|
Cat 5
Category 5 cable (Cat 5) is a twisted pair cable for computer networks. Since 2001, the variant commonly in use is the Category 5e specification (Cat 5e). The cable standard provides performance of up to 100 MHz and is suitable for most varieties of Ethernet over twisted pair up to 2.5GBASE-T but more commonly runs at (Gigabit Ethernet) speeds. Cat 5 is also used to carry other signals such as telephone and video. This cable is commonly connected using punch-down blocks and modular connectors. Most Category 5 cables are unshielded, relying on the balanced line twisted pair design and differential signaling for noise suppression. Standards Category 5 is currently defined in ISO/IEC 11801, IEC 61156 and EN 50173, though it was originally defined in ANSI/ TIA/EIA-568-A (with clarification in TSB-95). These documents specify performance characteristics and test requirements for frequencies up to 100 MHz. The cable is available i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. The interval of time between events is called the period. It is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times per minute (2 hertz), its period is one half of a second. Special definitions of frequency are used in certain contexts, such as the angular frequency in rotational or cyclical properties, when the rate of angular progress is measured. Spatial frequency is defined for properties that vary or cccur repeatedly in geometry or space. The unit of measurement of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) is the hertz, having the symbol Hz. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sybex
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company was founded in 1807 and produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son John (born in Flatbush, New York, October 4, 1808; died in East Orang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
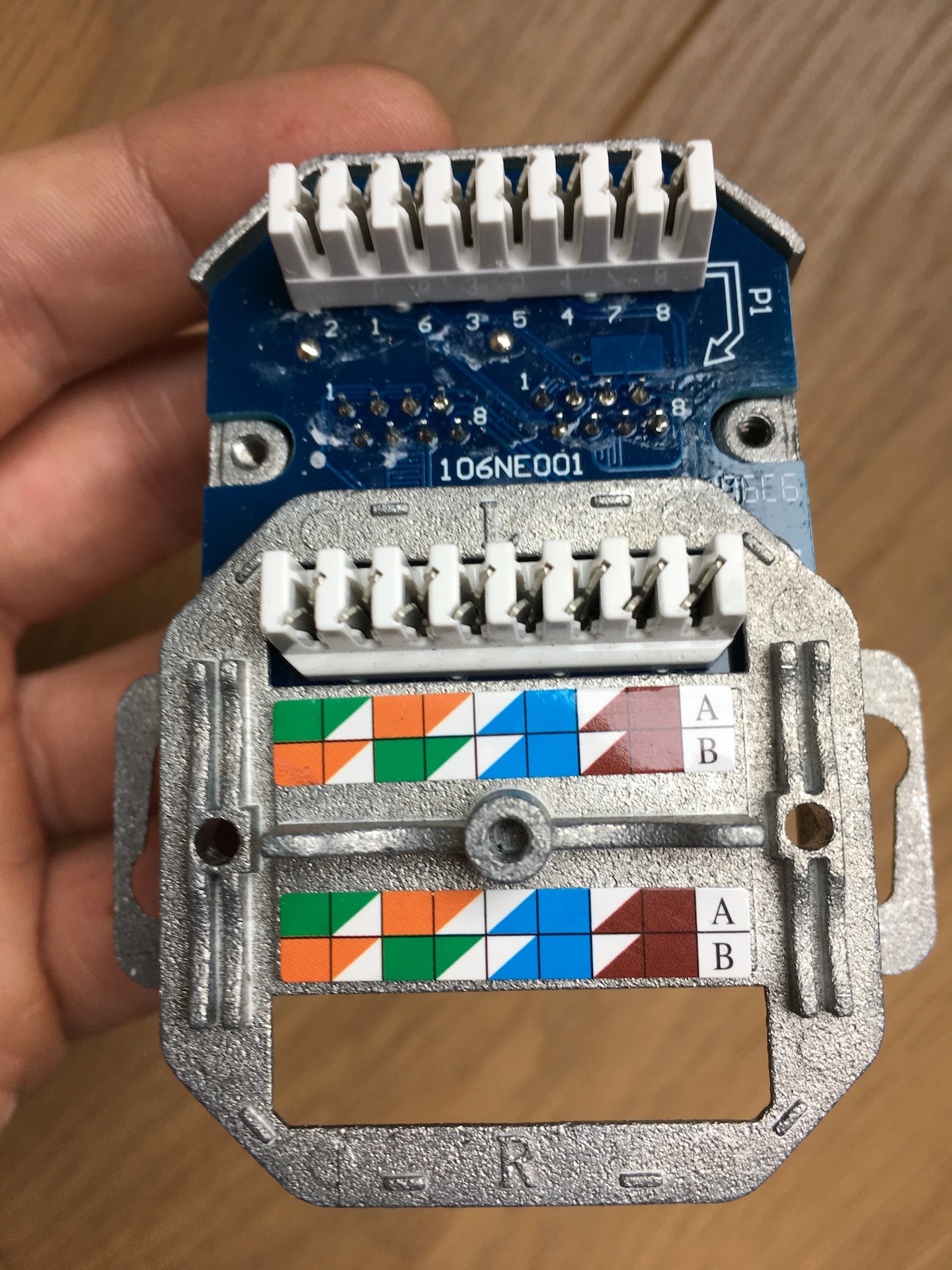
Registered Jack
A registered jack (RJ) is a standardized telecommunication network interface device, network interface for connecting voice and data equipment to a computer service provided by a local exchange carrier or long distance carrier. Registered interfaces were first defined in the ''Universal Service Ordering Code'' (USOC) of the Bell System in the United States for complying with the registration program for customer-supplied telephone equipment mandated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the 1970s. Subsequently, in 1980 they were codified in title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations Part 68. Registered jack connections began to see use after their invention in 1973 by Bell Labs. The specification includes physical construction, wiring, and signal semantics. Accordingly, registered jacks are primarily named by the letters ''RJ'', followed by two digits that express the type. Additional letter suffixes indicate minor variations. For example, RJ11, RJ14, and RJ25 are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
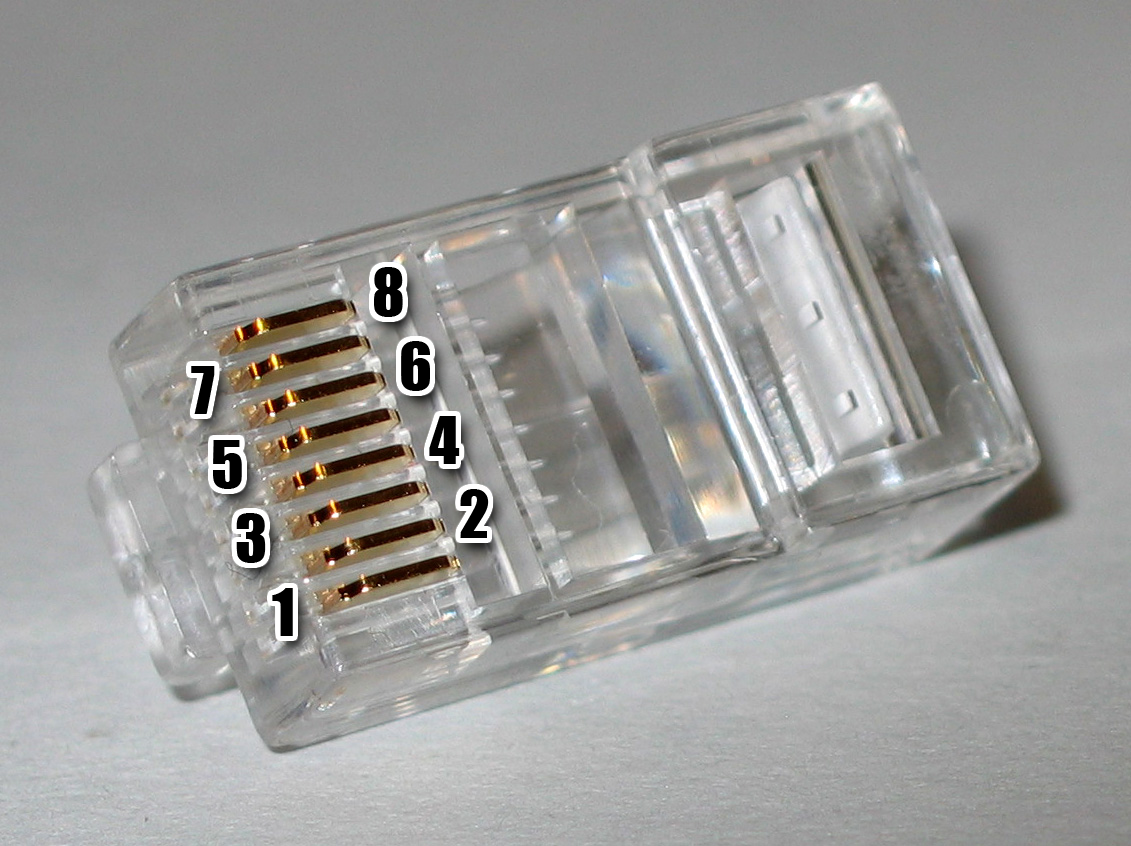
8P8C Modular Connector
A modular connector is a type of electrical connector for cords and cables of electronic devices and appliances, such as in computer networking, telecommunication equipment, and audio headsets. Modular connectors were originally developed for use on specific Bell System telephone sets in the 1960s, and similar types found use for simple interconnection of customer-provided telephone subscriber premises equipment to the telephone network. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) mandated in 1976 an interface registration system, in which they became known as registered jacks. The convenience of prior existence for designers and ease of use led to a proliferation of modular connectors for many other applications. Many applications that originally used bulkier, more expensive connectors have converted to modular connectors. Probably the best-known applications of modular connectors are for telephone and Ethernet. Accordingly, various electronic interface specifications exist f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANSI/TIA-568
ANSI/TIA-568 is a technical standard for commercial building cabling for telecommunications products and services. The title of the standard is ''Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard'' and is published by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), a body accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). , the revision status of the standard is ''ANSI/TIA-568-E'', published 2020, which replaced ANSI/TIA-568-D of 2015, revision C of 2009, revision B of 2001, and revision A of 1995, and the initial issue of 1991, which are now obsolete. Perhaps the best-known features of ANSI/TIA-568 are the pin and pair assignments for eight-conductor 100-ohm balanced twisted pair cabling. These assignments are named ''T568A'' and ''T568B''. History ANSI/TIA-568 was developed through the efforts of more than 60 contributing organizations including manufacturers, end-users, and consultants. Work on the standard began with the Electronic Industries Alliance (EI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat 5
Category 5 cable (Cat 5) is a twisted pair cable for computer networks. Since 2001, the variant commonly in use is the Category 5e specification (Cat 5e). The cable standard provides performance of up to 100 MHz and is suitable for most varieties of Ethernet over twisted pair up to 2.5GBASE-T but more commonly runs at (Gigabit Ethernet) speeds. Cat 5 is also used to carry other signals such as telephone and video. This cable is commonly connected using punch-down blocks and modular connectors. Most Category 5 cables are unshielded, relying on the balanced line twisted pair design and differential signaling for noise suppression. Standards Category 5 is currently defined in ISO/IEC 11801, IEC 61156 and EN 50173, though it was originally defined in ANSI/ TIA/EIA-568-A (with clarification in TSB-95). These documents specify performance characteristics and test requirements for frequencies up to 100 MHz. The cable is available i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backward Compatible
In telecommunications and computing, backward compatibility (or backwards compatibility) is a property of an operating system, software, real-world product, or technology that allows for interoperability with an older legacy system, or with input designed for such a system. Modifying a system in a way that does not allow backward compatibility is sometimes called " breaking" backward compatibility. Such breaking usually incurs various types of costs, such as switching cost. A complementary concept is '' forward compatibility''; a design that is forward-compatible usually has a roadmap for compatibility with future standards and products. Usage In hardware A simple example of both backward and forward compatibility is the introduction of FM radio in stereo. FM radio was initially mono, with only one audio channel represented by one signal. With the introduction of two-channel stereo FM radio, many listeners had only mono FM receivers. Forward compatibility for mono receivers w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category 6 Cable
Category 6 cable (Cat 6) is a standardized twisted pair cable for Ethernet and other network physical layers that is backward compatible with the Category 5/5e and Category 3 cable standards. Cat 6 must meet more stringent specifications for crosstalk and system noise than Cat 5 and Cat 5e. The cable standard specifies performance of up to 250 MHz, compared to 100 MHz for Cat 5 and Cat 5e. Whereas Category 6 cable has a reduced maximum length of when used for 10GBASE-T, Category 6A cable is specified for 500 MHz and has improved alien crosstalk characteristics, allowing 10GBASE-T to be run for the same maximum distance as previous Ethernet over twisted pair variants. History Cat 6, an unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) design, emerged as an advancement of the UTP Cat 5e and was formalised in 2001. The design of Cat 6 required more stringent precision in manufacturing, which enabled reduced noise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower Frequency, frequencies in a continuous Frequency band, band of frequencies. It is typically measured in unit of measurement, unit of hertz (symbol Hz). It may refer more specifically to two subcategories: ''Passband bandwidth'' is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. ''Baseband bandwidth'' is equal to the upper cutoff frequency of a low-pass filter or baseband signal, which includes a zero frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |