|
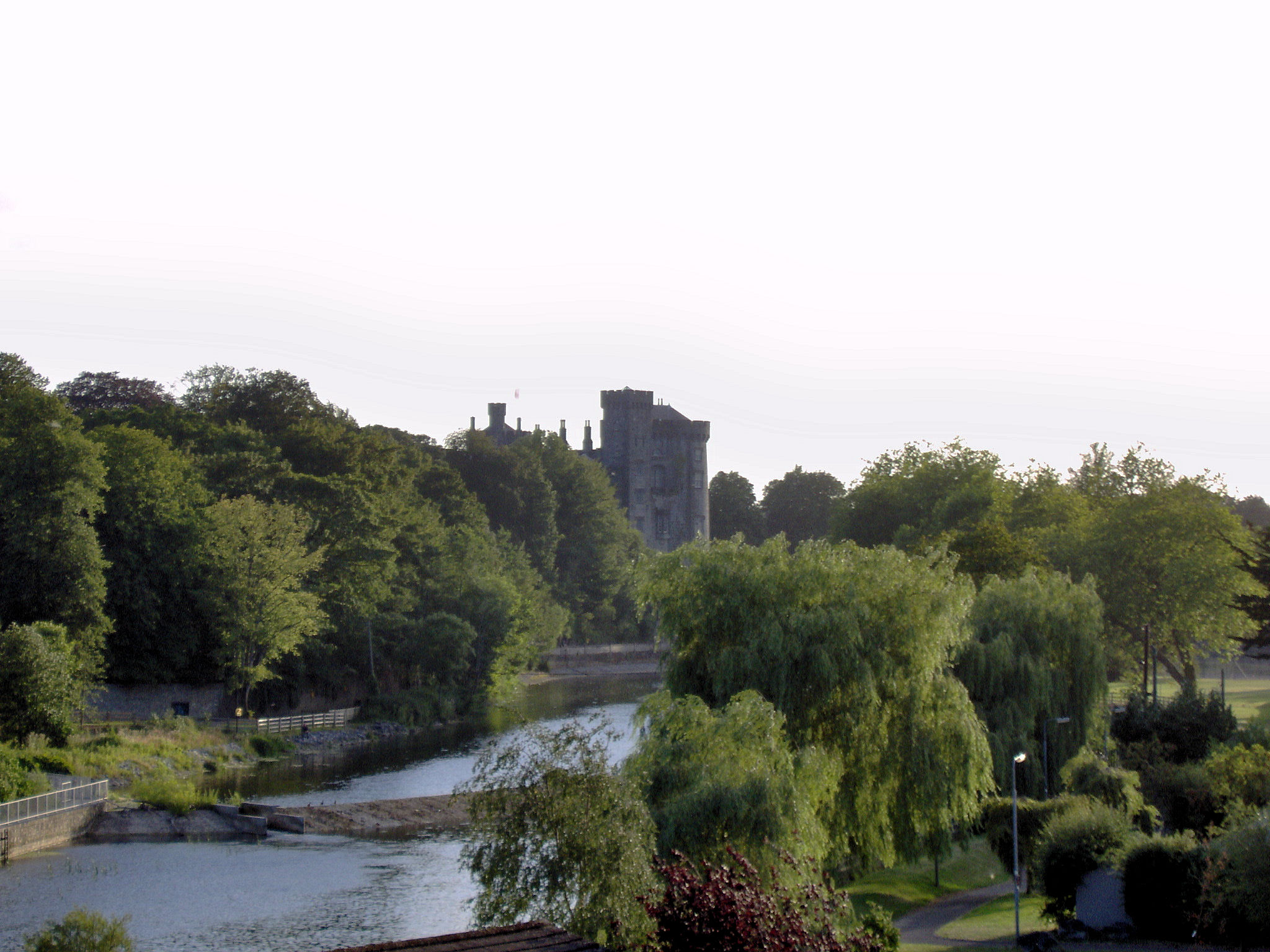
Castlecoote
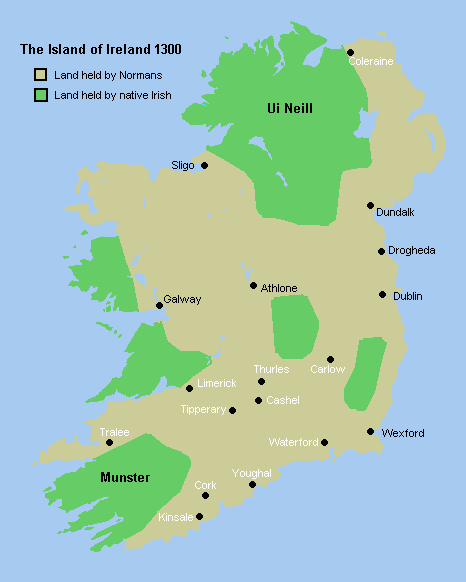
Castlecoote(otherwise known in ) is a townland within the civil parish of Fuerty on the R366 regional road near the town of Roscommon in County Roscommon, Ireland. Castlecoote is known for Castlecoote house and the ruins of a much older castle. The River Suck, which encircles Castlecoote House, is renowned for its trout and coarse fishing. History Castlecoote's English name is derived from 'Coote', literally translated meaning 'Coote's Castle', in which Sir Charles Coote, 'President of Connaught' during the rebellion of 1641 lived. Castlecoote is a primarily agricultural village. Castlecoote House The present Castlecoote house was built on the site of an earlier medieval castle, believed to have been built between 1570 and 1616. The castle was based at a strategic side and it is suggested that it was the base of the Chieftains of Fuerty, the MacGeraghty clan. In 1616 it was in the possession of Sir Charles Coote, who refortified and improved the castle. It was attacked th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castlecoote Castle Ruins
Castlecoote(otherwise known in ) is a townland within the civil parish of Fuerty on the R366 regional road near the town of Roscommon in County Roscommon, Ireland. Castlecoote is known for Castlecoote house and the ruins of a much older castle. The River Suck, which encircles Castlecoote House, is renowned for its trout and coarse fishing. History Castlecoote's English name is derived from 'Coote', literally translated meaning 'Coote's Castle', in which Sir Charles Coote, 'President of Connaught' during the rebellion of 1641 lived. Castlecoote is a primarily agricultural village. Castlecoote House The present Castlecoote house was built on the site of an earlier medieval castle, believed to have been built between 1570 and 1616. The castle was based at a strategic side and it is suggested that it was the base of the Chieftains of Fuerty, the MacGeraghty clan. In 1616 it was in the possession of Sir Charles Coote, who refortified and improved the castle. It was attacked th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R366 Road (Ireland)
The R366 road is a regional road in Ireland linking R362 regional road to the N63 national secondary road in Roscommon Town. It passes through the hamlets of Castlecoote and Fuerty en route. The road is long and is located entirely in County Roscommon. See also *Roads in Ireland *National primary road *National secondary road ReferencesRoads Act 1993 (Classification of Regional Roads) Order 2006– Department of Transport The Department for Transport (DfT) is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for the English transport network and a limited number of transport matters in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland that have not been devolved. The d ... {{Roads in Ireland Regional roads in the Republic of Ireland Roads in County Roscommon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Townlands Of County Roscommon
This is a sortable table of the approximately 2,060 townlands in County Roscommon, Ireland. Retrieved: 2010-09-10. Duplicate names occur where there is more than one townland with the same name in the county. Names marked in bold typeface are towns and villages, and the word ''Town'' appears for those entries in the Acres column. Townland list References {{reflist |
Townlands Of County Roscommon
This is a sortable table of the approximately 2,060 townlands in County Roscommon, Ireland. Retrieved: 2010-09-10. Duplicate names occur where there is more than one townland with the same name in the county. Names marked in bold typeface are towns and villages, and the word ''Town'' appears for those entries in the Acres column. Townland list References {{reflist |
Counties Of Ireland
The counties of Ireland (Irish language, Irish: ) are historic administrative divisions of the island into thirty-two units. They began as Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English (Ireland), Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level. Upon the partition of Ireland in 1921, six of the traditional counties became part of Northern Ireland. In Northern Ireland, Counties of Northern Ireland, counties ceased to be longer used for local government in 1973; Local government in Northern Ireland, districts are instead used. In the Republic of Ireland, some counties have been split resulting in the creation of new counties: there are currently 26 counties, 3 cities and 2 cities and counties that demarcate areas of local government in the Republic of Ireland, local government in the Republic. Terminology The word "county" has come to be used in different senses for di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Charles Coote, 1st Baronet
Sir Charles Coote, 1st Baronet (1581–1642) was an English soldier, administrator and landowner who lived in Ireland. Birth and origins He was born into a Devonshire family, the son of Sir Nicholas Coote. Early life In 1600 he moved to Ireland as a captain of the 100th Foot Regiment in the army of Lord Mountjoy, Lord Deputy of Ireland, where he fought in the last few years of the Nine Years War and was at the Siege of Kinsale in 1601–02, which ultimately led to the defeat of the O'Neills. In 1605 he was appointed Provost-Marshal of Connaught for life and in 1613 was appointed to the office of General Collector and Receiver of the King's Composition Money for Connaught, also for life. In 1620 he was promoted to vice-President of Connaught. Marriage and children Before 1617 he married Dorothea younger daughter and coheir of Hugh Cuffe of Cuffe's Wood, County Cork. Charles and Dorothea had five children, four sons: #Charles, who would be created Earl of Mountrath. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cromwellian Conquest Of Ireland
The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland or Cromwellian war in Ireland (1649–1653) was the re-conquest of Ireland by the forces of the English Parliament, led by Oliver Cromwell, during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Cromwell invaded Ireland with the New Model Army on behalf of England's Rump Parliament in August 1649. Following the Irish Rebellion of 1641, most of Ireland came under the control of the Irish Catholic Confederation. In early 1649, the Confederates allied with the English Royalists, who had been defeated by the Parliamentarians in the English Civil War. By May 1652, Cromwell's Parliamentarian army had defeated the Confederate and Royalist coalition in Ireland and occupied the country, ending the Irish Confederate Wars (or Eleven Years' War). However, guerrilla warfare continued for a further year. Cromwell passed a series of Penal Laws against Roman Catholics (the vast majority of the population) and confiscated large amounts of their land. As punishment for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Towns And Villages In The Republic Of Ireland
This is a link page for cities, towns and villages in the Republic of Ireland, including townships or urban centres in Dublin, Cork, Limerick, Galway, Waterford and other major urban areas. Cities are shown in bold; see City status in Ireland for an independent list. __NOTOC__ A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W Y See also *List of places in Ireland ** List of places in the Republic of Ireland **: List of cities, boroughs and towns in the Republic of Ireland, with municipal councils and legally defined boundaries. **: List of census towns in the Republic of Ireland as defined by the Central Statistics Office, sorted by county. Includes non-municipal towns and suburbs outside municipal boundaries. ** List of towns in the Republic of Ireland by population **: List of towns in the Republic of Ireland/2002 Census Records **: List of towns in the Republic of Ireland/2006 Censu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western European Summer Time
Western European Summer Time (WEST, UTC+01:00) is a summer daylight saving time scheme, 1 hour ahead of Greenwich Mean Time and Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in: * the Canary Islands * Portugal (including Madeira but not the Azores) * the Faroe Islands The following countries also use the same time zone for their daylight saving time but use a different title: *United Kingdom, which uses British Summer Time (BST) *Ireland, which uses Irish Standard Time (IST) ( (ACÉ)). Also sometimes erroneously referred to as "Irish Summer Time" (). The scheme runs from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October each year. At both the start and end of the schemes, clock changes take place at 01:00 UTC+00:00. During the winter, Western European Time (WET, GMT+0 or UTC±00:00) is used. The start and end dates of the scheme are asymmetrical in terms of daylight hours: the vernal time of year with a similar amount of daylight to late October is mid-February, well before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West European Time
Western European Time (WET, UTC±00:00) is a time zone covering parts of western Europe and consists of countries using UTC±00:00 (also known as Greenwich Mean Time, shortly called GMT). It is one of the three standard time zones in the European Union along with Central European Time and Eastern European Time. The following Western European countries and regions use UTC±00:00 in winter months: *Portugal, since 1912 with pauses (except Azores, UTC−01:00) *United Kingdom and Crown Dependencies, since 1847 in England, Scotland, Wales, the Channel Islands, and the Isle of Man, and since 1916 in Northern Ireland, with pauses *Ireland, since 1916, except between 1968 and 1971 *Canary Islands, since 1946 (rest of Spain is CET, UTC+01:00) *Faroe Islands, since 1908 *Madeira islands, since 1912 with pauses * North Eastern Greenland ( Danmarkshavn and surrounding area) *Iceland, since 1968, without summer time changes All the above countries except Iceland implement daylight savin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidy Towns (Ireland)
Tidy Towns (Irish: ''Bailte Slachtmhara'') is an annual competition, first held in 1958, organised by the Department of Rural and Community Development in order to honour the tidiest and most attractive cities, towns and villages in the Republic of Ireland. The competition is organised on a national basis, and entrants must complete modules including Overall Developmental Approach (5 Year Plan), The Built Environment, Landscaping, Wildlife & Natural Amenities, Litter Control, Tidiness, Waste Minimisation, Residential Areas, Roads and Streets & Back Areas. The Competition is judged during the summer months (May to August) by an independent adjudicator, who issues each town with a written report complimenting positive development and actions and providing positive suggestions on how the community can improve their general surroundings. This competition covers many aspects of environment and prizes are awarded to winners of all areas. Other than that, there's an overall winner which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Elphin
The Diocese of Elphin (; ga, Deoise Ail Finn) is a Roman Catholic diocese in the western part of Ireland. It is in the Metropolitan Province of Tuam and is subject to the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Tuam. The current bishop is Kevin Doran who was appointed in 2014. Geographical remit The diocese covers parts of the counties of Roscommon, Sligo and Galway, and Westmeath. Its Cathedral, which was originally established in the Roscommon town of Elphin, is now in Sligo. The major towns are Athlone, Boyle, Castlerea, Roscommon and Sligo. History The See dates to the earliest days of the Irish Church. From the time Christianity first arrived in Ireland in the second half of the 5th century (in the form of Saint Patrick's mission), the early church was centred on Monastic settlements. St. Patrick founded such a settlement in an area known as Corcoghlan, now known as Elphin, in 434 or 435. The first Abbot bishop of this monastic settlement was Assicus, who was said to be St. Pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |