|
Catherine-Ann MacPhee
Catherine-Ann MacPhee (Cathy-Ann MacPhee; Scottish Gaelic: Catriona-Anna Nic a' Phi; born 1959) is a Scottish Gaelic singer from Barra in the Hebrides, now resident in Canada. She has worked in the theatre and broadcasting as well as giving musical performances in Scotland, England, Canada and elsewhere. After a period living in Ottawa she moved to Halifax, Nova Scotia, in 2017. Acting career Catherine-Ann was born on 21 November 1959 in the Island of Barra, Scotland where she grew up with Scottish Gaelic as her first language. Electricity did not reach the island until she was six. At the age of five she started singing at candle-lit ceilidhs in the little village of Eoligarry. During the summer she sang for tourists. At the age of seventeen she joined "Fir Chlis" (Northern Lights). It was the first Scottish Gaelic repertory theatre company and did work for radio and television including the 1979 BBC Scotland Gaelic language course Can Seo. Following budget cuts the company ended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as both Irish and Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names. In the 2011 census of Scotland, 57,375 people (1.1% of the Scottish population aged over 3 years old) reported being able to speak Gaelic, 1,275 fewer than in 2001. The highest percentages of Gaelic speakers were in the Outer Hebrides. Nevertheless, there is a language revival, and the number of speakers of the language under age 20 did not decrease between the 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dingwall
Dingwall ( sco, Dingwal, gd, Inbhir Pheofharain ) is a town and a royal burgh in the Highland council area of Scotland. It has a population of 5,491. It was an east-coast harbour that now lies inland. Dingwall Castle was once the biggest castle north of Stirling. On the town's present-day outskirts lies Tulloch Castle, parts of which may date back to the 12th century. In 1411 the Battle of Dingwall is said to have taken place between the Clan Mackay and the Clan Donald. History Its name, derived from the Scandinavian (field or meeting-place of the ''thing'', or local assembly; compare Tynwald, Tingwall, Thingwall in the British Isles alone, plus many others across northern Europe), preserves the Viking connections of the town; Gaels call it (), meaning "the mouth of the Peffery" or meaning "cabbage town". The site of the , and of the medieval Moothill, thought to have been established by the Vikings after they invaded in the 8th century, lies beneath the Cromartie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh Festival
__NOTOC__ This is a list of arts and cultural festivals regularly taking place in Edinburgh, Scotland. The city has become known for its festivals since the establishment in 1947 of the Edinburgh International Festival and the Edinburgh Festival Fringe which runs alongside it. The latter is the largest event of its kind in the world. The term ''Edinburgh Festival'' is commonly used, but there is no single festival; the various festivals are put on by separate, unrelated organisations. However they are widely regarded as part of the same event, particularly the various festivals that take place simultaneously in August each year. The term ''Edinburgh Festival'' is often used to refer more specifically to the Fringe, being the largest of the festivals; or sometimes to the International Festival, being the original "official" arts festival. Within the industry, people refer to all the festivals collectively as the ''Edinburgh Festivals'' (plural). The festivals Listed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Scots replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands. The term is also used for the area north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault, although the exact boundaries are not clearly defined, particularly to the east. The Great Glen divides the Grampian Mountains to the southeast from the Northwest Highlands. The Scottish Gaelic name of ' literally means "the place of the Gaels" and traditionally, from a Gaelic-speaking point of view, includes both the Western Isles and the Highlands. The area is very sparsely populated, with many mountain range A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
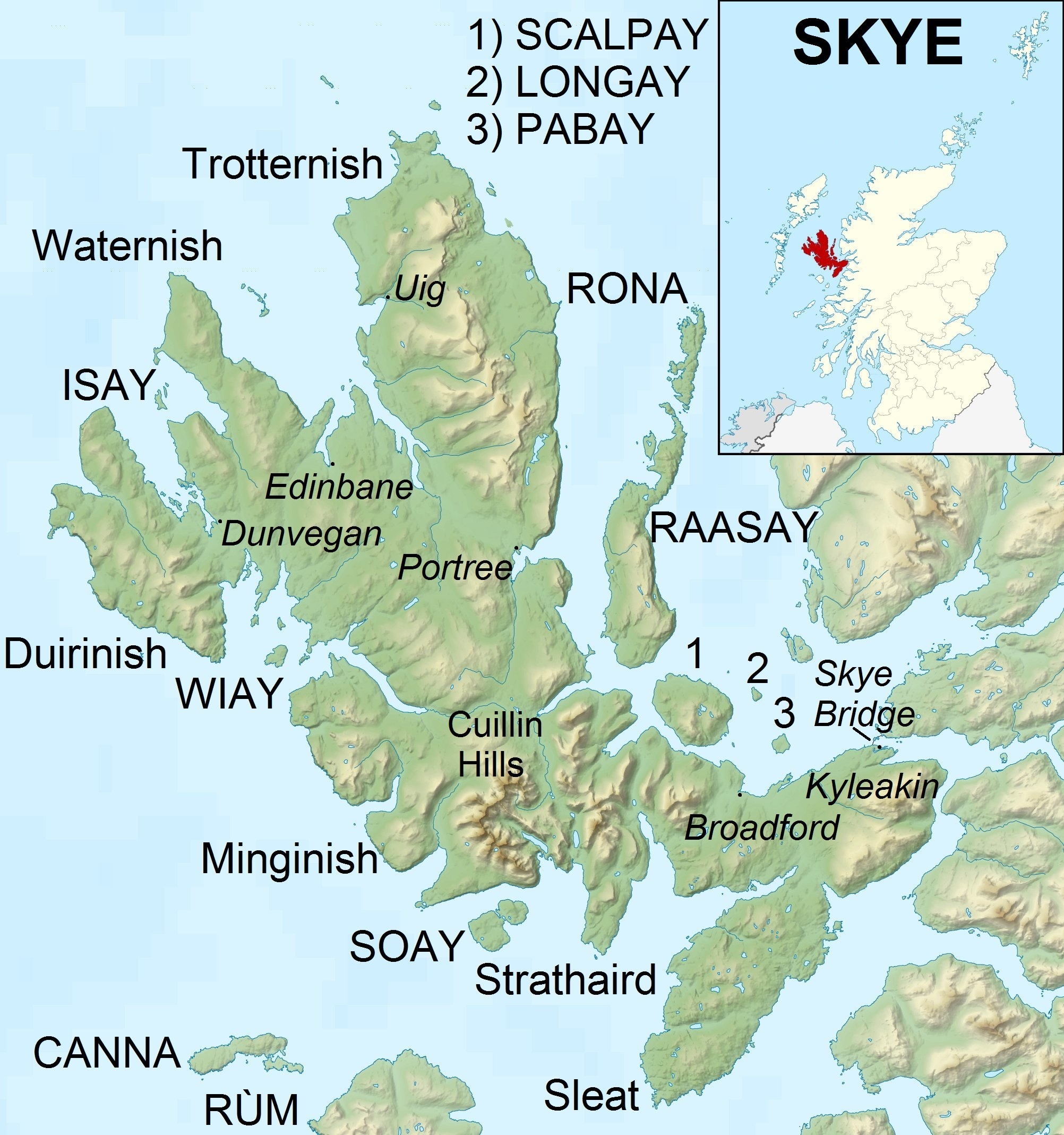
Isle Of Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of MacLeod and MacDonald. The island was considered to be under Norwegian suzerainty until the 1266 Treaty of Perth, which transferred control over to Scotland. The 18th-century Jacobite risings led to the breaking-up of the clan system and later clea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Màiri Mhòr Nan Òran
Mary MacPherson (), known as Màiri Mhòr nan Òran (English: Great Mary of the Songs) or simply Màiri Mhòr (10 March 1821 – 7 November 1898), was a Scottish Gaelic poet from the Isle of Skye, whose work focused on the Highland Clearances and the land struggle. Although she could read her own work when written she could not write it in Gaelic.Somhairle Mac Gill-eain, "Ris a' Bhruaithaich The Criticism and Prose Writing of Sorley MacLean" (Stornoway : Acair, 1985)251-2 She retained her songs and poems in her memory until others wrote them down for publication. She often referred to herself as ''Màiri Nighean Iain Bhàin'' (Mary, daughter of fair haired John), the name by which she would have been known in the Skye of her childhood. Life Mary MacDonald was born at Skeabost, Isle of Skye, in 1821 to John Macdonald and Flora MacInnes. She moved to Inverness in 1844 where she married shoemaker Isaac MacPherson on 11 November 1847. She and Isaac had five children who lived to ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland Clearances
The Highland Clearances ( gd, Fuadaichean nan Gàidheal , the "eviction of the Gaels") were the evictions of a significant number of tenants in the Scottish Highlands and Islands, mostly in two phases from 1750 to 1860. The first phase resulted from agricultural improvement, driven by the need for landlords to increase their income – many had substantial debts, with actual or potential bankruptcy being a large part of the story of the clearances. This involved the enclosure of the open fields managed on the run rig system and shared grazing. These were usually replaced with large-scale pastoral farms on which much higher rents were paid. The displaced tenants were expected to be employed in industries such as fishing, quarrying or the kelp industry. Their reduction in status from farmer to crofter was one of the causes of resentment. The second phase involved overcrowded crofting communities from the first phase that had lost the means to support themselves, through fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland Land League
The first Highland Land League ( gd, Dionnasg an Fhearainn) emerged as a distinct political force in Scotland during the 1880s, with its power base in the country's Highlands and Islands. It was known also as the Highland Land Law Reform Association and the Crofters' Party. It was consciously modelled on the Irish Land League. The Highland Land League was successful in getting Members of Parliament (MPs) elected in 1885 (in the 1885 general election). As a parliamentary force, it was dissipated by the Crofters' Act of 1886 and by the way the Liberal Party was seen to adopt Land League objectives. The Land League also used direct action protest tactics and the use of these tactics was to reappear in the early 20th century. The protests included rent strikes and land occupations (which came to be known as land raids) by crofters, cottars and squatters. Perhaps the Land League's best known slogan was ''Is treasa tuath na tighearna''. This Gaelic saying or proverb is usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Mrs Ackyroyd Band
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waulking Song
Waulking songs ( gd, Òrain Luaidh) are Scottish folk songs, traditionally sung in the Gaelic language by women while fulling (waulking) cloth. This practice involved a group of women, who traditionally prepared cloth, rhythmically beating newly woven tweed or tartan cloth against a table or similar surface to lightly felt it and shrink it to better repel water. Simple, beat-driven songs were used to accompany the work. A waulking session often begins with slow-paced songs, with the tempo increasing as the cloth becomes softer. As the singers work the cloth, they gradually shift it to the left so as to work it thoroughly. A tradition holds that moving the cloth anticlockwise is unlucky. Typically one person sings the verse, while the others join in the chorus. As with many folk music forms, the lyrics of waulking songs are not always strictly adhered to. Singers might add or leave out verses depending on the particular length and size of tweed being waulked. Verses from on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Age
New Age is a range of spiritual or religious practices and beliefs which rapidly grew in Western society during the early 1970s. Its highly eclectic and unsystematic structure makes a precise definition difficult. Although many scholars consider it a religious movement, its adherents typically see it as spiritual or as unifying Mind-Body-Spirit, and rarely use the term ''New Age'' themselves. Scholars often call it the New Age movement, although others contest this term and suggest it is better seen as a ''milieu'' or '' zeitgeist''. As a form of Western esotericism, the New Age drew heavily upon esoteric traditions such as the occultism of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, including the work of Emanuel Swedenborg and Franz Mesmer, as well as Spiritualism, New Thought, and Theosophy. More immediately, it arose from mid-twentieth century influences such as the UFO religions of the 1950s, the counterculture of the 1960s, and the Human Potential Movement. Its exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossian (band)
Ossian are a Scottish traditional music group, formed in 1976. The initial line-up brought together Billy Ross and former members of the group Contraband, Billy Jackson, John Martin, and George Jackson. One of their earliest gigs was at the 1976 Kinross Folk Festival. Each of the members was a multi-instrumentalist and singer. Their arrangements of songs, slow airs and dance tunes were meticulous, almost a chamber music approach to Scottish music. They sang in English, Scots, and Gaelic. Billy Jackson's wire-strung harp, the clàrsach, featured in most pieces, but he also played uilleann (Irish) pipes and whistles. John Martin, who played fiddle and cello, went on to become a member of The Tannahill Weavers. George Jackson (brother of Billy) played guitar, cittern, mandolin, fiddle, whistle and flute. Billy Ross was the main singer who played guitar, dulcimer and whistle. Their first two LPs were ''Ossian'' (1977) and '' St. Kilda Wedding'' (1978). Billy Ross left the band ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)
