|
Caño Manamo
The Caño Manamo is a distributary of the Orinoco River. It branches northwards from the main channel of the Orinoco to delimit the western edge of the Orinoco Delta, ultimately emptying into the Gulf of Paria. Tucupita, the capital of Delta Amacuro state, is located on the east bank (right) of the Caño Manamo. Manamo is a Warao word meaning "two." A flood control program in the 1960s dammed the Caño Manamo and thus reduced water levels in the upper delta. This part of the delta became tidal and much more saline than before, with a drastic impact on the flora and fauna of the Orinoco Delta swamp forests The Orinoco Delta swamp forests (NT0147) is an ecoregion of eastern Venezuela and northern Guyana covering the large and shifting Orinoco Delta. The vegetation is mostly permanently flooded rainforest. The ecoregion is relatively intact apart fro .... References Manamo Orinoco basin Gulf of Paria {{Venezuela-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
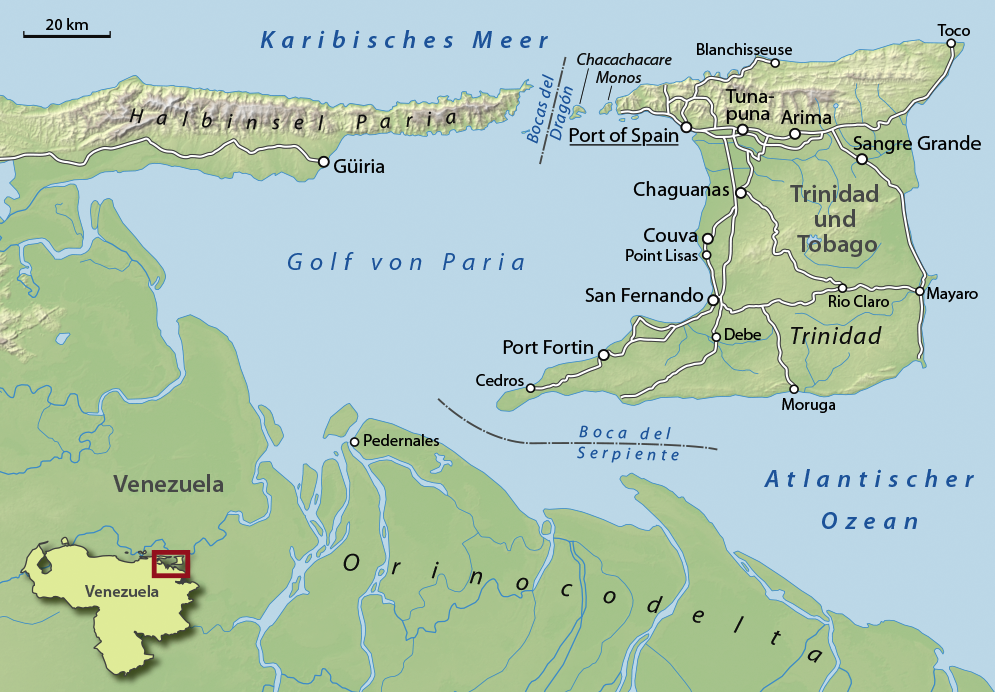
Gulf Of Paria
The Gulf of Paria ( ; es, Golfo de Paria) is a shallow (180 m at its deepest) semi-enclosed inland sea located between the island of Trinidad (Republic of Trinidad and Tobago) and the east coast of Venezuela. It separates the two countries by as little as 15 km at its narrowest and 120 km at its widest points. The tides within the Gulf are semi-diurnal in nature with a range of approximately 1m. The Gulf of Paria is considered to be one of the best natural harbors on the Atlantic coast of the Americas. The jurisdiction of the Gulf of Paria is split between Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela with Trinidad and Tobago having control over approximately (37.7%) and Venezuela the remainder (62.3%). It was originally named the Gulf of the Whale ( es, Golfo de la Ballena) by Christopher Columbus, but the 19th-century whaling industry eliminated whales from the area and populations have never recovered. Cartographic sources of the late 18th century repeatedly refer to it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. The Venezuelan government maintains a claim against Guyana to Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributary
A distributary, or a distributary channel, is a stream that branches off and flows away from a main stream channel. Distributaries are a common feature of river deltas. The phenomenon is known as river bifurcation. The opposite of a distributary is a tributary, which flows ''towards'' and joins another stream. Distributaries are often found where a stream approaches a lake or an ocean. They can also occur inland, on alluvial fans, or where a tributary stream bifurcates as it nears its confluence with a larger stream. In some cases, a minor distributary can divert so much water from the main channel that it can later become the main route. Related terms Common terms to name individual river distributaries in English-speaking countries are ''arm'' and ''channel''. These terms may refer to a distributary that does not rejoin the channel from which it has branched (e.g., the North, Middle, and South Arms of the Fraser River, or the West Channel of the Mackenzie River), or to on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orinoco River
The Orinoco () is one of the longest rivers in South America at . Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers , with 76.3 percent of it in Venezuela and the remainder in Colombia. It is the fourth largest river in the world by discharge volume of water. The Orinoco River and its tributaries are the major transportation system for eastern and interior Venezuela and the Llanos of Colombia. The environment and wildlife in the Orinoco's basin are extremely diverse. Etymology The river's name is derived from the Warao term for "a place to paddle", itself derived from the terms ''güiri'' (paddle) and ''noko'' (place) i.e. a navigable place. History The mouth of the Orinoco River at the Atlantic Ocean was documented by Christopher Columbus on 1 August 1498, during his third voyage. Its source at the Cerro Delgado–Chalbaud, in the Parima range, was not explored until 453 years later, in 1951. The source, near the Venezuelan–Brazilian border, at ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orinoco Delta
The Orinoco Delta is a vast river delta of the Orinoco River, located in eastern Venezuela. Location The Orinoco Delta is one of the eight natural regions of Venezuela. It covers the whole of Delta Amacuro State and a few square kilometers of Monagas State and Sucre State, comprising all the mouths of the Orinoco. It is divided into two sections: the principal, at the northernmost part of the system, located between Caño Manamo and the left shore of Caño Araguao, where the majority of villages are established, including the state capital Tucupita; and the secondary, between the right shore of Caño Araguao and Río Grande. The Warao people live in the region. Hydrology The delta is fan-shaped, formed by the Orinoco River as it splits into numerous distributaries, called ''caños'', which meander through the delta on their way to the sea. The main distributary is called the Rio Grande, which empties south-southeast through the southern portion of the delta, and the second maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tucupita
Tucupita () is the capital city of the Venezuelan state of Delta Amacuro. Geography Delta Amacuro consists almost entirely of the swampy Orinoco River delta. Tucupita is hot and humid, and lies well into the delta on the Caño Manamo river (one of the two major branches of the Orinoco river delta). It is approached by a road which runs along the top of a barrier constructed in the 1960s to create dry land. The project is considered by many to be a failure since little dry land was created and massive ecological disruption was caused by salt water penetration of the delta. The delta is covered mostly by mangrove swamp but there is a huge range of other flora and fauna, making it one of the world's more ecologically diverse places. Significant amounts of oil have been discovered in the western parts of the delta and there is apprehension that exploitation of this oil will cause substantial ecological damage. Religion Tucupita is the cathedral see of the Roman Catholic Ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Amacuro
Delta Amacuro State ( es, Estado Delta Amacuro, ) is one of the 23 states of Venezuela, and is the location of the Orinoco Delta. The Paria Gulf and the Atlantic Ocean are found to the north, Bolívar State is found to the south, the Atlantic Ocean and Guyana are found to the east, and Monagas State is found to the west. The state capital city is Tucupita. Delta Amacuro State covers a total surface area of and, in 2011, had a census population of 171,413. History Pre-Colonial Period Based on theories, anthropological evidence and oral tradition, the antecedents of human activity within this territory date from the time of the first displacements through America; Groups from the eastern slopes of the Peruvian Andes were introduced into the Lower Orinoco, they are called Kotoch or Chavinses; They developed knowledge of pottery (of which formal and technical reminiscences in ceramics are kept), and horticulture. With time other groups established themselves in its sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warao Language
Warao (also known as Guarauno, Guarao, Warrau) is the native language of the Warao people. A language isolate, it is spoken by about 33,000 people primarily in northern Venezuela, Guyana and Suriname. It is notable for its unusual object–subject–verb word order. The 2015 Venezuelan film ''Gone with the River'' was spoken in Warao. Classification Warao appears to be a language isolate, unrelated to any recorded language in the region or elsewhere. Terrence Kaufman (1994) included it in his hypothetical Macro-Paezan family, but the necessary supporting work was never done. Julian Granberry connected many of the grammatical forms, including nominal and verbal suffixes, of Warao to the Timucua language of North Florida, also a language isolate. However, he has also derived Timucua morphemes from Muskogean, Chibchan, Paezan, Arawakan, and other Amazonian languages, suggesting multi-language creolization as a possible explanation for these similarities. Waroid hypothesis Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orinoco Delta Swamp Forests
The Orinoco Delta swamp forests (NT0147) is an ecoregion of eastern Venezuela and northern Guyana covering the large and shifting Orinoco Delta. The vegetation is mostly permanently flooded rainforest. The ecoregion is relatively intact apart from a large area that was damaged by a failed flood control program in the 1960s. It is inaccessible, so logging is difficult, and the soil is unsuitable for farming. The main threat comes from oil exploration, which would bring an influx of settlers into the delta. Location The Orinoco Delta swamp forests in the lower delta plain of the Orinoco River are one of Earth's largest intact areas of wetlands. They cover an area of . The forests extend from the base of the Paria Peninsula in the northeast of Venezuela south across the Orinoco Delta floodplain to the Waini River of Guyana. The ecoregion is bounded on the Gulf of Paria and the Atlantic Ocean by stretches of Amazon-Orinoco-Southern Caribbean mangroves. It contains sections of Ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivers Of Venezuela
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague. Rivers are part of the water cycle. Water generally collects in a river from precipitation through a drainage basin from surface runoff and other sources such as groundwater recharge, springs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orinoco Basin
The Orinoco Basin is the part of South America drained by the Orinoco river and its tributaries. The Orinoco watershed covers an area of about 990000 km2, making it the third largest in South America, covering most of Venezuela and eastern part of Colombia. The Orinoco is one of the most important rivers in the world due to its length and flow (2140 km and more than 30000 m3/s), the extent of its basin (1 million km2) and especially its historical importance and economic and the meaning it has had for Venezuela, where most of its basin is spread, with almost two-thirds of it. It is probably the largest river in the world in relation to its basin, similar in extent to that of the Danube but five times greater in volume. Its discharge is the third largest of any river worldwide, after the Amazon and the Congo, and much greater than that of many rivers of greater length and basin area. Geography Extension The Orinoco basin covers an area of almost 989000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |