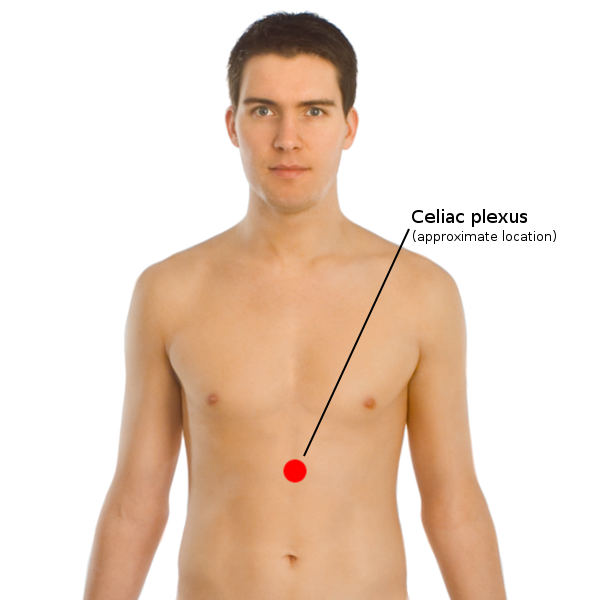
Solar Plexus
The celiac plexus, also known as the solar plexus because of its radiating nerve fibers, is a complex network of nerves located in the abdomen, near where the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, and renal arteries branch from the abdominal aorta. It is behind the stomach and the omental bursa, and in front of the crura of the diaphragm, on the level of the first lumbar vertebra. The plexus is formed in part by the greater and lesser splanchnic nerves of both sides, and fibers from the anterior and posterior vagal trunks. The celiac plexus proper consists of the celiac ganglia with a network of interconnecting fibers. The aorticorenal ganglia are often considered to be part of the celiac ganglia, and thus, part of the plexus. Structure The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses: Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus: Terminology The celiac plexus is often popularly referred to as the solar plexus. In the context of sparring or inj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of logical truths. It is a formal science investigating how conclusions follow from premises in a topic-neutral way. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Formal logic contrasts with informal logic, which is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. While there is no general agreement on how formal and informal logic are to be distinguished, one prominent approach associates their difference with whether the studied arguments are expressed in formal or informal languages. Logic plays a central role in multiple fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises together with a conclusion. Premises and conclusions are usually un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reasoning
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, language, mathematics, and art, and is normally considered to be a distinguishing ability possessed by humans. Reason is sometimes referred to as rationality. Reasoning is associated with the acts of thinking and cognition, and involves the use of one's intellect. The field of logic studies the ways in which humans can use formal reasoning to produce logically valid arguments. Reasoning may be subdivided into forms of logical reasoning, such as: deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, and abductive reasoning. Aristotle drew a distinction between logical discursive reasoning (reason proper), and intuitive reasoning, in which the reasoning process through intuition—however valid—may tend toward the personal and the subjectively opaq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtle Body
A subtle body is a "quasi material" aspect of the human body, being neither solely physical nor solely spiritual, according to various esoteric, occult, and mystical teachings. This contrasts with the mind–body dualism that has dominated Western thought. The subtle body is important in the Taoism of China and Dharmic religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, mainly in the branches which focus on tantra and yoga, where it is known as the ''Sūkṣma-śarīra'' ( sa, सूक्ष्म शरीर). However, while mostly associated with Asian cultures, non-dualistic approaches to the mind and body are found in many parts of the world. Subtle body concepts and practices can be identified as early as 2nd century BCE in Taoist texts found in the Mawangdui tombs. Although "evidently present" in Indian thought as early as the 4th to 1st century BCE when the Taittiriya Upanishad describes the Panchakoshas, a series of five interpenetrating sheaths of the body. A fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Search Of The Miraculous
''In Search of the Miraculous: Fragments of an Unknown Teaching'' is a 1949 book by Russian philosopher P. D. Ouspensky which recounts his meeting and subsequent association with George Gurdjieff George Ivanovich Gurdjieff (; rus, Гео́ргий Ива́нович Гурджи́ев, r=Geórgy Ivánovich Gurdzhíev, p=ɡʲɪˈorɡʲɪj ɪˈvanəvʲɪd͡ʑ ɡʊrd͡ʐˈʐɨ(j)ɪf; hy, Գեորգի Իվանովիչ Գյուրջիև; c. 1 .... According to Sophia Wellbeloved, the book is generally regarded as the most comprehensive account of Gurdjieff's system of thought ever published, as it often forms the basis from which Gurdjieff and his teachings are understood. Editions * ''In Search of the Miraculous: The Definitive Exploration of G. I. Gurdjieff's Mystical Thought and Universal View'', Harvest Book; New edition, 2001. . : "In Search of the Miraculous - August 2010 - identical copy of first hardback edition. Paul H. Crompton Ltd. See also * Fragments of an Unknow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Will
Free will is the capacity of agents to choose between different possible courses of action unimpeded. Free will is closely linked to the concepts of moral responsibility, praise, culpability, sin, and other judgements which apply only to actions that are freely chosen. It is also connected with the concepts of advice, persuasion, deliberation, and prohibition. Traditionally, only actions that are freely willed are seen as deserving credit or blame. Whether free will exists, what it is and the implications of whether it exists or not are some of the longest running debates of philosophy and religion. Some conceive of free will as the right to act outside of external influences or wishes. Some conceive free will to be the capacity to make choices undetermined by past events. Determinism suggests that only one course of events is possible, which is inconsistent with a libertarian model of free will. Ancient Greek philosophy identified this issue, which remains a major focus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Of Creation
The Ray of Creation is an esoteric cosmology which was taught by G. I. Gurdjieff. It is a diagram which better represents the place which Earth occupies in the Universe. The diagram has eight levels, each corresponding to Gurdjieff's Law of Octaves (see ''In Search of the Miraculous'', chapter 7). Levels The first level is "The Absolute", followed by "All Worlds", "All Suns", "Sun", "All Planets", "Earth", "Moon", and "The Absolute": * The heaviest/last level - "The Absolute" * Earth's satellite - "The Moon" * Our planet - "Earth" * All of the planets in the solar system to which Earth belongs to - "All Planets" * The planets belong to the "Sun" or the solar system * The Sun belongs to the Milky Way galaxy or the "All Suns" combined * All galaxies put together belong to "All Worlds" * All Worlds form a final whole called "The Absolute" This lineage indicates and compares the construction of all of the levels, matters, and laws of the Universe, placing them in scale with one anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Way Enneagram
The Fourth Way enneagram is a figure published in 1949 in ''In Search of the Miraculous'' by P.D. Ouspensky, and an integral part of the Fourth Way esoteric system associated with George Gurdjieff. The term " enneagram" derives from two Greek words, ''ennea'' (nine) and ''gramma'' (something written or drawn), and was coined by Gurdjieff in the period before the 1940s. The enneagram is a nine-pointed figure usually inscribed within a circle. Within the circle is a triangle connecting points 9, 3 and 6. The inscribed figure resembling a web connects the other six points in a cyclic figure 1-4-2-8-5-7. This number is derived from or corresponds to the recurring decimal . 142857 = 1/7. These six points together with the point numbered 9 are said to represent the main stages of any complete process, and can be related to the notes of a musical octave, 9 being equivalent to "Do" and 1 to "Re" etc. The points numbered 3 and 6 are said to represent "shock points" which affect the way a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
