|
Celtic Peoples
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century bc, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . " e Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe."; in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts In Europe-fr
The Celts (, see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century bc, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . "[T]he Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe."; in Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Celtic
The pre-Celtic period in the prehistory of Central Europe and Western Europe occurred before the expansion of the Celts or their culture in Iron Age Europe and Anatolia (9th to 6th centuries BC), but after the emergence of the Proto-Celtic language and cultures. The area involved is that of the maximum extent of the Celtic languages in about the mid 1st century BC. The extent to which Celtic language, culture and genetics coincided and interacted during this period remains very uncertain and controversial. Languages Proto-Celtic is mainly dated to approximately 800 BC, coincident with the Hallstatt culture, while the earliest possible divergence of pre-proto-Celtic dialects from Proto-Indo-European is mainly dated to between 3000 BC and 2000 BC. In continental Europe, pre-Celtic languages of the European Bronze Age may be taken to comprise two distinct groups. * Non-Indo-European languages (i.e. pre-Indo-European languages); these include Basque, Rhaetic, Etrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul ( la, Gallia Cisalpina, also called ''Gallia Citerior'' or ''Gallia Togata'') was the part of Italy inhabited by Celts (Gauls) during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC. After its conquest by the Roman Republic in the 200s BC it was considered geographically part of Roman Italy but remained administratively separated until 42 BC. It was a Roman province from c. 81 BC until 42 BC, when it was ''de jure'' merged into Roman Italy as indicated in Caesar's unpublished acts (''Acta Caesaris''). Cisalpine means "on this side of the Alps" (from the perspective of the Romans), as opposed to Transalpine Gaul ("on the far side of the Alps"). Gallia Cisalpina was further subdivided into ''Gallia Cispadana'' and ''Gallia Transpadana'', i.e. its portions south and north of the Po River, respectively. The Roman province of the 1st century BC was bounded on the north and west by the Alps, in the south as far as Placentia by the river Po, and then by the Apennines and the river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (), ** * Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica'' ** ** * french: Péninsule Ibérique * mwl, Península Eibérica * eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defining the westernmost edge of Eurasia. It is principally divided between Spain and Portugal, comprising most of their territory, as well as a small area of Southern France, Andorra, and Gibraltar. With an area of approximately , and a population of roughly 53 million, it is the second largest European peninsula by area, after the Scandinavian Peninsula. Name Greek name The word ''Iberia'' is a noun adapted from the Latin word "Hiberia" originating in the Ancient Greek word Ἰβηρία ('), used by Greek geographers under the rule of the Roman Empire to refer to what is known today in English as the Iberian Peninsula. At that time, the name did not describe a single geographical entity or a distinct population; the same name was us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, and over six thousand smaller islands."British Isles", ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. They have a total area of and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland (which covers roughly five-sixths of Ireland), and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Channel Islands, off the north coast of France, are normally taken to be part of the British Isles, even though they do not form part of the archipelago. The oldest rocks are 2.7 billion years old and are found in Ireland, Wales and the northwest of Scotland. During the Silurian period, the north-western regions collided with the south-east, which had been part of a separate continental landmass. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Migration
Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location (geographic region). The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another (external migration), but internal migration (within a single country) is also possible; indeed, this is the dominant form of human migration globally. Migration is often associated with better human capital at both individual and household level, and with better access to migration networks, facilitating a possible second move. It has a high potential to improve human development, and some studies confirm that migration is the most direct route out of poverty.Age is also important for both work and non-work migration. People may migrate as individuals, in family units or in large groups. There are four major forms of migration: invasion, conquest, colonization and emigration/immigration. Persons moving from their home due to forced displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-cultural Diffusion
In cultural anthropology and cultural geography, cultural diffusion, as conceptualized by Leo Frobenius in his 1897/98 publication ''Der westafrikanische Kulturkreis'', is the spread of cultural items—such as ideas, styles, religions, technologies, languages—between individuals, whether within a single culture or from one culture to another. It is distinct from the diffusion of innovations within a specific culture. Examples of diffusion include the spread of the war chariot and iron smelting in ancient times, and the use of automobiles and Western business suits in the 20th century. Types Five major types of cultural diffusion have been defined: * Expansion diffusion: an innovation or idea that develops in a source area and remains strong there, while also spreading outward to other areas. This can include hierarchical, stimulus, and contagious diffusion. * Relocation diffusion: an idea or innovation that migrates into new areas, leaving behind its origin or source of the cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
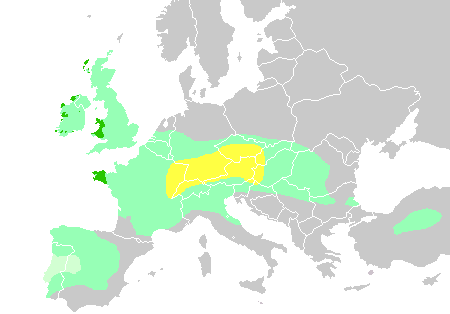
La Tène (archaeological Site)
La Tène is a protohistoric archaeological site on the northern shore of Lake Neuchâtel, Switzerland. Dating to the second part of the European Iron Age it is the type site of the La Tène culture, which dates to about 450 BCE to the 1st century BCE and extends from Ireland to Anatolia and from Portugal to Czechia. La Tène is listed as a property of national significance. Location The site is located in the ''lieu-dit'' La Tène, which is related to the Latin ''tenuis'' evoking the shallow waters of the lake's northernmost extremity. It is also the point where the Thielle river leaves the lake and flows in the direction of lake Biel. Being constantly in the vicinity of the lake, the artifacts were marked by the changes in the lake level. Research history Discovery The site of La Tène was discovered in 1857 during a period dubbed the "lake dwelling fever" (in French: ''"fièvre lacustre''"). Pile-dwellings were found on the banks of many Swiss lakes, most of the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
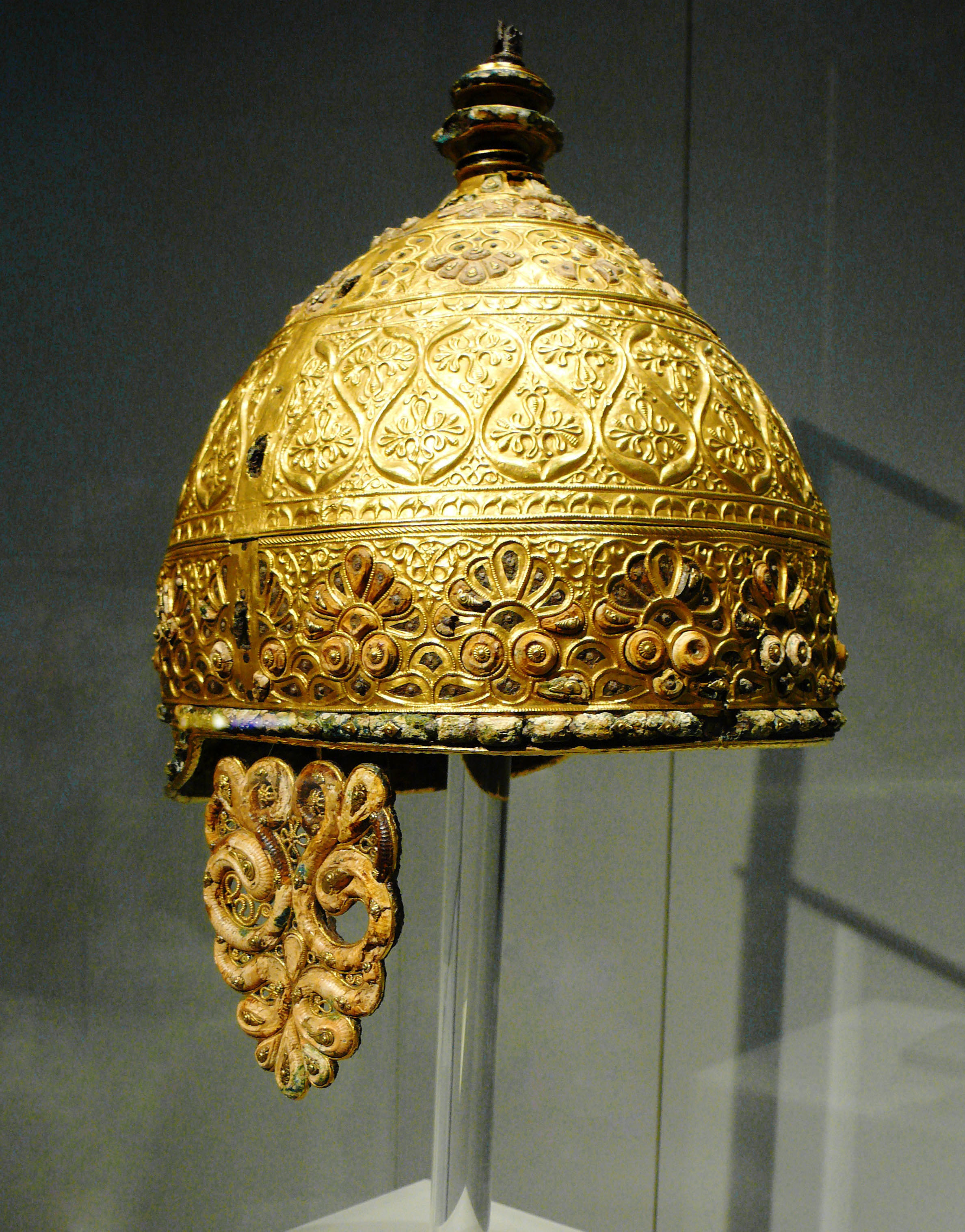
La Tène Culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscans, and the Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences. La Tène culture's territorial extent corresponded to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Austria, England, Southern Germany, the Czech Republic, parts of Northern Italy and Central Italy, Slovenia and Hungary, as well as adjacent parts of the Netherlands, Slovakia, Serbia, Croatia, Transylvania (western Romania), and Transcarpathia (western Ukraine). The Celtiberians of western Iberia shared many aspects of the culture, though not generally the artistic style. To the north extended the contemporary Pre-Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallstatt
Hallstatt ( , , ) is a small town in the district of Gmunden, in the Austrian state of Upper Austria. Situated between the southwestern shore of Hallstätter See and the steep slopes of the Dachstein massif, the town lies in the Salzkammergut region, on the national road linking Salzburg and Graz. Hallstatt is known for its production of salt, dating back to prehistoric times, and gave its name to the Hallstatt culture, the archaeological culture linked to Proto-Celtic and early Celtic people of the Early Iron Age in Europe, c. 800–450 BC. Hallstatt is at the core of the Hallstatt-Dachstein/Salzkammergut Cultural Landscape declared as one of the World Heritage Sites in Austria by UNESCO in 1997. It is an area of overtourism. History Finds at Hallstatt extend from about 1200 BC until around 500 BC, and are divided by archaeologists into four phases: Iron Age In 1846, Johann Georg Ramsauer (1795–1874) discovered a large prehistoric cemetery at the Salzberg mines n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallstatt Culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European Archaeological culture, culture of Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe (Hallstatt C, Hallstatt D) from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC (Bronze Age Europe, Late Bronze Age) and followed in much of its area by the La Tène culture. It is commonly associated with Proto-Celtic populations. Older assumptions of the early 20th century of Illyrians having been the bearers of especially the Eastern Hallstatt culture are indefensible and archeologically unsubstantiated. It is named for its type site, Hallstatt, a lakeside village in the Austrian Salzkammergut southeast of Salzburg, Austria, Salzburg, where there was a rich salt mine, and some 1,300 burials are known, many with fine artifacts. Material from Hallstatt has been classified into four periods, des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |