|
Cen Can
Cen Shen or Cen Can (), 715–770, was one of the great Chinese poets of the Tang dynasty. His poems were included in the Three Hundred Poems anthology. Name He is also called Cen Jiazhou (). During the reign of Emperor Suzong he was made governor () of Jia Prefecture (''Jiazhou'' in Chinese), which earned him the name Cen Jiazhou.'' Kanjigen'' entry "Cen Can" (Shinshin/Shinjin). Gakken 2006. Life He was born to a bureaucratic family in Nanyang (in today's Henan), but later moved to Jiangling, Jizhou (in today's Hubei). His great-grandfather Cen Wenben, granduncle Cen Changqian and uncle Cen Xi were all chancellors. His father Cen Zhi was Governor (Cishi) of Jingzhou. When Cen Shen was 10, his father died, and the financial situation of his family worsened. After then, Cen learned with assiduity, reading a lot of scriptures and history books. He moved to Chang'an when he was 20 and obtained jinshi in 744. In 749, Cen's ambitions lead him towards a stint of military servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cen (surname)
Cen is the Mandarin pinyin romanization of the Chinese surname written in Chinese character. It is romanized Ts'en in Wade–Giles, and variously as Sam, Sum, Sham, Shum in Cantonese, Gim, Khim, Chim in Taiwanese Hokkien and Chen in other pinyin forms. Cen is listed 67th in the Song dynasty classic text ''Hundred Family Surnames''. As of 2008, it is the 235th most common surname in China, shared by 340,000 people. Cen is considered a rare surname. A person with a rare surname like Cen may be able to trace his or her origins to a single ancestral area. Notable people * Cen Peng ( 岑彭; died 36 AD). Han dynasty general. * Cen Hun ( 岑昏; died 280). Government Minister of Eastern Wu. * Cen Derun ( 岑德潤; circa 5th - 6th century), Southern Dynasties poet. * Cen Wenben ( 岑文本; 595–645). Viscount Xian of Jiangling, Tang dynasty chancellor. * Cen Changqian ( 岑長倩; died 691), Tang dynasty chancellor, nephew of Cen Wenben. * Cen Xi ( 岑羲; died 713), Tang dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Examination
The imperial examination (; lit. "subject recommendation") refers to a civil-service examination system in Imperial China, administered for the purpose of selecting candidates for the state bureaucracy. The concept of choosing bureaucrats by merit rather than by birth started early in Chinese history, but using written examinations as a tool of selection started in earnest during the Sui dynasty (581–618) then into the Tang dynasty of 618–907. The system became dominant during the Song dynasty (960–1279) and lasted for almost a millennium until its abolition in the late Qing dynasty reforms in 1905. Aspects of the imperial examination still exist for entry into the civil service of contemporary China, in both the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Republic of China (ROC). The exams served to ensure a common knowledge of writing, Chinese classics, and literary style among state officials. This common culture helped to unify the empire, and the ideal of achievement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quan Tangshi
(''Complete Tang Poems'') is the largest collection of Tang poetry, containing some 49,000 lyric poems by more than twenty-two hundred poets. In 1705, it was commissioned at the direction of the Qing dynasty Kangxi Emperor and published under his name. The is the major reservoir of surviving Tang dynasty poems, from which the pre-eminent shorter anthology, ''Three Hundred Tang Poems'', is largely drawn. Compilation In 1705, the Kangxi Emperor issued an edict to Cao Yin, a trusted imperial bondservant, official, and a literary figure in his own right. He commanded Cao to compile and publish all the surviving (lyric poems) of the Tang, inaugurating the first of the great literary projects for which the Manchu dynasty became famous. The emperor also appointed nine scholars of the Hanlin Academy to oversee the collation of the texts. The team compared texts from various libraries as well as checking into private collections. Cao trained calligraphers in a common style of wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Thousand Years Of Chinese Poetry
3 is a number, numeral, and glyph. 3, three, or III may also refer to: * AD 3, the third year of the AD era * 3 BC, the third year before the AD era * March, the third month Books * ''Three of Them'' (Russian: ', literally, "three"), a 1901 novel by Maksim Gorky * ''Three'', a 1946 novel by William Sansom * ''Three'', a 1970 novel by Sylvia Ashton-Warner * ''Three'' (novel), a 2003 suspense novel by Ted Dekker * ''Three'' (comics), a graphic novel by Kieron Gillen. * ''3'', a 2004 novel by Julie Hilden * ''Three'', a collection of three plays by Lillian Hellman * ''Three By Flannery O'Connor'', collection Flannery O'Connor bibliography Brands * 3 (telecommunications), a global telecommunications brand ** 3Arena, indoor amphitheatre in Ireland operating with the "3" brand ** 3 Hong Kong, telecommunications company operating in Hong Kong ** Three Australia, Australian telecommunications company ** Three Ireland, Irish telecommunications company ** Three UK, British telecomm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disasters Of Partisan Prohibitions
The Disasters of the Partisan Prohibitions (黨錮之禍) refers to two incidents in which a number of Confucian scholars who served as officials in the Han imperial government and opposed to powerful eunuchs, and the university students in the capital Luoyang who supported them (collectively referred to by the eunuchs as "partisans" (黨人, ''dangren''), were imprisoned. Some were executed; some were released but lost their civil rights. The first incident (in 166) was largely bloodless, but the second incident (in 169), which came after the Confucian scholars Dou Wu (the father of Empress Dowager Dou) and Chen Fan were defeated by eunuchs in a physical confrontation, saw a large number of the partisans lose their lives. The restrictions on civil liberties imposed on the surviving partisans were not lifted until 184 when Emperor Ling was concerned that the partisans would join the Yellow Turban Rebellion. First Disaster of the Partisan Prohibitions The root of the first Disas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Later Han
The ''Book of the Later Han'', also known as the ''History of the Later Han'' and by its Chinese name ''Hou Hanshu'' (), is one of the Twenty-Four Histories and covers the history of the Han dynasty from 6 to 189 CE, a period known as the Later or Eastern Han. The book was compiled by Fan Ye and others in the 5th century during the Liu Song dynasty, using a number of earlier histories and documents as sources. Background In 23 CE, Han dynasty official Wang Mang was overthrown by a peasants' revolt known as the Red Eyebrows. His fall separates the Early (or Western) Han Dynasty from the Later (or Eastern) Han Dynasty. As an orthodox history, the book is unusual in being completed over two hundred years after the fall of the dynasty. Fan Ye's primary source was the ''Dongguan Han Ji'' (東觀漢記; "Han Records of the Eastern Lodge"), which was written during the Han dynasty itself. Contents References Citations Sources ; General * Chavannes, Édouard (1906).T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Poetry
Tang poetry () refers to poetry written in or around the time of or in the characteristic style of China's Tang dynasty, (June 18, 618 – June 4, 907, including the 690–705 reign of Wu Zetian) and/or follows a certain style, often considered as the Golden Age of Chinese poetry. The ''Quan Tangshi'' includes over 48,900 poems written by over 2,200 authors. During the Tang dynasty, poetry continued to be an important part of social life at all levels of society. Scholars were required to master poetry for the civil service exams, but the art was theoretically available to everyone. This led to a large record of poetry and poets, a partial record of which survives today. The two most famous poets of the period were Li Bai and Du Fu. Through the ''Three Hundred Tang Poems'', Tang poetry has remain familiar to educated Chinese in modern times. Periodization The periodization scheme employed in this article is the one detailed by the Ming dynasty scholar Gao Bing (1350–1423) in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantangshi
(''Complete Tang Poems'') is the largest collection of Tang poetry, containing some 49,000 lyric poems by more than twenty-two hundred poets. In 1705, it was commissioned at the direction of the Qing dynasty Kangxi Emperor and published under his name. The is the major reservoir of surviving Tang dynasty poems, from which the pre-eminent shorter anthology, ''Three Hundred Tang Poems'', is largely drawn. Compilation In 1705, the Kangxi Emperor issued an edict to Cao Yin, a trusted imperial bondservant, official, and a literary figure in his own right. He commanded Cao to compile and publish all the surviving (lyric poems) of the Tang, inaugurating the first of the great literary projects for which the Manchu dynasty became famous. The emperor also appointed nine scholars of the Hanlin Academy to oversee the collation of the texts. The team compared texts from various libraries as well as checking into private collections. Cao trained calligraphers in a common style of writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Hundred Tang Poems
The ''Three Hundred Tang Poems'' () is an anthology of poems from the Chinese Tang dynasty (618–907). It was first compiled around 1763 by Sun Zhu (1722–1778Yu, 64–65), who was a Qing Dynasty scholar and was also known as Hengtang Tuishi (, "Retired Master of Hengtang"). Various later editions also exist. All editions contain slightly more than 300 total poems. The number 300 (or more exactly 305) was a classic number for a poetry collection due to the influence of the ''Classic of Poetry'' (, ''Shijing''), which was generally known as ''The Three Hundred Poems''. Dissatisfied with the anthology ''Poems by a Thousand Masters'' (, ''Qianjiashi'') compiled by Liu Kezhuang in the late Southern Song, and influenced by Ming Dynasty poetry anthologies, Sun selected the poems based on their popularity and educational value. The collection has been popular ever since and can be found in many Chinese households. For centuries, elementary students memorized the poems and used them to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
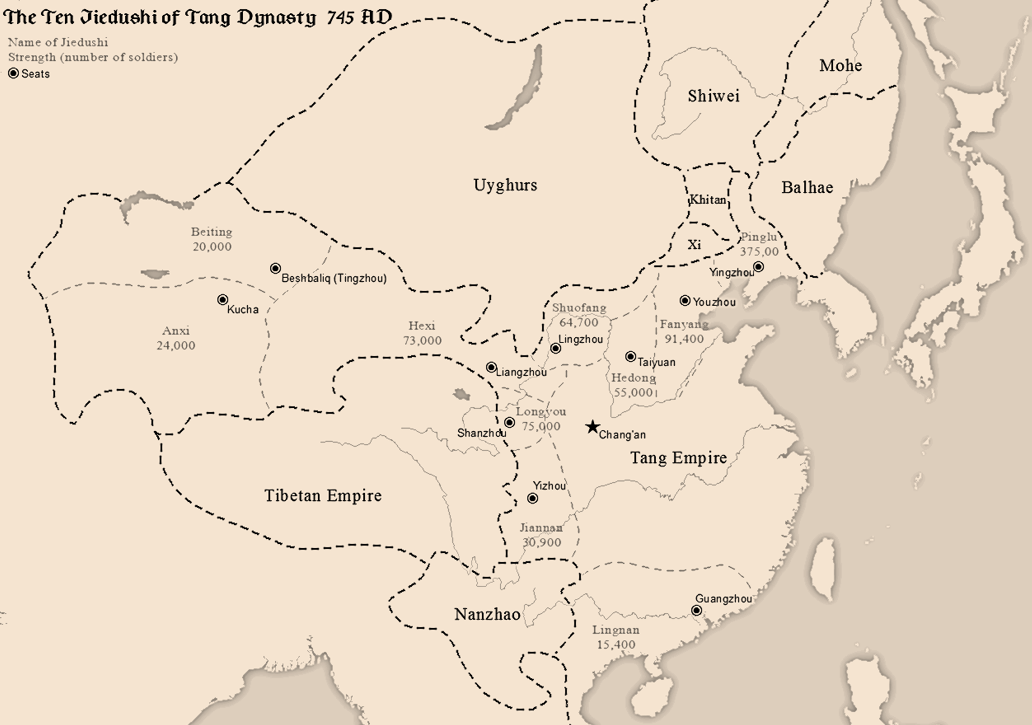
An Shi Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general officer of the Tang military system. The event involved military activity and direct deaths from battle, but also significant associated population loss from famine, and population dislocations. The event is also known, especially in Chinese historiography, either as the An–Shi Rebellion or as the An–Shi Disturbances (). The use of the term ''luàn'' ("chaos") indicates the extreme social instability and population loss which eventually resulted, far beyond the initial consequences of the rebellion. Traditionally, Chinese family names have begun with the family name first. In this case the family name of the initial rebel leader is An. The term ''Ān-Shǐ'' is used to recognize that the rebellion continued after An Lushan's death, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Du Fu
Du Fu (; 712–770) was a Tang dynasty poet and politician. Along with his elder contemporary and friend Li Bai (Li Po), he is frequently called the greatest of the Chinese poets.Ebrey, 103. His greatest ambition was to serve his country as a successful civil servant, but he proved unable to make the necessary accommodations. His life, like the whole country, was devastated by the An Lushan Rebellion of 755, and his last 15 years were a time of almost constant unrest. Although initially he was little-known to other writers, his works came to be hugely influential in both Chinese and Japanese literary culture. Of his poetic writing, nearly fifteen hundred poems have been preserved over the ages. He has been called the "Poet-Historian" and the "Poet-Sage" by Chinese critics, while the range of his work has allowed him to be introduced to Western readers as "the Chinese Virgil, Horace, Ovid, Shakespeare, Milton, Burns, Wordsworth, Béranger, Hugo or Baudelaire".Hung, 1. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |