|
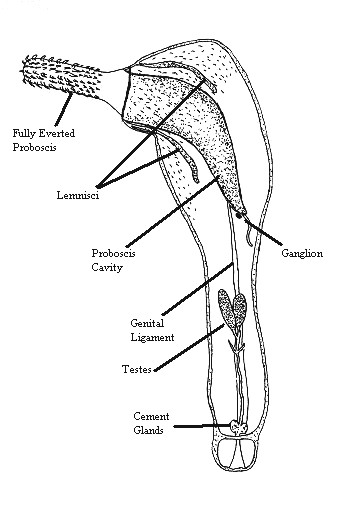
Cement Glands
Cement glands are small organs found in Acanthocephala that are used to temporarily close the posterior end of the female after copulation. Cement glands are also mucus-secreting organs that can attach embryos or larvae to a solid substrate. These can be found in frogs such as those in the genus Xenopus, fish such as the Mexican tetra The Mexican tetra (''Astyanax mexicanus''), also known as the blind cave fish, blind cave characin, and blind cave tetra, is a freshwater fish of the family Characidae of the order Characiformes. The type species of its genus, it is native to th ..., and crustaceans. References Animal anatomy Parasites {{Animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
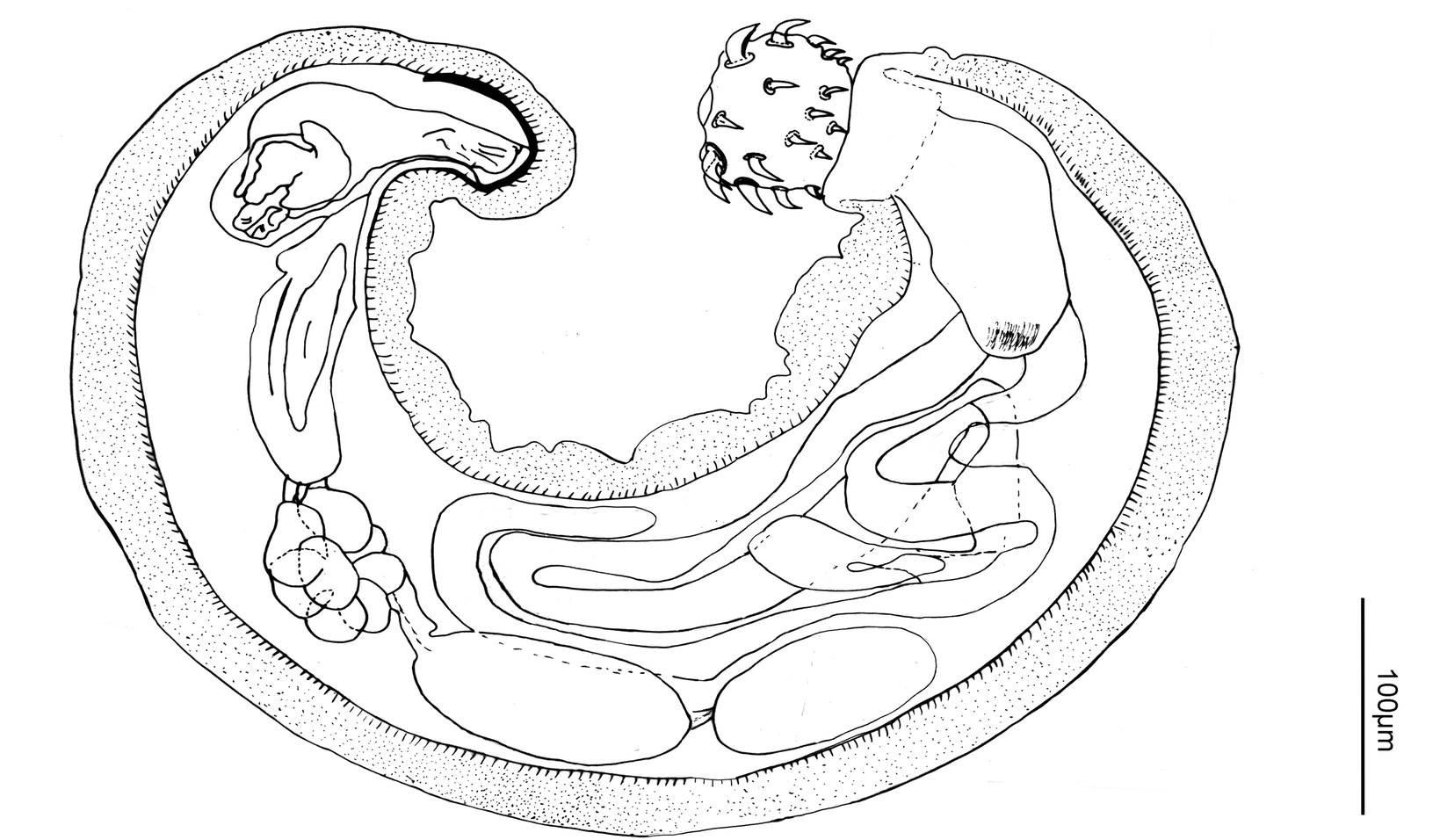
Pachysentis Lauroi
''Pachysentis'' is a genus in Acanthocephala (thorny-headed worms, also known as spiny-headed worms) that parasitize primates and carnivorans. They are distributed across Africa, the Middle East, and the Americas. ''Pachysentis'' species attach themselves to the inner lining of the gastrointestinal tract of their hosts using their hook-covered proboscis. Their life cycle includes an egg stage found in host feces, a cystacanth (larval) stage in an intermediate host such as the Egyptian cobra, and an adult stage where cystacanths mature in the intestines of the host. This genus appears identical to the closely related '' Oncicola'' apart from a greater number of hooks on the proboscis. There are eleven species assigned to this genus, although ''P. septemserialis'' is of uncertain taxonomic status. The female worms range from long and wide in ''P. lauroi'' to long and wide in ''P. dollfusi''. Virtually all of the length is the trunk, with a short proboscis. There is pronounced s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthocephala
Acanthocephala (Greek , ', thorn + , ', head) is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described. The Acanthocephala were thought to be a discrete phylum. Recent genome analysis has shown that they are descended from, and should be considered as, highly modified rotifers. This unified taxon is known as Syndermata. History The earliest recognisable description of Acanthocephala – a worm with a proboscis armed with hooks – was made by Italian author Francesco Redi (1684).Crompton 1985, p. 27 In 1771, Joseph Koelreuter proposed the name Acanthocephala. Philipp Ludwig Statius Müller independently called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenopus
''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos''=strange, πους, ''pous''=foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known species of this genus are ''Xenopus laevis'' and ''Xenopus tropicalis'', which are commonly studied as model organisms for developmental biology, cell biology, toxicology, neuroscience and for modelling human disease and birth defects. The genus is also known for its polyploidy, with some species having up to 12 sets of chromosomes. Characteristics ''Xenopus laevis'' is a rather inactive creature. It is incredibly hardy and can live up to 15 years. At times the ponds that ''Xenopus laevis'' is found in dry up, compelling it, in the dry season, to burrow into the mud, leaving a tunnel for air. It may lie dormant for up to a year. If the pond dries up in the rainy season, ''Xenopus laevis'' may migrate long distances to another pond, main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Tetra
The Mexican tetra (''Astyanax mexicanus''), also known as the blind cave fish, blind cave characin, and blind cave tetra, is a freshwater fish of the family (biology), family Characidae of the order (biology), order Characiformes. The type species of its genus, it is native to the Nearctic realm, originating in the lower Rio Grande and the Nueces River, Neueces and Pecos Rivers in Texas, as well as the central and eastern parts of Mexico. Growing to a maximum total length of , the Mexican tetra is of typical characin shape, with unremarkable, drab coloration. Its Blind fish, blind cave form, however, is notable for having no eyes or pigment; it has a pinkish-white color to its body (resembling an Albinism in biology, albino). This fish, especially the blind variant, is reasonably popular among aquarists. ''A. mexicanus'' is a peaceful species that spends most of its time in midlevel water above the rocky and sandy bottoms of pools and backwaters of creeks and rivers of its nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |