|
Cavernous
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica. Structure The cavernous sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses of the head. It is a network of veins that sit in a cavity. It sits on both sides of the sphenoidal bone and pituitary gland, approximately 1 × 2 cm in size in an adult. The carotid siphon of the internal carotid artery, and cranial nerves III, IV, V (branches V1 and V2) and VI all pass through this blood filled space. Both sides of cavernous sinus is connected to each other via intercavernous sinuses. The cavernous sinus lies in between the inner and outer layers of dura mater. Nearby structures * Above: optic tract, optic chiasma, internal carotid artery. * Inferiorly: foramen lacerum, and the junction of the body and greater wing of sphenoid bone. * Medially: pituitary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Carotid Artery
The internal carotid artery (Latin: arteria carotis interna) is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these bifurcate at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges. Classification Terminologia Anatomica in 1998 subdivided the artery into four parts: "cervical", "petrous", "cavernous", and "cerebral". However, in clinical settings, the classification system of the internal carotid artery usually follows the 1996 recommendations by Bouthillier, describing seven anatomical segments of the internal carotid artery, each with a corresponding alphanumeric identifier—C1 cervical, C2 petrous, C3 lacerum, C4 cavernous, C5 clinoid, C6 ophthalmic, and C7 communicating. The Bouthillier nom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Ophthalmic Vein
The superior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that drains venous blood from structures of the upper orbit. It is fromed by the union of the angular vein, and supraorbital vein. It passes backwards within the orbit alongside the ophthalmic artery, then exits the orbit through the superior orbital fissure to drain into the cavernous sinus. The superior ophthalmic vein can be a path for the spread of infection from the danger triangle of the face to the cavernous sinus and the pterygoid plexus. It may also be affected by an arteriovenous fistula of the cavernous sinus. Structure The superior ophthalmic vein - together with the inferior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit (with the superior ophthalmic vein being the larger of the two). The superior ophthalmic vein drains venous blood from structures of the upper orbit. The superior ophthalmic vein is the largest and the most consistently present vein of the orbit. It usually measures 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Ophthalmic Vein
The inferior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that - together with the superior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit. It begins from a venous network in the front of the orbit, then passes backwards through the lower orbit. It drains several structures of the orbit. It may end by splitting into two branches, one draining into the pterygoid venous plexus and the other ultimately (i.e. directly or indirectly) into the cavernous sinus. Structure The inferior ophthalmic vein - together with the superior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit. Origin The inferior ophthalmic vein originates from a venous network at the anterior part of the floor and anterior part of the medial wall of the orbit. Course The inferior ophthalmic vein passes posterior-ward through the inferior orbit. Distribution The inferior ophthalmic vein drains venous blood from the inferior rectus muscle, inferior oblique muscle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Petrosal Sinus
The inferior petrosal sinuses are two small sinuses situated on the inferior border of the petrous part of the temporal bone, one on each side. Each inferior petrosal sinus drains the cavernous sinus into the internal jugular vein. Structure The inferior petrosal sinus is situated in the inferior petrosal sulcus, formed by the junction of the petrous part of the temporal bone with the basilar part of the occipital bone. It begins below and behind the cavernous sinus and, passing through the anterior part of the jugular foramen, ends in the superior bulb of the internal jugular vein. Function The inferior petrosal sinus receives the internal auditory veins and also veins from the medulla oblongata, pons, and under surface of the cerebellum. Additional images File:Gray568.png, Sagittal section of the skull, showing the sinuses of the dura. See also * Dural venous sinuses The dural venous sinuses (also called dural sinuses, cerebral sinuses, or cranial sinuses) are veno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Petrosal Sinus
The superior petrosal sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses located beneath the brain. It receives blood from the cavernous sinus and passes backward and laterally to drain into the transverse sinus. The sinus receives superior petrosal veins, some cerebellar veins, some inferior cerebral veins, and veins from the tympanic cavity. They may be affected by arteriovenous malformation or arteriovenous fistula, usually treated with surgery. Structure The superior petrosal sinus is located beneath the brain. It originates from the cavernous sinus. It passes backward and laterally to drain into the transverse sinus. The sinus runs in the attached margin of the tentorium cerebelli, in a groove in the petrous part of the temporal bone formed by the sinus itself - the superior petrosal sulcus. Function The superior petrosal sinus drains many veins of the brain, including superior petrosal veins, some cerebellar veins, some inferior cerebral veins, and veins from the tympan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoparietal Sinus , communicating rami from the The sphenoparietal sinus is a paired dural venous sinus situated along the posterior edge of the lesser wing of either sphenoid bone. It drains into the cavernous sinus. Anatomy A sphenoparietal sinus is situated under each lesser wing of the sphenoid bone near the posterior edge of this bone, between the anterior cranial fossa and middle cranial fossa. It terminates by draining into the anterior part of the cavernous sinus. Tributaries A sphenoparietal sinus receives small veins from the adjacent dura and sometimes the frontal ramus of the middle meningeal vein The pterygoid plexus (; in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Ophthalmic Vein
The inferior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that - together with the superior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit. It begins from a venous network in the front of the orbit, then passes backwards through the lower orbit. It drains several structures of the orbit. It may end by splitting into two branches, one draining into the pterygoid venous plexus and the other ultimately (i.e. directly or indirectly) into the cavernous sinus. Structure The inferior ophthalmic vein - together with the superior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit. Origin The inferior ophthalmic vein originates from a venous network at the anterior part of the floor and anterior part of the medial wall of the orbit. Course The inferior ophthalmic vein passes posterior-ward through the inferior orbit. Distribution The inferior ophthalmic vein drains venous blood from the inferior rectus muscle, inferior oblique muscle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Orbital Fissure
The superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. It gives passage to multiple structures, including the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, ophthalmic nerve, abducens nerve, ophthalmic veins, and sympathetic fibres from the cavernous plexus. Structure The superior orbital fissure is usually 22 mm wide in adults, and is much larger medially. Its boundaries are formed by the (caudal surface of the) lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, and (medial border of the) greater wing of the sphenoid bone. Contents The superior orbital fissure is traversed by the following structures: * (superior and inferior divisions of the) oculomotor nerve (CN III) * trochlear nerve (CN IV) * lacrimal, frontal, and nasociliary branches of ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) * abducens nerve (CN VI) * superior ophthalmic vein and superior division of the inferior ophthalmic vein * sympathetic fibres from the cavernous ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
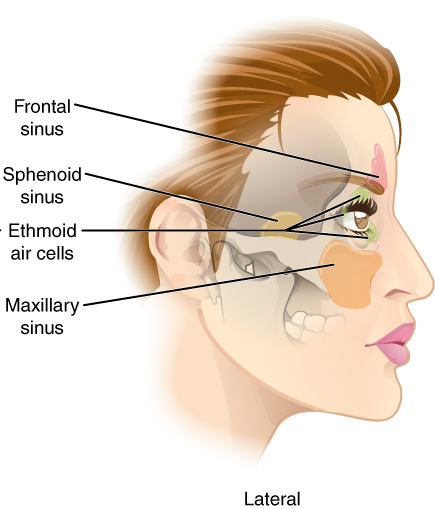
Sphenoidal Air Sinus
The sphenoid sinus is a paired paranasal sinus occurring within the within the body of the sphenoid bone. It represents one pair of the four paired paranasal sinuses.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 64 The pair of sphenoid sinuses are separated in the middle by a septum of sphenoid sinuses. Each sphenoid sinus communicates with the nasal cavity via the opening of sphenoidal sinus. The two sphenoid sinuses vary in size and shape, and are usually asymmetrical. Anatomy On average, a sphenoid sinus measures 2.2 cm vertical height, 2 cm in transverse breadth; and 2.2 cm antero-posterior depth. Each spehoid sinus is contained within the body of sphenoid bone, being situated just inferior to the sella turcica. The two sphenoid sinuses are separated medially by the septum of sphenoidal sinuses (which is usually asymmetrical). An opening of sphenoidal sinus forms a passage between each sphenoidal sinus, and the nasal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoparietal Sinus , communicating rami from the The sphenoparietal sinus is a paired dural venous sinus situated along the posterior edge of the lesser wing of either sphenoid bone. It drains into the cavernous sinus. Anatomy A sphenoparietal sinus is situated under each lesser wing of the sphenoid bone near the posterior edge of this bone, between the anterior cranial fossa and middle cranial fossa. It terminates by draining into the anterior part of the cavernous sinus. Tributaries A sphenoparietal sinus receives small veins from the adjacent dura and sometimes the frontal ramus of the middle meningeal vein The pterygoid plexus (; in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |