|
Cavan Fitzgerald
Cavan ( ; ) is the county town of County Cavan in Ireland. The town lies in Ulster, near the border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. The town is bypassed by the main N3 road that links Dublin (to the south) with Enniskillen, Ballyshannon and Donegal Town (to the north). History Gaelic Cavan 1300–1607 Cavan was founded by the Irish clan chief and Lord of East Breifne, Giolla Íosa Ruadh O’Reilly, between 1300 and his death in 1330. During his lordship, a friary run by the Dominican Order was established close to the O’Reilly stronghold at Tullymongan and was at the centre of the settlement close to a crossing over the river and to the town's marketplace. It is recorded that the (Cavan) Dominicans were expelled in 1393, replaced by an Order of Conventual Franciscan friars. The friary's location is marked by an eighteenth-century tower in the graveyard at Abbey Street which appears to incorporate remains of the original medieval friary tower. The imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavan Cathedral
The Cathedral of Saint Patrick and Saint Felim, also known as Cavan Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic cathedral located in Cavan, Ireland. It is the seat of the Bishop of Kilmore, and the mother church of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Kilmore. History In 1152, the Diocese of Kilmore was formally established by Cardinal Giovanni Paparoni at the synod of Kells. In 1454, Pope Nicholas V gave permission for the ancient church at Kilmore (founded in the sixth century by Saint Felim) to be the cathedral church of Kilmore diocese. It was rebuilt and became known in Irish as ''An Chill Mhór'' (meaning ''Great Church'') and anglicised as Kilmore, which gave its name to the diocese, a name which has remained ever since. During the Reformation, the Roman Catholic diocese lost possession of the cathedral and all the other temporalities and passed into the hands of the Church of Ireland. Following the completion of the new Anglican cathedral in 1860, the pre-Reformation cathedral became a Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 census of Ireland, 2016 census it had a population of 1,173,179, while the preliminary results of the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census recorded that County Dublin as a whole had a population of 1,450,701, and that the population of the Greater Dublin Area was over 2 million, or roughly 40% of the Republic of Ireland's total population. A settlement was established in the area by the Gaels during or before the 7th century, followed by the Vikings. As the Kings of Dublin, Kingdom of Dublin grew, it became Ireland's principal settlement by the 12th century Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. The city expanded rapidly from the 17th century and was briefly the second largest in the British Empire and sixt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cavan
The Battle of Cavan took place in Cavan, Ireland on 11 February 1690 between forces of Williamite and Jacobite troops during the Williamite War in Ireland. It ended in a victory for the Williamites who captured, sacked and burned the town of Cavan before withdrawing to their forwarding base at Belturbet and further afield Enniskillen. The Williamite commander over Ennisskillen (Inniskillinger) cavalry troops was Colonel William Wolseley had been instructed by his overall commander Marshal Schomberg to observe and harry Cavan, as Jacobites were using it as a forwarding base to launch relief raids across Ulster for Jacobite forces. At the time Cavan was one of the few remaining settlements in Ulster still loyal to James II of Ireland. The Duke of Berwick led a reinforcement to the Jacobite garrison commanded by Brigadier John Wauchope. Wolseley left Belturbet with a force of 1,200 infantry and 300 cavalry. He hoped to catch the Jacobites by surprise by using a roundabout rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and VII of England and Scotland in November 1688, and his replacement by his daughter Mary II and her husband and James's nephew William III of Orange, de facto ruler of the Dutch Republic. A term first used by John Hampden (1653–1696), John Hampden in late 1689, it has been notable in the years since for having been described as the last successful invasion of England as well as an internal coup, with differing interpretations from the Dutch and English perspectives respectively. Despite his personal Catholicism, a religion opposed by the Protestant majority in England and Scotland, James became king in February 1685 with widespread support in both countries, since many feared that his exclusion would lead to a repetition of the 16391651 Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James I Of England
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and King of Ireland, Ireland as James I from the Union of the Crowns, union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until his death in 1625. The kingdoms of Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of England, England were individual sovereign states, with their own parliaments, judiciaries, and laws, though both were ruled by James in personal union. James was the son of Mary, Queen of Scots, and a great-great-grandson of Henry VII of England, Henry VII, King of England and Lord of Ireland, and thus a potential successor to all three thrones. He succeeded to the Scottish throne at the age of thirteen months, after his mother was compelled to abdicate in his favour. Four different regents governed during his minority, which ended officially in 1578, though he did not gain full control of his government until 1583. In 1603, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
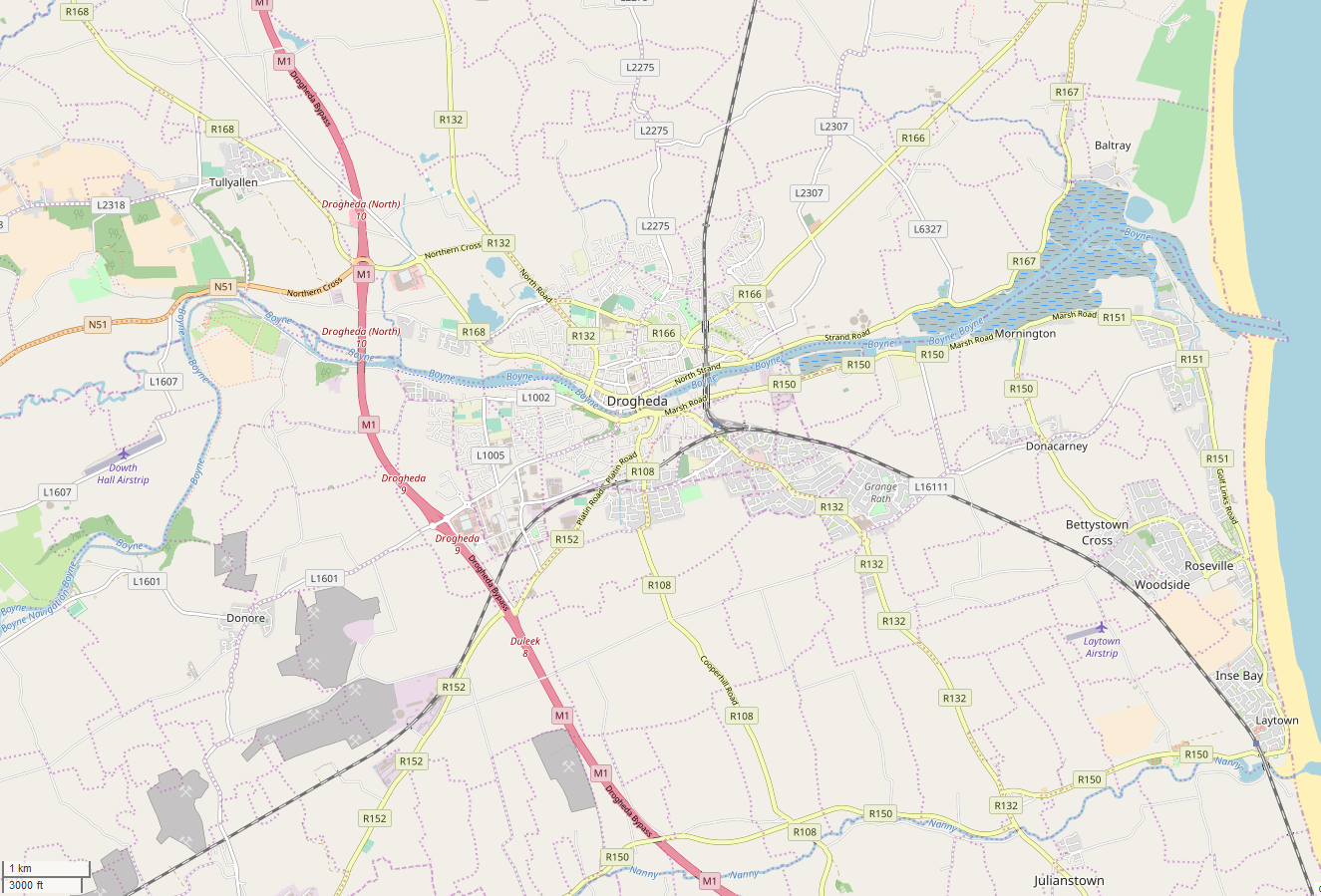
Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth but with the south fringes of the town in County Meath, north of Dublin. Drogheda has a population of approximately 41,000 inhabitants (2016), making it the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, eleventh largest settlement by population in all of Ireland, and the largest town in the Republic of Ireland by both population and area. It is the last bridging point on the River Boyne before it enters the Irish Sea. The UNESCO World Heritage Site of Newgrange is located west of the town. Drogheda was founded as two separately administered towns in two different territories: Drogheda-in-Kingdom of Meath, Meath (i.e. the Lordship of Meath, Lordship and Liberty of Meath, from which a charter was granted in 1194) and Drogheda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
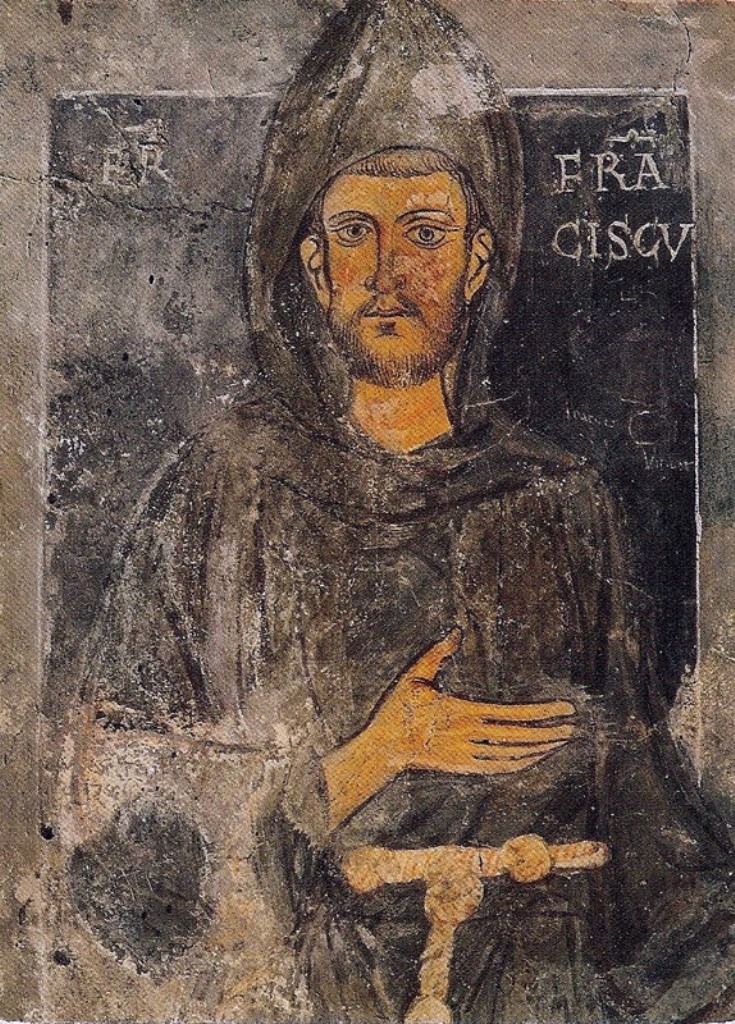
Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related Mendicant orders, mendicant Christianity, Christian Catholic religious order, religious orders within the Catholic Church. Founded in 1209 by Italian Catholic friar Francis of Assisi, these orders include three independent orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor being the largest contemporary male order), orders for women religious such as the Order of Saint Clare, and the Third Order of Saint Francis open to male and female members. They adhere to the teachings and spiritual disciplines of the founder and of his main associates and followers, such as Clare of Assisi, Anthony of Padua, and Elizabeth of Hungary. Several smaller Franciscan spirituality in Protestantism, Protestant Franciscan orders exist as well, notably in the Anglican and Lutheran traditions (e.g. the Community of Francis and Clare). Francis began preaching around 1207 and traveled to Rome to seek approval from Pope Innocent III in 1209 to form a new religious order. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
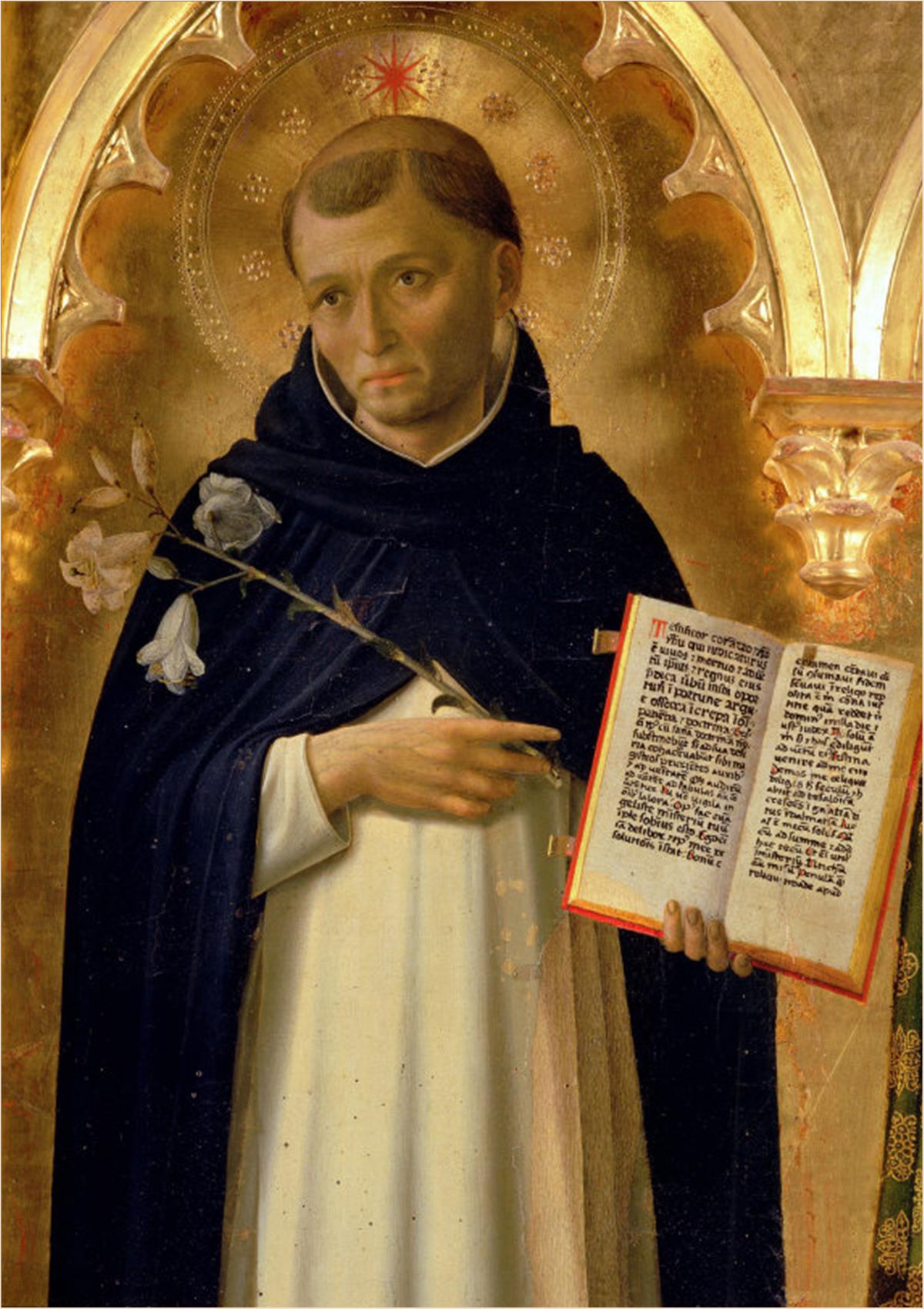
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers ( la, Ordo Praedicatorum) abbreviated OP, also known as the Dominicans, is a Catholic mendicant order of Pontifical Right for men founded in Toulouse, France, by the Spanish priest, saint and mystic Dominic of Caleruega. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull ''Religiosam vitam'' on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as ''Dominicans'', generally carry the letters ''OP'' after their names, standing for ''Ordinis Praedicatorum'', meaning ''of the Order of Preachers''. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, active sisters, and lay or secular Dominicans (formerly known as tertiaries). More recently there has been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries. Founded to preach the Gospel and to oppose heresy, the teaching activity of the order and its scholastic organisation placed the Preachers in the forefront of the intellectual life of the Middle Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priory
A priory is a monastery of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. Priories may be houses of mendicant friars or nuns (such as the Dominicans, Augustinians, Franciscans, and Carmelites), or monasteries of monks or nuns (as with the Benedictines). Houses of canons regular and canonesses regular also use this term, the alternative being "canonry". In pre-Reformation England, if an abbey church was raised to cathedral status, the abbey became a cathedral priory. The bishop, in effect, took the place of the abbot, and the monastery itself was headed by a prior. History Priories first came to existence as subsidiaries to the Abbey of Cluny. Many new houses were formed that were all subservient to the abbey of Cluny and called Priories. As such, the priory came to represent the Benedictine ideals espoused by the Cluniac reforms as smaller, lesser houses of Benedictines of Cluny. There were likewise many conventual priories in Germany and Italy du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Breifne
The Kingdom of East Breifne or Breifne O'Reilly ( sga, Muintir-Maelmordha; ga, Bréifne Uí Raghallaigh, ) was an historic kingdom of Ireland roughly corresponding to County Cavan that existed from 1256 to 1607. It took its present boundaries in 1579 when East Breifne was renamed Cavan, after Cavan town, and shired into Ulster. Originally part of the older Kingdom of Breifne, East Breifne came into existence following a protracted war between the ruling O'Rourke clan and the ascendant O'Reillys which culminated in the division of the kingdom in 1256. The Kingdom was ruled by the dynasty of the Ó Raghallaigh (O'Reilly) and lasted until the early 17th century. Origins and etymology The area of modern-day east County Cavan has been inhabited for over 5,000 years. The O'Reilly are descendant from a kin-group known as Uí Briúin, who settled the east Breifne area in the eighth century AD. At some point they splintered off from the Uí Briúin sept and became known as Muintir-Maelmordh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Of The Name
The Chief of the Name, or in older English usage Captain of his Nation, is the recognised head of a family or clan (''fine'' in Irish and Scottish Gaelic). The term has sometimes been used as a title in Ireland and Scotland. In Ireland In Elizabethan times, the position of Chief of the Name was more important to some Irish leaders than English titles. There are instances where Norman lords of the time like FitzGerald, took to using the Gaelic style of "The" or "Mór" (great) to indicate that the individual was the primary person of his family in Ireland. Chiefs were elected from their clan's "Derbfine", a group of cousins who were all at least the great-grandsons of former chiefs. In the Tudor period the Kingdom of Ireland was established in 1542, and many of the former autonomous clan chiefs were assimilated under the English legal system via the policy of surrender and regrant. At the same time mentions were made in official records of locally-powerful landlords described as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavan Towne Map 1591
Cavan ( ; ) is the county town of County Cavan in Ireland. The town lies in Ulster, near the border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. The town is bypassed by the main N3 road that links Dublin (to the south) with Enniskillen, Ballyshannon and Donegal Town (to the north). History Gaelic Cavan 1300–1607 Cavan was founded by the Irish clan chief and Lord of East Breifne, Giolla Íosa Ruadh O’Reilly, between 1300 and his death in 1330. During his lordship, a friary run by the Dominican Order was established close to the O’Reilly stronghold at Tullymongan and was at the centre of the settlement close to a crossing over the river and to the town's marketplace. It is recorded that the (Cavan) Dominicans were expelled in 1393, replaced by an Order of Conventual Franciscan friars. The friary's location is marked by an eighteenth-century tower in the graveyard at Abbey Street which appears to incorporate remains of the original medieval friary tower. The imprint of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |