|
Ceftaroline Fosamil
Ceftaroline fosamil (INN) , brand name Teflaro in the US and Zinforo in Europe, is a cephalosporin antibiotic with anti-MRSA activity. Ceftaroline fosamil is a prodrug of ceftaroline. It is active against methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) and other Gram-positive bacteria. It retains some activity of later-generation cephalosporins having broad-spectrum activity against Gram-negative bacteria, but its effectiveness is relatively much weaker. It is currently being investigated for community-acquired pneumonia and complicated skin and skin structure infection. Ceftaroline is being developed by Forest Laboratories, under a license from Takeda. Ceftaroline received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia and acute bacterial skin infections on 29 October 2010. ''In vitro'' studies show it has a similar spectrum to ceftobiprole, the only other fifth-generation cephalosporin to date, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, and meningitis caused by methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus''. Blood levels may be measured to determine the correct dose. Vancomycin is also taken by mouth as a treatment for severe ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis. When taken by mouth it is poorly absorbed. Common side effects include pain in the area of injection and allergic reactions. Occasionally, hearing loss, low blood pressure, or bone marrow suppression occur. Safety in pregnancy is not clear, but no evidence of harm has been found, and it is likely safe for use when breastfeeding. It is a type of glycopeptide antibiotic and works by blocking the construction of a cell wall. Vancomycin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1958. It is on the World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetate
An acetate is a salt (chemistry), salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. Alkali metal, alkaline, Alkaline earth metal, earthy, Transition metal, metallic, nonmetallic or radical Radical (chemistry), base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate acid, conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called an anion) typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula . The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a ''positive'' ion (called a cation) are also commonly called "acetates" (hence, ''acetate of lead'', ''acetate of aluminum'', etc.). The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate (called acetic acid) with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic ion, polyatomic anion , or . Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In nature, acetate is the most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rash
A rash is a change of the human skin which affects its color, appearance, or texture. A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracked or blistered, swell, and may be painful. The causes, and therefore treatments for rashes, vary widely. Diagnosis must take into account such things as the appearance of the rash, other symptoms, what the patient may have been exposed to, occupation, and occurrence in family members. The diagnosis may confirm any number of conditions. The presence of a rash may aid diagnosis; associated signs and symptoms are diagnostic of certain diseases. For example, the rash in measles is an erythematous, morbilliform, maculopapular rash that begins a few days after the fever starts. It classically starts at the head, and spreads downwards. Differential diagnosis Common causes of rashes include: * Food allergy * Medication side effects * Anxiet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat. Over 30 definitions of nausea were proposed in a 2011 book on the topic. Nausea is a non-specific symptom, which means that it has many possible causes. Some common causes of nausea are gastroenteritis and other gastrointestinal disorders, food poisoning, motion sickness, dizziness, migraine, fainting, low blood sugar, anxiety, and lack of sleep. Nausea is a side effect of many medications including chemotherapy, or morning sickness in early pregnancy. Nausea may also be caused by disgust and depression. Medications taken to prevent and treat nausea and vomiting are called antiemetics. The most commonly prescribed antiemetics in the US are promethazine, metoclopramide, and the newer ondansetron. The word nausea is from Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to either a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea are: short duration watery diarrhea, short duration bloody diarrhea, and persistent diarrhea (lasting more than two weeks, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
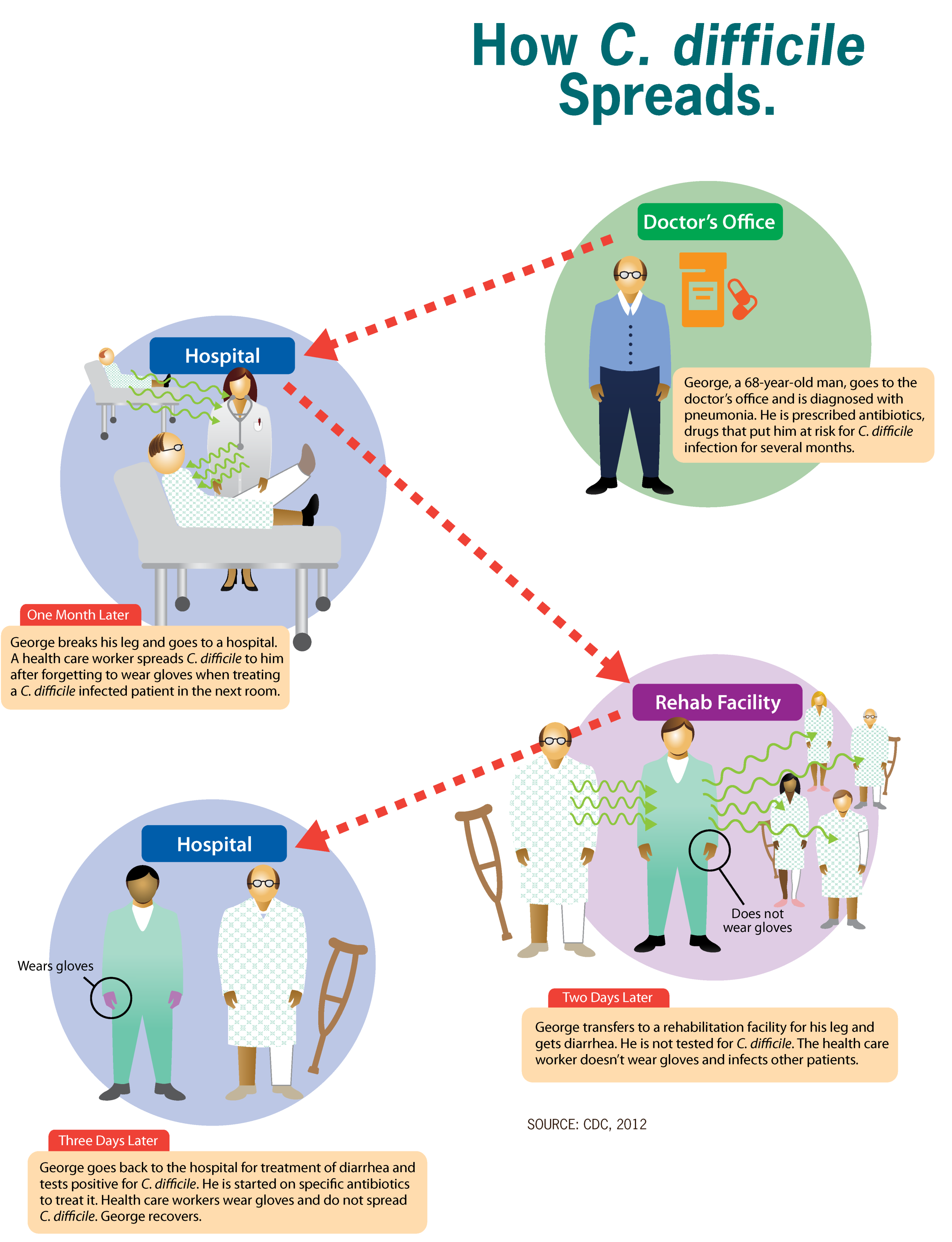
Clostridium Difficile Colitis
''Clostridioides difficile'' infection (CDI or C-diff), also known as ''Clostridium difficile'' infection, is a symptomatic infection due to the spore-forming bacterium ''Clostridioides difficile''. Symptoms include watery diarrhea, fever, nausea, and abdominal pain. It makes up about 20% of cases of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Antibiotics can contribute to detrimental changes in gut microbiota; specifically, they decrease short-chain fatty acid absorption which results in osmotic, or watery, diarrhea. Complications may include pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon, perforation of the colon, and sepsis. ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection is spread by bacterial spores found within feces. Surfaces may become contaminated with the spores with further spread occurring via the hands of healthcare workers. Risk factors for infection include antibiotic or proton pump inhibitor use, hospitalization, other health problems, and older age. Diagnosis is by stool culture or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the following: an itchy rash, throat closing due to swelling which can obstruct or stop breathing; severe tongue swelling which can also interfere with or stop breathing; shortness of breath, vomiting, lightheadedness, loss of consciousness, low blood pressure, and medical shock. These symptoms typically start in minutes to hours and then increase very rapidly to life-threatening levels. Urgent medical treatment is required to prevent serious harm or death, even if the patient has used an epipen or has taken other medications in response, and even if symptoms appear to be improving. Common causes include allergies to insect bites and stings, allergies to foods – including nuts, milk, fish, shellfish, eggs and some fresh fruits or dried fruits; a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) refers to undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. They are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and these reactions may be damaging and uncomfortable. This is an immunologic term and is not to be confused with the psychiatric term of being hypersensitive which implies to an individual who may be overly sensitive to physical (i.e. sound, touch, light, etc.) and/or emotional stimuli. Although there is a relation between the two – studies have shown that those individuals that have ADHD (a psychiatric disorder) are more likely to have hypersensitivity reactions such as allergies, asthma, eczema than those who do not have ADHD. Hypersensitivity reactions can be classified into four types. Type I: IgE mediated immediate reaction Type II: Antibody-mediated reaction (IgG or IgM antibodies) Type III: Immune complex-mediated rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceftaroline
Ceftaroline fosamil (INN) , brand name Teflaro in the US and Zinforo in Europe, is a cephalosporin antibiotic with anti-MRSA activity. Ceftaroline fosamil is a prodrug of ceftaroline. It is active against methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) and other Gram-positive bacteria. It retains some activity of later-generation cephalosporins having broad-spectrum activity against Gram-negative bacteria, but its effectiveness is relatively much weaker. It is currently being investigated for community-acquired pneumonia and complicated skin and skin structure infection. Ceftaroline is being developed by Forest Laboratories, under a license from Takeda. Ceftaroline received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia and acute bacterial skin infections on 29 October 2010. ''In vitro'' studies show it has a similar spectrum to ceftobiprole, the only other fifth-generation cephalosporin to date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin And Skin Structure Infection
Skin and skin structure infections (SSSIs), also referred to as skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), or acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSIs), are infections of skin and associated soft tissues (such as loose connective tissue and mucous membranes). Historically, the pathogen involved has most frequently been a bacterial species—always, since redescription of SSSIs as ABSSSIs—and as such, these infections require treatment by antibiotics. Types Until 2008, a distinction was made between two types: complicated SSSIs (cSSSIs) and uncomplicated SSSIs (uSSSIs), which had different regulatory approval requirements. Uncomplicated SSSIs included "simple abscesses, impetiginous lesions, furuncles, and cellulitis." Complicated SSSIs included "infections either involving deeper soft tissue or requiring significant surgical intervention, such as infected ulcers, burns, and major abscesses or a significant underlying disease state that complicates the response to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community-acquired Bacterial Pneumonia
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) refers to pneumonia (any of several lung diseases) contracted by a person outside of the healthcare system. In contrast, hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is seen in patients who have recently visited a hospital or who live in long-term care facilities. CAP is common, affecting people of all ages, and its symptoms occur as a result of oxygen-absorbing areas of the lung (alveoli) filling with fluid. This inhibits lung function, causing dyspnea, fever, chest pains and cough. CAP, the most common type of pneumonia, is a leading cause of illness and death worldwide. Its causes include bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. CAP is diagnosed by assessing symptoms, performing a physical examination, by x-ray or by sputum examination. Patients with CAP sometimes require hospitalization, and it is treated primarily with antibiotics, antipyretics and cough medicine. Some forms of CAP can be prevented by vaccination and by abstaining from tobacco products ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |